Organic Soils, i.e. Histosols - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
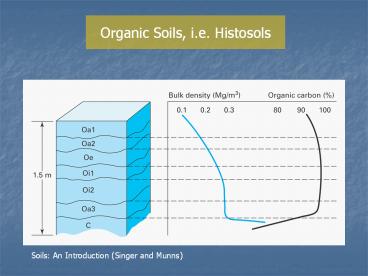
Organic Soils, i.e. Histosols
Description:
Organic Soils, i.e. Histosols Soils: An Introduction (Singer and Munns) Non-agricultural Use of Soil Using Soil as a Recycler Solid Waste Liquid Waste Disposal ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:401
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Organic Soils, i.e. Histosols
1
Organic Soils, i.e. Histosols
Soils An Introduction (Singer and Munns)
2
Non-agricultural Use of Soil
- Using Soil as a Recycler
3
Solid Waste
4
Liquid Waste
5
Disposal/Treatment Options
Two options On-site Septic System Off-site
Sewage Trt Plants
Soils An Introduction (Singer and Munns)
http//ga.water.usgs.gov/edu/wuww.html
6
Waste Water Treatment Plants(WWTP)
- Combined OR
- Separate sewage from runoff
Soils An Introduction (Singer and Munns)
7
WWTP Goals
- Clean water (effluent) to return to streams
- remove excess nutrients
- minimize pathogens
- appropriate temperature
- Sanitary solids disposal
- landfill
- incinerate
- land application
8
Biosolids solids after trtmt
Soils An Introduction (Singer and Munns)
9
Biosolids Processing
10
Phosphorus (P) Crop Need vs Water Quality
greenfacts.org
Soil crop production
Water eutrophication
Goal Satisfy P need, minimize P loss
11
Balance
www.milorganite.com
NP ratio in these sources less than plant
requires
12
Effects of Biosolids Treatment
- Biosolids
- concentrated with P
- disposalland application
- Do biosolids differ in P availability as compared
to manure or fertilizer?
13
P Removal Method Lime
- solids pumped to this tank
- addition of lime
- raise pH
- reduce pathogens
- precipitate P as Ca-P
- (very insoluble)
Baraboo, WI
14
P Removal Method Fe or Al
- add at influent entry
- Fe
- precipitate Fe-P
- can become soluble in reducing conditions
- Al
- precipitate Al-P
- too much Al can cause toxicity in soil
- separate for solids
Lodi (Al) Portage (Fe) WI
15
P Removal Method Biological
- primary influent trt
- microorganisms eat dissolved P
- solids removed by settling for further trt
Madison, WI
16
Biosolids Trtmt Effects
lime (Ca)
Fe or Al
biological
P Removal Method
17
Experimental Approaches
- Field Study
- with plant
- real environment
- Incubations
- no plant
- controlled conditions
18
Biosolids History Incubation
Soil ID Soil Series Field Biosolids History
1A Plano None
1B Plano 15 apps
2A Plano None
2B Plano 2 apps
3B Ringwood 13 apps
P Source Treatment TP () PWEP ()
Madison Biological 4.45 11.3
Baraboo Lime 1.05 0.1
Lodi Alum (Al) 3.67 0.3
Portage Iron (Fe) 3.63 1.2
Manure - 0.67 33.8
KH2PO4 - 22.8 100
PWEPpercent of TP that is water extractable
19
Soil Classification
- Plano
- Fine-silty, mixed, superactive, mesic Typic
Argiudolls - Ringwood
- Fine-loamy, mixed, superactive, mesic Typic
Argiudolls - Both soils are typical of MMSD land-application
program
20
Effects on Bray P1
KH2PO4
bars within a soil followed by the same letter
are not statistically different at p0.05
21
Effects on PBC
PBC P rate/?STP
Plano 1 Plano 1 Plano 2 Plano 2 Ringwood
1A 1B 2A 2B 3B
P Sources (0) (15 apps) (0) (2 apps) (13 apps)
--------------------------PBC (kg P ha-1)-------------------------- --------------------------PBC (kg P ha-1)-------------------------- --------------------------PBC (kg P ha-1)-------------------------- --------------------------PBC (kg P ha-1)-------------------------- --------------------------PBC (kg P ha-1)--------------------------
Lime 8.4 10.5 6.6 8.5 8.3
Al 19.9 -104.7 23.8 45.4 -222.9
Fe 9.2 12.6 10.6 17.4 16.7
Biological 7.0 5.8 8.3 8.2 7.2
Manure 7.3 5.2 7.3 7.9 6.2
KH2PO4 4.2 2.7 4.5 3.7 3.7
22
Predicting STP
Biosolid and manure properties Biosolid and manure properties Biosolid and manure properties Biosolid and manure properties Biosolid and manure properties
Soil Extractant WEP AmOxP TP P to FeAl ratio P to FeAl ratio
---------------------------r--------------------------- ---------------------------r--------------------------- ---------------------------r--------------------------- ---------------------------r--------------------------- ---------------------------r---------------------------
All Soils (n100) All Soils (n100) All Soils (n100) All Soils (n100) All Soils (n100)
?WEP 0.58 0.36 0.22 0.22 0.46
?BP1 0.53 ns -0.39 -0.39 0.52
?M3 0.48 ns -0.37 -0.37 0.40
, , indicate statistical significance at
p0.05, 0.01, and 0.001, respectively
23
Effects on Bray P1
Arlington Field Experiment
24
Conclusions
- P source treatment greatly influences P
availability - lime and biologically treated biosolids change
BP1 similar to a typical dairy manure - Fe and Al treated biosolids have significantly
greater PBC - P fertilizer has the smallest PBC
- Field results follow same trends as Incubations
- WEP of biosolids could be used to predict PBC
25
Implications
- Is there a best method for P removal?
- Does P removal method have implications for the
functionality of biosolids for other purposes
(besides keeping P from leaving in runoff)? - What do WWTP operates need to take into account
when deciding on a P removal process? - How is soil being used as a recycler?
26
Green Waste
- Reduce Reuse Recycle
27
BackgroundP Chemistry
- Solubility in Soils - pH dependent
Optimum P availability between pH 6-7.
Brady and Weil, 1999
28
Effects on WEP
KH2PO4