Respiratory System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 44
Title:
Respiratory System
Description:
After studying this chapter, you will be able to: ... Endoscopy. Bronchoscopy. 27. Laboratory Tests. Diagnostic, Procedural, and. Laboratory Tests ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:75
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Respiratory System
1
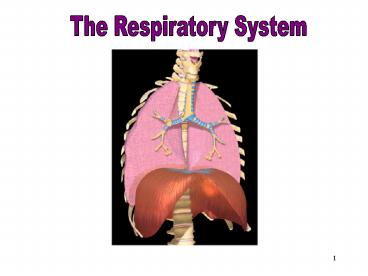
Respiratory System
The Respiratory System
2
Objectives
Objectives
After studying this chapter, you will be able to
- Name the parts of the respiratory system and
discuss the function of each part. - Define combining forms used in building words
that relate to the respiratory system and its
parts. - Identify the meaning of related abbreviations.
3
Objectives Part 2
Objectives cont'd
- Name the common diagnoses, clinical procedures,
and laboratory tests used in treating disorders
of the respiratory system. - List and define the major pathological conditions
of the respiratory system. - Explain the meaning of the surgical terms related
to the respiratory system.
4
Structure and Function
Structure and Function
The respiratory system performs two major tasks
- Exchanging air between the body and the outside
environment known as external respiration - Bringing oxygen to the cells and removing carbon
dioxide from them referred to as internal
respiration
5
External Respiration
Structure and Function
External Respiration
Air from the outside environment enters the nose
or mouth during inspiration (inhalation).
The Nose
- Also called external nares
- Divided into two halves by the nasal septum
- Contains the paranasal sinuses where air is
warmed - Contains cilia which is responsible for filtering
out foreign bodies
6
Pharynx
Structure and Function
Pharynx
Also known as the throat is a passageway for both
air and food
Three Sections of the Pharynx
Nasopharynx
-contains the pharyngeal tonsils (adenoids) which
aid in the bodys immune defense
Oropharynx
-back portion of the mouth that contains the
palatine tonsils which aid in the bodys immune
defense
Laryngopharynx
-bottom section of the pharynx where the
respiratory tract divides into the esophagus and
the larynx
7
Epiglottis
Structure and Function
The epiglottis, a movable flap of cartilage that
covers the opening to the larynx (voice box)
prevents food from entering the larynx during
swallowing.
Occasionally, a person may swallow and inhale at
the same time so some food may enter the larynx
and choking occurs.
A technique called the Heimlich maneuver has
saved many people from choking to death.
8
Larynx
Structure and Function
Larynx
Serves as a passageway to the trachea and the
area where sounds are produced
Vocal Cords
Size and thickness determine the pitch of sound
- Short and thin high pitch
- Thick and long low pitch
9
Trachea
Structure and Function
Trachea
- Also known as the windpipe
- Connects the larynx to the right and left bronchi
- Point at which it divides into the right and left
bronchi is called the mediastinum
10
Internal Respiration
Structure and Function
Internal Respiration
Air from the bronchi travels to the bronchioles
then to the tiny air sacs (alveoli) which connect
to lung capillaries.
Oxygen and carbon dioxide are exchanged and
oxygen is delivered to the body cells.
11
Lungs
Structure and Function
Lungs
- Consist of a right and left lobe
- Covered by a double layer of membrane that makes
movement in the thoracic cavity easier. The outer
layer is the parietal pleura and the inner layer
is the visceral pleura - The space between the two pleurae is called the
pleural cavity - Consist of an apex (top section), hilum (middle
section) and base (lower section)
12
Inhale/Exhale
Structure and Function
The passage of air from the external environment
to the lung capillaries, bloodstream and out
consists of one inhalation and one exhalation.
13
Muscles for Breathing
Structure and Function
Muscles for Breathing
The major muscles that contract to enlarge the
thoracic cavity during inspiration are the
- Diaphragm
- Intercostal muscles
Note The diaphragm lowers itself when it
contracts during inhalation
14
Combining Forms Abbreviations adenoid(o)
Combining Forms and Abbreviations
Combining Form
Meaning
adenoid (o) alveol (o) bronch (o) bronchiol
(o) capn (o) epiglott (o) laryng (o)
15
Combining Forms Abbreviations lob(o)
Combining Forms and Abbreviations
Combining Form
Meaning
lob (o) mediastin (o) nas (o) or (o) ox
(o) pharyng (o) phon (o)
16
Combining Forms Abbreviations phren(o)
Combining Forms and Abbreviations
Combining Form
Meaning
phren(o) pleur(o) pneum (o) rhin (o) spir
(o) steth (o) thorac (o)
17
Combining Forms Abbreviations ABG
Combining Forms and Abbreviations
Abbreviation
Meaning
ABG AFB AP AP ARD ARDS ARF
18
Combining Forms Abbreviations BS
Combining Forms and Abbreviations
Abbreviation
Meaning
BS COLD COPD CPR CTA CXR DOE
19
Combining Forms Abbreviations DPT
Combining Forms and Abbreviations
Abbreviation
Meaning
DPT ENT ET tube FEF FEV FVC HBOT
20
Combining Forms Abbreviations IMV
Combining Forms and Abbreviations
Abbreviation
Meaning
IMV IPPB IRDS IRV LLL LUL MBC
21
Combining Forms Abbreviations MDI
Combining Forms and Abbreviations
Abbreviation
Meaning
MDI PA PCP PEEP PFT PND RD
22
Combining Forms Abbreviations RDS
Combining Forms and Abbreviations
Abbreviation
Meaning
RDS RLL RUL SIDS SOB TA TB
23
Combining Forms Abbreviations TLC
Combining Forms and Abbreviations
Abbreviation
Meaning
TLC TPR URI VC V/Q scan
24
Diagnostic, Procedural Laboratory Tests
Diagnostic, Procedural, and Laboratory Tests
Methods Used to Diagnose Respiratory Disorders
- Auscultation
- Assessing respiratory rate
- Percussion
- Sputum analysis
Normal Adult respiratory rate is 15 to 20
respirations per minute.
25
Pulmonary Function Tests
Diagnostic, Procedural, and Laboratory Tests
Pulmonary function tests measure the mechanics of
breathing.
Peak flow meter
- measures the capacity for breathing
Spirometer
- a pulmonary function testing machine that
measures the lungs volume and capacity
Forced Vital Capacity
Forced Expiratory Volume
Highest breathing capacity following the deepest
breath
Shows breathing capacity at different parts of
the respiratory cycle
26
Abnormalities/Masses
Diagnostic, Procedural, and Laboratory Tests
Abnormalities such as masses and restricted blood
flow within the lungs can be detected via
- Chest x-rays
- MRI
- Lung scans
Structures of the respiratory system can be
observed via
- Endoscopy
- Bronchoscopy
27
Laboratory Tests
Diagnostic, Procedural, and Laboratory Tests
Laboratory Tests
- Throat Cultures
- Sputum Sample
- Arterial Blood Gases
- Sweat Test
28
Pathology
Pathology
epiglottitis
adenoiditis
bronchitis
laryngitis
pharyngitis
pneumonitis
rhinitis
sinusitis
tonsillitis
laryngotracheobronchitis
29
Breathing Patterns
Pathology
Breathing Patterns
Other Conditions
- Cheyne Stokes Respiration
- Hyperventilation
- Hypoxemia
30
Upper Respiratory Infection
Pathology
Upper respiratory infection is a term that covers
an infection of some or all of the respiratory
tract.
Other Conditions
- Croup
- Diptheria
- Epistaxis
- Rhinorrhea
- Pertussis
31
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease
Pathology
Chronic Obstructive Pulmonary Disease (COPD) is a
term for any disease with chronic obstruction of
the bronchial tubes and lungs such as
- Emphysema
- Chronic Bronchitis
Asthma causes narrowing of the bronchi leading to
dyspnea, wheezing and coughing.
32
Hemoptysis
Pathology
Hemoptysis
Lung or bronchial hemorrhage that results in the
spitting of blood.
Cystic Fibrosis
Disease of the exocrine glands that causes
secretion of abnormally thick mucus which leads
to chronic obstruction.
Atelectasis
Collapsed alveoli leading to collapse of a lung
or part of a lung.
Pneumonia
Acute infection of the alveoli.
33
Environmental Conditions
Pathology
Conditions caused by environmental agents
Pneumoconiosis
- Caused by dust in the lungs
Anthracosis
- Caused by coal dust
Asbestosis
- Caused by asbestos particles released during
construction of ships and buildings
Silicosis
- Caused by the silica dust from grinding rocks or
glass
34
Disorders of the Pleura
Pathology
Disorders of the Pleura
Pneumothorax
- Accumulation of air or gas in the pleural cavity.
Empyema
- Pus in the pleural cavity.
Hemothorax
- Blood in the pleural cavity.
Pleural Effusion
- Escape of fluid into the pleural cavity.
35
Otorhinolaryngologists
Surgical Terms
Otorhinolaryngologists are physicians that
specialize in disorders of the upper respiratory
tract.
Surgical Removal Conditions
- Laryngectomy
- Tonsillectomy
- Adenoidectomy
- Pneumonectomy
- Lobectomy
36
Surgical Repair
Surgical Terms
Surgical Repair
37
Surgical Incisions
Surgical Terms
Surgical Incisions
- Laryngotracheotomy
- Sinusotomy
- Thoracotomy
- Tracheotomy
- Endotracheal intubation is the insertion of a
tube through the nose or mouth, pharynx, larynx
and into the trachea to establish an airway.
38
Pharmacology
Pharmacology
Antibiotics, antihistamines and anticoagulants
are used for respiratory disorders just as with
other system disorders.
Medications specific to Respiratory Conditions
Bronchodilators
- Dilate the bronchial walls
Expectorants
- Promote coughing and expulsion of mucus
39
Mechanical Devices
Pharmacology
Mechanical Devices that aid in Respiration
Ventilators
- Actually serve as a breathing substitute for
patients who can not breathe on their own.
Nebulizers
- Deliver medication through the mouth or nose to
ease breathing problems
40
Agents to Treat Respiratory Conditions
Pharmacology
Agents Used to Treat Respiratory Conditions
Antitussive
Expectorants
(relieves coughing)
(promotes coughing and expelling of mucus)
Decongestants
(decreases and prevents mucus buildup)
41
Apply Your Knowledge
Apply Your Knowledge
Identify the following respiratory structures
A. Trachea
B. Bronchi
C. Alveolus
42
Apply Your Knowledge Part 2
Apply Your Knowledge
An obstruction in which of the following would be
MOST fatal?
A. BRONCHIOLE B. TRACHEA C. BRONCHI
Answer B. Trachea
43
Apply Your Knowledge Part 3
Apply Your Knowledge
Mr. Davis has had hoarseness for the past six
months. He recently went to his physician and
received a diagnosis of cancer of his voice box.
Which of the following procedures might be
indicated for Mr. Davis?
A. Pharyngectomy B. Pneumonectomy C.
Laryngectomy
Answer C. Laryngectomy
44
Apply Your Knowledge Part 4
Apply Your Knowledge
Melissa has very thick respiratory secretions.
She visits a local pharmacy looking for something
to help her with her dry cough.
Which of the following types of medication should
Melissa consider taking?
A. Expectorant B. Antitussive C. Antibiotic
Answer A. Expectorant