Respiratory System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 19
Title:
Respiratory System
Description:
Respiratory System Respiratory System Why do we need to breathe? Gas exchange system Requirements of respiratory membranes: must be moist. Must be thin must be ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:50
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Respiratory System
1
Respiratory System
2
Respiratory System
- Why do we need to breathe?
- Gas exchange system
- Requirements of respiratory membranes
- must be moist.
- Must be thin
- must be permeable to gases.
- All organisms must have a mechanism with which to
transport gases. (circulatory system) - Movement of gases happens by simple diffusion.
3
(No Transcript)
4
Surface Area and other Respiratory Characteristics
- Cutaneous Respiration
- Examples
- Why are our lungs located within the chest cavity
and rib cage? - Moisture
- protection
- Importance of surface area.
- We have a respiratory surface area of about 60 to
70 square meters.
5
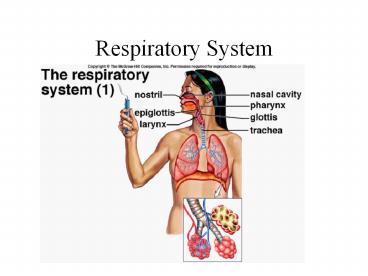
Human Respiratory Tract
- Why is it so easy for humans to choke?
- Vocal cords
- trachea
- cartilage rings
- incomplete rings
- trachea
- bronchi
- bronchioles
- alveoli
- capillaries
- Nostrils
- nasal septum
- nasal cavity
- Role of mucous membranes and hairs?
- Pharynx
- glottis
- epiglottis
- larynx
- Adams apple
6
(No Transcript)
7
(No Transcript)
8
How do we breathe?
- Thoracic cavity
- pleura
- pleurisy
- diaphragm
- intercostal muscles
- Role of pressure
- inspiration
- What happens with pressure and the volume of the
chest cavity?
- Expiration
- What happens with pressure and the volume of the
chest cavity?
9
(No Transcript)
10
Gas Exchange
- Where does it occur?
- What gases are exchanged?
- Simple diffusion is responsible.
- Erythrocytes
- RBCs
- Role of hemoglobin
- Structure of hemoglobin
- Oxyhemoglobin
- 4 oxygens at a time.
- Effects of CO
- Carbon dioxide is largely transported as a
dissolved gas in the plasma although some is
transported by hemoglobin
11
(No Transcript)
12
Control of breathing
- Respiratory Center
- Medulla Oblongata
- Brainstem
- Peripheral Chemoreceptors
- aorta and carotid arteries
- increase in Carbon dioxide increases H ion
concentration.
- Central chemoreceptors in the brain are sensitive
to this. - Increase CO2, Increase breathing rate.
- Hyperventilation
13
Other mechanisms of breathing
- Gills
- Structure
- Why do fish suffocate on land?
- Countercurrent flow
- Insects
- spiracles
- tracheae
- tracheoles
- Why cant this work in us?
- Snail and Frogs
- Have lungs, but very little respiratory surface
area. - Cutaneous Breathing.
14
(No Transcript)
15
(No Transcript)
16
(No Transcript)
17
(No Transcript)
18
(No Transcript)
19
(No Transcript)