GIS Defined - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 38
Title:
GIS Defined
Description:
Zip Codes. Cities. Counties ... real time weather statistics for specific areas by selecting an area on the map. ... a specific area on the map document and ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:41
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: GIS Defined
1
GIS Defined
Geographic Information System
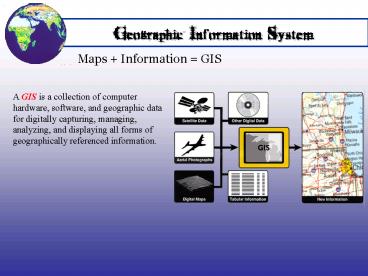
Maps Information GIS
A GIS is a collection of computer hardware,
software, and geographic data for digitally
capturing, managing, analyzing, and displaying
all forms of geographically referenced
information.
2
GIS Components
A GIS is a comprised of five components people,
hardware, software, data, and methods. People are
required to collect data and use methods,
hardware, and software to manipulate data.
3
Feature, Layer, Spatial Data Defined
GIS Layer
GIS integrates all the layersto create digital
reality.
A geographic feature is any real-world object on
a map, such as a single building. A layer is
the visual representation of a set of geographic
features. Layers must contain spatial data.
Spatial data indicates the geographic location
and shape of the feature. In the example,
buildings, school districts, streets, zip codes,
cities, and counties are layers that are
combined, or layered, using GIS to create
reality.
- Buildings
- School Districts
- Streets
- Zip Codes
- Cities
- Counties
4
Attribute Defined
GIS Attribute
Attributes are additional information about the
features. Attribute data is stored in a
database, such as Excel or Access, and is
associated to a layer in the GIS. Each feature
making up the layer is associated with at least
one attribute in the database. The attributes
included for each layer are at the discretion of
the individual creating the GIS. The GIS user
may edit the attribute data as changes are
necessary. GIS allows attributes to be linked to
geographic location. With GIS you link people to
address, buildings to parcels of land, and so
forth. The examples illustrate some common
attribute data for buildings and schools layers.
For buildings, the address is important. For
schools, the principals name and school contact
information are important.
5
GIS is a Smart Map
Location is Important
GIS uses tools like computers and software to
enhance the fundamental tenant of geography
Location is important in peoples lives. GIS
helps locate new businesses and track
environmental degradation. It helps route
garbage trucks and manage road paving. GIS helps
marketers find new prospects and it helps farmers
grow healthier, larger crops. GIS can be used in
ANY field of study. In fact, GIS has an effect
upon everyones life, yet most people do not
realize it.
6
Weather
Meteorologists
If you watch the weather, GIS affects you.
Meteorologists use GIS to forecast the weather.
The GIS consists of weather models and satellite
data to forecast the weather and predict weather
system patterns. In the event of a weather
related emergency, GIS is used to determine who
should be evacuated.
http//www.wcyb.tv/weather.asp
Locally, the WCYB Pinpoint Weather website hosts
a weather GIS. Individuals may view real time
weather statistics for specific areas by
selecting an area on the map.
7
Navigation and GPS
Navigation
If you use GPS, GIS affects you.
Road atlases are becoming a thing of the past due
to the popularity and affordability of navigation
systems. Navigation systems derive directions
by acquiring geographic (longitude and latitude)
coordinates from satellites. Travelers, airline
pilots, the military, and the general public
enjoy the benefits of navigation systems.
Handheld navigation systems are often used by
hunters and fishermen to pinpoint locations they
tend to revisit while helping them find their way
through the forest.
8
Environmental Concerns
Who Uses GIS?
If you like to live in a healthy environment, GIS
affects you.
GIS is used to monitor various environmental
concerns across the world. Coastal subsidence,
deforestation, and pollution are a few
environmental concerns that may be addressed
using GIS. The example uses GIS to monitor U.S.
air quality. Areas identified as unhealthy are
more easily depicted on a map than in stacks of
reports.
9
Developers
Developers
If new development occurs in your community, GIS
affects you.
GIS is useful in determining the placement of
roads, stop lights, businesses, parks, schools,
and any feature. Since GIS provides a digital
version of reality, developers may use GIS to
select the prime location for a new structure.
GIS allows developers to input specific criteria
for a location, then the GIS pinpoints all the
locations within the study area that meet all the
criteria.
For example, a park is best located near
residential areas while a gas station should be
located along a busy roadway but not in a
location where multiple gas stations are already
located.
10
Law Enforcement
Law Enforcement
GIS is used by law enforcement officers to
pinpoint the location of criminal incidents. In
Wise County, each police department is equipped
with GPS units which are used to gather the
location information of each crime within the
county. The GPS location information is input
into GIS and used by law enforcement to detect
criminal patterns.
11
GIS Software
GIS Software
The Environmental Systems Research Institute,
ESRI, is largest provider of GIS software
today. ArcGIS 9.2 is the latest mapping software
available from ESRI. ArcGIS allows a user to
create GIS data, import existing GIS data,
manipulate and edit data, and analyze data
Specifically, ArcGIS 9.2 also allows a user to
author data, maps, globes, and models on a
personal computer and then serve the data to a
widely used GIS server and use the products on
the web, personal computer, and mobile computer.
ArcGIS is made up of a set of tools which
includes the following three products ArcMap,
ArcCatalog, and ArcToolbox.
12
ArcMap
GIS Software
ArcMap is the software used to view, edit, and
analyze GIS data. The geographic data view
allows a user to symbolize, analyze, and compile
GIS data. The table of contents is used to
organize the GIS data. The page layout view
resembles the geographic data view, but also
allows a user to add common map elements such as
titles, scale bars, legends, and north arrows to
the map. The page layout view is used to create
print or publish quality maps.
13
ArcCatalog
GIS Software
ArcCatalog organizes and manages all GIS
information such as maps, globes, datasets,
models, metadata, and services. ArcCatalog is
very similar to the Windows Explorer application.
ArcCatalog allows the user to search and browse
for, and manage geographic data. ArcCatalog is
also used when creating a new geographic dataset.
14
ArcToolbox
GIS Software
ArcToolbox includes an assortment of tools
necessary for analyzing, converting, and managing
GIS data. GIS is often used as an analysis tool.
ArcToolbox contains a set of preformatted
analysis tools to enable a user for pinpoint
locations fitting into specific criteria. For
example, a user may use the analysis tools to
find buildings within Big Stone Gap, Virginia
that are within 1 mile of Mountain Empire
Community College. The GIS user inputs a simple
mathematical query into the analysis tools and
the results will automatically appear in ArcMap.
15
Common Tools
Common Tools
A GIS is created, maintained, and viewed in a
user friendly environment. The ArcGIS software
and most online geographic information systems
use the same set of common tools which allows
individuals easy use of the system even if they
have never used GIS before. GIS allows a user to
zoom, pan, identify features, search for specific
features, create queries, and measure distances.
The examples used to illustrate the common GIS
tools are provided through the Wise County WebGIS
at http//arcims2.webgis.net/wise/default.asp.
16
Zoom to Full Extent
Zoom to Full Extent
Zoom to Full Extent Returns the map to the
original extent.
17
Zoom In
Zoom In
Zoom In Allows the user to use the computer
mouse to click a specific area on the map
document and automatically zoom into that area.
18
Zoom Out
Zoom Out
Zoom Out Allows the user to zoom out in order
to view a larger portion of the map.
19
Pan
Common Tools
Pan Allows the user to use the computer mouse
to slide the map in any direction in order to
view another portion of the map.
20
Identify
Identify
Identify Allows the user to obtain attribute
information about a map feature.
21
Search
Search
Search Allows the user to search for specific
features or attributes. This feature may be
preformatted to meet common search needs.
22
Query
Query
Query A query is a mathematical expression used
to find locations that fall into a set of
criteria.
23
Measure
Measure
Measure Allows the user to measure distances on
the map.
24
GIS Education at MECC
GIS Education
MECC offers an online GIS Career Studies
Certificate Program. The MECC online system,
blackboard, and the ESRI virtual campus are used
to administer the GIS courses necessary for the
completion of the GIS Career Studies Certificate
Program.
25
GIS Certificate Requirements
GIS Education
GIS Career Studies Certificate
4 core GIS fundamentals courses 16 1 GIS
specialty course 4 Presentation Software
3 Speech 3 Required Credit Hours 26
GIS Certified
26
GIS Core Courses
GIS Core Courses
GIS 200 Geographical Information Systems
I Provides hand on introduction to a dynamic
desktop GIS. Introduces the components of a
desktop GIS and their functionality. Emphasizes
manipulation of data for the purpose of analysis,
presentation, and decision making. GIS 201
Geographical Information Systems II Provides a
continuation of GIS 200, with emphasis on
advanced topics in problem solving, decision
making, modeling, programming, and data
management. Covers map projections and data
formats, and methods for solving the problems
they create. GIS 205 GIS 3 Dimensional
Analysis Introduces GIS 3D concepts and practices
with a concentration on displaying, creating and
analyzing spatial GIS data using 3D. Covers 3D
shapefiles, 3D data formats such as TINs, DEMs,
and grids, and controlling the perspective and
scale of 3D data through rotating, panning, and
zooming. GIS 210 Understanding Geographic
Data Provides the student an introduction to
geographic data and the principles behind their
construction. Introduces the concepts for
measuring location and characteristics of
entities in the real world. Exposes the student
to the limitation and common characteristics of
geographic data.
27
GIS Specialty Courses
GIS Specialty Courses
GIS 215 Software Platforms Applications Assist
s users with the transition to newer GIS software
platforms and application. Covers concepts and
terminology needed to become proficient in the
latest GIS software. GIS 220- Intro to Regional
Urban Planning Provides overview of how GIS is
used in urban and regional planning. Emphasis
will be on the use of GIS software to address
real world social, economic, and environmental
planning problems. GIS 225 GIS Applications for
Tax Assessors Introduces the use of GIS in the
local government tax assessment process.
Includes creating spatial queries, map
production, statistical reports, and more. Also,
employs technical skills in major topic areas
including special regulations, ratio studies,
comparable sales, and parcel data development and
maintenance. GIS 295 Solving Disaster
Management Using GIS Introduces how GIS
technology can apply to many activities related
to the improvement, response, and recovery phases
of emergency management. Illustrates the
difference between emergency management and risk
management.
28
Conclusion
Conclusion
Test your general knowledge of GIS by completing
the following GIS assessment.
If you would like additional information
regarding GIS and its uses, please visit the ESRI
website at http//www.gis.com, or contact Melanie
Salyer at msalyer_at_courtbar.org. For additional
information regarding the MECC GIS Career Studies
Certificate Program, please contact Susan Kennedy
at skennedy_at_me.vccs.edu.
29
Tutorial Assessment 1
True or False?
A GIS is a collection of computer hardware,
software, and geographic data for digitally
capturing, managing, analyzing, and displaying
all forms of geographically referenced
information.
TRUE
30
Tutorial Assessment 2
True or False?
People are a necessary component of GIS.
TRUE
31
Tutorial Assessment 3
True or False?
The pan tool allows the user to use the computer
mouse to slide the map in any direction in order
to view another portion of the map.
TRUE
32
Tutorial Assessment 4
True or False?
A geographic layer is a single real-world object
on a map.
FALSE
A geographic FEATURE is a single real-world
object on a map.
33
Tutorial Assessment 5
True or False?
An attribute is additional information about a
feature.
TRUE
34
Tutorial Assessment 6
True or False?
GIS attribute data is stored in paper format and
maintained by the GIS manager.
FALSE
GIS attribute data is stored in a database, such
as Excel or Access.
35
Tutorial Assessment 7
True or False?
ArcToolbox allows the user to create a print
quality map including titles, scale bars, and
north arrows.
FALSE
ArcMap allows the user to create a print quality
map including titles, scale bars, and north
arrows.
36
Tutorial Assessment 8
True or False?
ArcCatalog is similar to the Windows Explorer
application.
TRUE
37
Tutorial Assessment 9
True or False?
A GIS is created, used, and maintained in a
user-friendly environment.
TRUE
38
Tutorial Assessment 10
True or False?
Location is important in everyday life.
Therefore, GIS is a tool that may be used in any
career and by anyone on a day to day basis.
TRUE