The Human Body Lesson 4 Introduction Body is composed of - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 47
Title:
The Human Body Lesson 4 Introduction Body is composed of
Description:
The Human Body Lesson 4 Introduction Body is composed of different organs/tissues working together Minor injury/illness may damage only a specific body part/function ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:147
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Human Body Lesson 4 Introduction Body is composed of
1
Lesson 4
- The Human Body
2
Introduction
- Body is composed of different organs/tissues
working together - Minor injury/illness may damage only a specific
body part/function - Serious injury or sudden illness can threaten
vital body functions - Understanding human body can help you recognize
effects of injuries/illnesses
3
Body Regions and Directions
- Special terms are used by healthcare providers
for body regions - Directional/positional terms used to describe
relationship of body structures
4
Body Regions and Cavities
- Extremities refers to both arms and legs
- Thorax refers to chest area enclosed by the ribs
- Thoracic cavity is area inside chest
- Abdomen refers to area immediately below thoracic
cavity
5
Body Regions and Cavities continued
- Abdominal cavity includes stomach, intestines,
other organs - Pelvis refers to area below abdomen-- pelvic
bones between hip/lower spine - Pelvic cavity contains bladder and other organs
- Spine, or spinal column, refers to bones of
neck/back and nerves, or spinal cord, that run
through vertebrae
6
Abdominal Quadrants
- Used to describe specific injuries or
signs/symptoms - Upper and lower quadrants are divided by a line
passing through umbilicus - Quadrants are based on anatomical position, with
face forward and palms facing forward
7
Directional Terms
- All positional and directional terms are based on
anatomical position - Right and left refer to the patients right and
left, divided by midline down center of body - Lateral and medial
- Anterior and posterior
- Proximal and distal
- Superior and inferior
- Prone and supine
8
Body Systems
- Organs have one or more specific functions
- The organs that work together for a specific
function are called a body system
9
Examples of Interrelated Body Systems
- Blood carries oxygen from lungs to body cells
- Nerve sensors detect amount of oxygen and carbon
dioxide in the blood and speed up or slow down
heart beat /breathing to change oxygen level - If body temperature drops, muscles in extremities
start shivering to produce heat, which is carried
by blood to vital organs
10
Respiratory
11
Functions of Respiratory System
- To bring air into lungs
- To allow oxygen from air to enter blood
- To remove carbon dioxide from blood into air
breathed out (exhaled) - This process is called respiration
12
Respiratory System Primary Organs
- ltFig 3-3gt
13
The Breathing Process
- Breathing depends on muscular movements under
control of nervous system - When the diaphragm contracts/moves down, thoracic
cavity/lungs expand, pulling air into lungs - In lungs, oxygen enters blood and carbon dioxide
leaves blood - When diaphragm relaxes/moves up, thoracic cavity
contracts, and air carrying carbon dioxide flows
back out of lungs
14
Emergency Care Related to the Respiratory System
- Respiration can be affected by different
injuries/illnesses - An airway obstruction is blockage of airway
preventing air flow - A broken rib may puncture a lung, making
breathing ineffective - A penetrating injury into lungs may alter lung
pressures keeping lungs from filling with air
15
Emergency Care Related to the Respiratory System
continued
- Poisoning/drug overdose may depress nervous
system functions, slowing or stopping breathing - Asthma is a common illness in which airway
tissues swell making it hard to breathe - In infants/children, anatomical structures are
smaller and airway is more easily obstructed - Uncorrected respiratory problem is the primary
cause of cardiac arrest in infants/children
16
Circulatory
17
Functions of the Circulatory System
- To transport oxygen and nutrients in the blood to
all parts of body - To remove carbon dioxide and other wastes
18
Cardiovascular System Primary Organs
- Heart
- Blood
- Blood vessels
19
Pathway of Blood
- Ventricles pump blood through two loops or cycles
in body - Right ventricle pumps blood to lungs picking up
oxygen and releasing carbon dioxide - Blood returns to left atrium, from which it moves
to left ventricle - Left ventricle pumps oxygenated blood into body
to release oxygen and pick up carbon dioxide for
removal - Blood returns to right atrium, moving to right
ventricle to be pumped again to lungs
20
Pulses
- Pulsing blood pressure changes occur in arteries
that can be felt as pulse - Commonly measured pulses
- Carotid
- Femoral
- Radial
- Brachial
21
Heart Rate
- Heart rate, measured as pulse, is affected by
many factors - Average resting heart rate in adult males is 64-
72 beats/ minute in females, 72 - 80 beats/
minute - Heart rate of infants and children is higher
- With exercise, fever, or emotional excitement,
heart rate increases to meet bodys greater need
for oxygen
22
Emergency Care Related to the Cardiovascular
System
- Cells begin to die in vital organs such as brain
after only a few minutes without oxygen - Oxygen delivery diminished by injury/illness
affecting heart, blood, or blood vessels - Severe bleeding leaves not enough blood in
circulation to provide body with oxygen - Arterial bleeding is most severe - blood may
spurt out under pressure, leading to
life-threatening shock - Bleeding from veins generally slower but can
still be serious or life-threatening if it
continues - Capillary bleeding usually minor and stops by
itself as blood clots
23
Cardiovascular Illness
- Stroke is problem involving arteries in brain
reduced circulation may cause mental and physical
impairments - If heart muscle does not receive enough
oxygenated blood because of blocked cardiac
arteries, cardiac muscle tissue may die - The heart may stop (cardiac arrest)
- Dysrhythmia (or arrhythmia), an irregular
heartbeat, may reduce hearts pumping ability - Fibrillation, a serious dysrhythmia, common after
heart attack
24
Musculoskeletal System
25
Functions of the Musculoskeletal System
- Skeletal system provides shape/support for body
as a whole - Muscles act on bones, allowing for movement
- Groups of bones protect vital internal organs
- Ribs protect heart and lungs
- Skull protects brain
- Vertebrae protect spinal cord
- Pelvic bones protect bladder and other organs
26
Musculoskeletal System Primary Organs
- Bones
- Muscles
- Ligaments
- Tendons
27
Emergency Care Related to the Musculoskeletal
System
- Most fractures are not life-threatening
- In a dislocation, one or more bones move out of
position in joint - Sprain is damage to ligaments and other
structures in a joint - Strain is muscle/tendon tear usually caused by
overexerting muscle
28
Musculoskeletal Injuries Associated with Other
Injuries
- Vertebral fractures likely to injure spinal cord
and cause nervous system damage - Fractures of femur often cause much soft-tissue
damage and bleeding - Pelvis fracture may damage bladder/other organs
in pelvic cavity - A skull fracture may cause brain damage
29
Nervous System
30
Nervous System Primary Functions
- Sensory receptors gather information about
environment and send to brain - Brain integrates and analyzes information
- Nerve signals from brain lead to actions
throughout body to accomplish tasks or maintain
homeostasis
31
Nervous System Primary Organs
- Brain
- Spinal cord
- Sensory receptors
- Nerves
32
Nervous System Emergencies
- Head and spinal injuries
- Serious/life-threatening
- Injury to part of brain or stroke
- May destroy or impair one or more functions
- Damage to spinal cord
- Complete loss of function to body area/paralysis
33
Nervous System Emergencies continued
- Altered mental status from
- Head injuries
- Any injury causing decreased oxygenation
- Sudden illness (i.e., stroke, seizure, diabetes)
- Severe infection/fever
- Poisoning/drug overdose
34
Nervous System Effects Associated with Other
Injuries
- Injuries and some illnesses also affect nervous
system - Pain results from damage to nerve fibers in many
areas of body - Crushing pain in chest may be caused by heart
attack - Abdominal pain that begins in umbilicus and
settles into lower abdomen on right side may be
a sign of appendicitis - Pain should always be taken seriously
35
Other Body Systems
36
Integumentary System Primary Functions
- Protect body
- Help regulate body temperature
- Help prevent water loss
- Remove some body wastes
- Produce Vitamin D
- Sensation (i.e. touch, pressure, pain,
temperature)
37
Integumentary System Emergencies
- Cuts and scrapes
- Bleeding
- Openings in skin
- Allow pathogens into body
- Heat and chemical burns
- Loss of body heat
- Loss of body fluid
38
Importance of Skin Condition
- Skin often reveals important information about
body condition - Skin of hypothermia victim
- Skin of heatstroke victim
- Skin of victim with low blood oxygen levels
- Skin of victim in shock
- Sweating/pale skin
- Many sudden illnesses cause sweating and skin
color changes (flushed or pale)
39
Gastrointestinal System
- Digests food and extracts nutrients
- Organs easily injured by traumatic forces
40
Emergency Care Related to the Gastrointestinal
System
- Abdominal cavity not protected by bones,
gastrointestinal organs may be easily injured by
traumatic forces - In closed injury, pain/tenderness along with
swollen/rigid abdomen may suggest internal injury - In an open wound, internal organs may be exposed,
raising risk of infection - Ingested poison is absorbed in the same manner as
nutrients from food and enters the bloodstream to
affect body - Various illnesses may cause vomiting or diarrhea,
which can lead to dehydration especially in
infants - Vomiting blood is likely sign of a serious
internal injury
41
Functions of the Urinary System
- Removes metabolic wastes from body in urine
- Helps body maintain fluid and electrolyte
balances
42
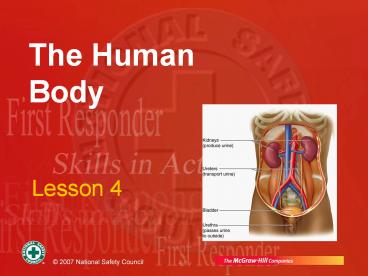
Urinary System
- Blood transports wastes to kidneys
- Kidneys filter wastes and produce urine
43
Urinary System
- Traumatic injury may damage organs
- Look for blood in urine
- Health problems
- May cause change in urination
- Dehydration
- Lack of urination
44
Reproductive System
- Female
- Produces eggs
- Supports and nurtures fetus in uterus
- Childbirth
- Lactation
- Male
- Produces and transports sperm
45
Emergency Care Related to the Reproductive System
- Abdominal injuries may damage genitals/reproductiv
e organs - such wounds may require special care, including
concern for victims privacy - Complications may develop in pregnancy
- Childbirth may occur unexpectedly away from a
healthcare facility
46
Endocrine System
- Glands that produce hormones
- Most problems develop slowly and are rarely
emergencies
47
Lymphatic System
- Helps defend against disease
- Part of immune system
- Problems seldom cause emergencies