The Causes and Risks of Population Growth - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 44
Title:
The Causes and Risks of Population Growth
Description:
The Causes and Risks of Population Growth Crispin Pierce, Ph.D. (crispo_at_u.washington.edu) How fast is population size increasing? What are the causes of increase? – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:143
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Causes and Risks of Population Growth
1
The Causes and Risks of Population Growth Crispin
Pierce, Ph.D. (crispo_at_u.washington.edu)
2
(No Transcript)
3
Unlike plagues of the dark ages or contemporary
diseases we do not understand, the modern plague
of overpopulation is soluble by means we have
discovered and with resources we possess. What is
lacking is not sufficient knowledge of the
solution but universal consciousness of the
gravity of the problem and education of the
billions who are its victim. Martin Luther King,
Jr., 1929-1968
4
The list of environmental problems aggravated by
growing populations includes deforestation and
desertification, loss of topsoil, poisoning of
drinking water and pollution of oceans, shrinking
wetlands, shortage of fuels such as firewood,
exhaustion of oil reserves and of various mineral
resources, siltation in rivers and estuaries,
dropping water tables, erosion of the ozone
layer, loss of species and wilderness areas,
global warming, rising sea levels, nuclear waste,
air pollution, and acid rain. Rebecca Clay,
Environmental Health Perspectives, vol. 103
(1995).
5
Currently the U.S. has no policy on population
even though both the Rockefeller Commission in
1972 and the Presidents Commission on
Sustainable Development in 1995 recommended that
the U.S. adopt policies to stabilize the U.S.s
population. COPHP Student, 2003
6
(No Transcript)
7
(No Transcript)
8
(No Transcript)
9
Overpopulation exists if the activities of the
current population are depleting the capacity of
the environment to provide for future populations.
10
- How fast is population size increasing?
- What are the causes of increase?
- What are the effects of increase?
- Population increase myths.
- Which tools are effective at slowing population
increase? - What can I do?
11
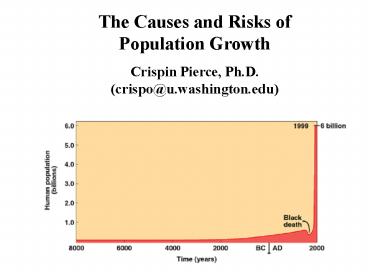
How fast is population size increasing?
12
(No Transcript)
13
- Currently at 274 million, the U.S. population is
growing by about 2.5 million people each year,
making the United States one of the world's
fastest-growing industrialized nation. The U.S.
fertility is currently at 2.0, up from 1.8 in
1988. - Immigration adds at least another 800,000 people
annually to our nation's population.
14
What are the causes of increase?
- Improved medicine, sanitation, and nutrition have
produced a major decline in death rates,
particularly in the last century. For example,
life expectancy in Egypt increased by twenty
years between 1940 and 1960. - Birth rates have declined much more slowly.
15
- Households in rural areas of developing countries
often have little or no assurance that they will
receive an income when old there is no social
security system, no employer subsidized funds, no
medical insurance or life insurance. Children may
be viewed as an asset which will generate income
when the parents are old.
16
- In many countries, the degraded status of women
is another contributing factor to high
birthrates. Women are often denied opportunities
for education, employment, land ownership, and
governmental service. As a result, they have few
alternatives to their childbearing roles.
17
- Developing areas such as Africa, Latin America
and parts of Asia are still primarily agrarian
therefore, incentives for having larger families
still exist. - Following adoption of basic technology that
improved living conditions, death rates plunged
dramatically. As a result, these populations are
growing rapidly.
18
Why do households have more children than may be
best for society?
- People may not recognize the implications of
falling death rates for their fertility
decisions. - Family size choices may have consequences for
other families that are not considered. For
example, publicly funded education, child care,
tax deductions, and child welfare programs.
Similarly, congestion costs of overpopulation and
degraded air, water, and soil quality in large
cities will not be fully realized by households.
19
- For large extended families that are typical in
rural areas, there are often perceived decreased
costs associated with having children. For
example, the private costs of a child to one
mother may be lower if she expects her sister to
help in child rearing. - Societies and religions have developed social
norms to encourage child rearing (e.g.
celebration of childbirth), and to discourage
birth control.
20
What are the effects of increase?
21
- As human population increases, the diversity and
number of plants and animals decreases. We lose
one or more entire species of animal or plant
life every 20 minutes 27,000 species a year.
This is a rate and scale of extinction greater
than any in the last 65 million years.
22
- Six million acres of prime farmland an area
the size of Vermont were lost in the United
States alone between 1982 and 1992. Four of those
six million acres were lost to urban and suburban
expansion. The other 2 million acres were lost
through erosion caused by deforestation,
unsustainable farming practices, and animal
over-grazing.
23
- Global carbon dioxide emissions have quadrupled
since 1950, largely from deforestation and the
burning of fossil fuels. This greenhouse gas
addition causes global warming and disruption in
weather patterns. - Five storms over the span of five years have cost
the insurance industry in the United States 25.7
billion. - Increased spread of malaria, cholera, typhoid
fever, and dengue fever worldwide are expected.
24
Population increase myths.
- Per capita food production is increasing, so the
Earth must be able to sustain population growth. - Per capita meat production has increased
25
(No Transcript)
26
- Per capita production of grains has decreased
since 1984
27
(No Transcript)
28
- It takes 23 times more water, and ten times more
energy to produce one ton of beef than it does to
produce one ton of grain. - Current unsustainable agricultural practices have
led to widespread cropland losses and extensive
water pollution from pesticides and fertilizers
(e.g., the Mississipi River and the death zone in
the Gulf of Mexico).
29
- Technology and market forces will provide
solutions to problems associated with population
increase. - As populations grow, especially in rural areas,
increased scarcity of land (and other resources)
may drive people to innovate and adopt new
methods and technologies that use them more
efficiently. It is often argued, for example,
that the agricultural revolution in the UK and
other European countries after 1650 was driven by
population growth.
30
- Market systems subsidize industries such as
logging, mining and grazing without considering
environmental costs. Degradation of commonly
held resources such as groundwater levels or
atmospheric and ocean quality is not included.
Nor do markets consider Earth's "services," such
as regulation of climate, detoxification of
pollutants or provision of pollinators, much less
questions of human equity and social justice.
31
- The entire population of the world could fit
into an area the size of Texas. - Dividing the world's 6 billion humans into
Texas's 261,914 square miles, each person would
have 0.028 acres of land. However this land in
Texas, (or even all the land in North America for
that matter), would not be able to sustain these
people. A minimum of 0.17 acres of arable land is
needed to sustain a person on a largely
vegetarian diet without the intense use of
fertilizers and pest controls.
32
- The tiny amount of land per person in the Texas
scenario could not accommodate the intense
demands we place on our lands (particularly in
developed countries) roads, businesses, grazing
lands, lawns, airports, etc.
33
Group Projects
- Exponential Growth Questions
- Questions of Freedom
- The Economic Costs of Population Growth
34
Exponential Growth Questions
- Would you rather receive 10,000, or the amount
after thirty days, where you receive one cent on
day one, two cents on day two, four cents on day
three, etc.?
35
- If the current rate of world population increase
is 1.31, how many additional people will inhabit
the planet in one year? - Which costs would you include in the price of
gasoline to adequately reflect the natural
resource costs of petroleum exploration,
development, and use?
36
Questions of Freedom
- Which freedoms in American society decrease with
increased numbers of people? - Are there freedoms that are increased with
increased population density? - Who should decide on losses of freedom vs.
population stabilization?
37
The Economic Costs of Population Growth
- There are three major areas of U.S. taxation
property taxes, income taxes, and sales taxes.
Which of these taxes is disproportionally spent
(but not collected) on families with large
numbers of children? Which of these taxes is
disproportionally lower for families with large
numbers of children?
38
- Should municipal entities, such as schools, city
boundaries, and water and sewage systems be
designed and built for a target population size?
Should additional residents (born children and/or
migrants) have to live elsewhere once a city has
reached its maximum size?
39
Which tools are effective at slowing population
increase?
- Improve the health of women and children.
- Improved family planning supports women in
choosing to delay motherhood, prevent unwanted
pregnancies, and avoid STDs (including AIDS) and
dangerous abortions. Improved family planning
could reduce child and infant mortality by 25,
preventing three million deaths per year.
40
- Guarantee access to family planning resources.
- Eradicate violence against women.
- Abused women are afraid to use family planning
services for fear of reprisal from their
husbands. - Educate and involve men in family planning and
child care.
41
- Create gender equity.
- Insist on womens rights to own property, to get
an education, to earn income, and to participate
in government. - Actively conserve cropland, freshwater, energy,
and other environmental resources.
42
What can I do?
- Plan the size of my family. Consider having two
or fewer children, and/or adoption. - Support domestic and international family
planning programs. - Become involved in programs supporting equal
rights, and educational and job opportunities for
women worldwide.
43
- Conserve energy and natural resources (one U.S.
citizen consumes about 30 times as much as a
citizen of India). - Encourage reduction of western patterns of
consumption. - The richest fifth of the world consumes 86 of
all goods and services and produces 53 of all
carbon dioxide emissions, while the poorest fifth
consumes 1.3 of goods and services and accounts
for just 3 of C02 output.
44
References Zero Population Growth The Union of
Concerned Scientists Cornell University PregnantPa
use