Blood consists of a pale yellow fluid called plasma in which are suspended white blood cells, platel - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Blood consists of a pale yellow fluid called plasma in which are suspended white blood cells, platel
Description:
Blood consists of a pale yellow fluid called plasma in which are suspended white ... If blood is centrifuged the cells precipitate leaving the plasma as a supernatant. ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:471
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Blood consists of a pale yellow fluid called plasma in which are suspended white blood cells, platel
1
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
THE HEART
II.7 ANIMAL TRANSPORT
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
ROUND UP
BLOOD AND BLOOD CELLS
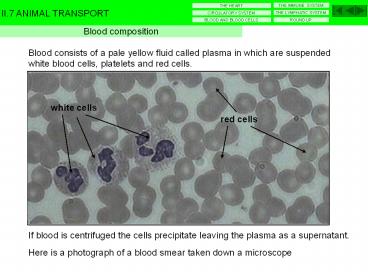
Blood composition
Blood consists of a pale yellow fluid called
plasma in which are suspended white blood cells,
platelets and red cells.
Microscope drawing of blood smear
Centrifuged whole blood
white cells
red cells
plasma
white cells
red cells
If blood is centrifuged the cells precipitate
leaving the plasma as a supernatant.
Here is a photograph of a blood smear taken down
a microscope
2
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
THE HEART
II.7 ANIMAL TRANSPORT
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
ROUND UP
BLOOD AND BLOOD CELLS
Blood composition
Can you label the arrows?
Microscope drawing of blood smear
Soluble products of digestion from the small
intestine to other organs
Urea from the liver to the kidneys
Plasma contains a variety of dissolved solutes
such as urea, glucose, hormones.
platelet
red blood cell
whiteblood cell
It also contains plasma proteins that remain in
the blood all the time.
3
IGCSE BIOLOGY 11.7 TRANSPORT
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
THE HEART
II.7 ANIMAL TRANSPORT
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
ROUND UP
BLOOD AND BLOOD CELLS
Blood composition
Microscope drawing of blood smear
white cells
White cells
Have a nucleus
Form part of the bodys defence system against
microbes
4
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
THE HEART
II.7 ANIMAL TRANSPORT
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
ROUND UP
BLOOD AND BLOOD CELLS
Blood composition
Red cells
Microscope drawing of blood smear
Have no nucleus
Are packed with a red pigment called haemoglobin
In the lungs oxygen combines with haemoglobin to
form oxyhaemoglobin
red cells
In other organ oxyhaemoglobin splits into
haemoglobin O2
5
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
THE HEART
II.7 ANIMAL TRANSPORT
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
ROUND UP
BLOOD AND BLOOD CELLS
Blood composition
Design features of red blood cells for oxygen
carriage
Microscope drawing of blood smear
No nucleus making more room for haemoglobin
Doughnut shaped giving greater surface area for
gas exchange
red cells
6
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
THE HEART
II.7 ANIMAL TRANSPORT
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
ROUND UP
BLOOD AND BLOOD CELLS
Blood composition
Platelets
Platelets are small fragments of cells
Platelets have no nucleus
Platelets help blood to clot at the site of a
wound
platelets
Light microscope photograph of a stained blood
sample (X3000) Platelets are stained blue
7
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
THE HEART
II.7 ANIMAL TRANSPORT
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
ROUND UP
BLOOD AND BLOOD CELLS
The immune system
White blood cells
If pathogens gain entry to the body 2 types of
white cells attack them
lymphocyte
Makes antibodies which attach to the pathogen and
help disable or destroy it
Produces antitoxins which neutralise any toxins
produced by the pathogen
phagocyte
Phagocytic - engulfs the pathogen and digests it.
Microscope photo of a human blood smear
8
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
THE HEART
II.7 ANIMAL TRANSPORT
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
ROUND UP
BLOOD AND BLOOD CELLS
The immune system
White blood cells
phagocytosis and antibody action
Pathogen engulfed by white cell
engulfs and digests pathogens by phagocytosis
Invading pathogens usually a bacteria or viruses
Phagocyte.
Pathogen toxin
produces antibodies to attack the pathogens or
their toxins
Lymphoctye
Pathogen or toxins produced by the pathogen
antibody
9
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
THE HEART
II.7 ANIMAL TRANSPORT
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
ROUND UP
BLOOD AND BLOOD CELLS
The immune system
Re-infection
Once they have produced antibodies against a
particular bacterium or virus, white memory cells
can produce them quicker, and in greater quantity
if the pathogen returns, giving the person
immunity against that disease
Memory cells rapid and massive antibody
production
Level of antibody in the blood
The pathogen is eliminated but the damaging
symptoms of disease will have already occurred
The pathogen is eliminated before disease
symptoms and dangers occur
Time
initial infection
infection over
new infection
10
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
THE HEART
II.7 ANIMAL TRANSPORT
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
ROUND UP
BLOOD AND BLOOD CELLS
The immune system
Vaccination
Introducing a mild or dead form of the disease
into a person causes the production of antibodies
without the symptoms of disease
HOW VACCINATION WORKS
Memory cells rapid and massive antibody
production
Level of antibody in the blood
The pathogen is eliminated before disease
symptoms and dangers occur
Antibodies produced but no disease symptoms
Time
Infection with the real virulent pathogen
Vaccination with mild or dead pathogen
11
IGCSE BIOLOGY 11.7 TRANSPORT
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
THE HEART
II.7 ANIMAL TRANSPORT
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
ROUND UP
BLOOD AND BLOOD CELLS
Blood clotting
When a blood vessel is damaged, either by a cut
or other means, the blood clots for 2 reasons
To prevent leakage of blood
To prevent the entry of pathogens
fibrinogen
A blood clot forming the blood protein fibrin
(white) acts like a net at the point of damage.
It catches red blood cells and they form a clump
which blocks the opening in the blood vessel
fibrin
12
IGCSE BIOLOGY 11.7 TRANSPORT
THE IMMUNE SYSTEM
THE HEART
II.7 ANIMAL TRANSPORT
CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
THE LYMPHATIC SYSTEM
ROUND UP
BLOOD AND BLOOD CELLS
Blood clotting
White blood cells move to the clot to kill
bacteria of viruses entering through the point of
damage
white blood cell
puss a mixture of fibrin and dead white blood
cells
fibrin
trapped red blood cell
13
IGCSE BIOLOGY 11.7 TRANSPORT
II.7 ANIMAL TRANSPORT
CLICK HERE TO RETURN TO THE CIRCULATORY SYSTEM
William Harvey was born in England in 1578. In
1628 Harvey published An Anatomical Study of the
Motion of the Heart and of the Blood in Animals
which explained how blood was pumped from the
heart throughout the body, then returned to the
heart and recirculated. The views this book
expressed were very controversial and lost Harvey
many patients, but it became the basis for all
modern research on the heart and blood vessels.
14
Immunity
Types of immunity
- Natural active immunity
Immune system activation due to infection
- Artificial active immunity (vaccination)
Immune system activation by vaccination
- Artificial passive immunity
Injection with antibodies. Used against
potentially fatal and fast acting diseases e.g.
tetanus antitoxin
- Natural passive immunity
Mothers antibodies crossing the placenta e.g.
measles. Also IgA in colostrum prevents
bacterial / viral growth