The Mauryan Dynasty - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 25
Title:
The Mauryan Dynasty
Description:
The Mauryan Dynasty Invasions of India India s princes fought over their small kingdoms for centuries, until two big invasions taught them a lesson. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:1114
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The Mauryan Dynasty
1
The Mauryan Dynasty
2
Invasions of India
- Indias princes fought over their small kingdoms
for centuries, until two big invasions taught
them a lesson. - The Persians invaded the Indus Valley in the
500s BC, and made it part of the great Persian
Empire. - Then, Alexander the Great invaded India in 327
BC. - The short-lived invasion did have one important
effect. It led to the first great Indian empire.
3
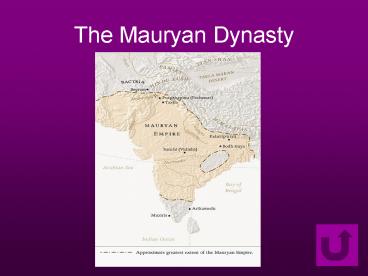
Indias First Empire
- Indias first empire was founded by Chandragupta
Maurya. - Chandragupta was an Indian prince who conquered a
large are in the Ganges River Valley soon after
Alexander invaded western India. - Alexanders invasion weakened many of Indias
kingdoms. When he left it gave Chandragupta the
opportunity to conquer and unite almost all of
northern India.
4
The Mauryan Dynasty
- He founded the Mauryan dynasty in 321 BC.
- To run his empire, Chandragupta set up a
centralized government. In a centralized
government, rulers run everything from a capital
city. - To control everything from his capital,
Pataliputra, Chandragupta had to have a strong
army, and a good spy system to make sure no one
was planning to rebel. - He set up a postal system to ease communications.
5
Emperor Asokas Reign
- Chandragupta founded the Mauryan dynasty, but
many believe that the empires greatest king was
Asoka (273 BC 232 BC). - Asoka was a strong military leader, but he came
to hate bloodshed. After one bloody fight, he
walked over the battlefield and made a vow as he
viewed the dead and wounded. - He dedicated his life to following the teachings
of Buddha.
6
The Buddhist King
- Asoka was historys first great Buddhist king.
- He built hospitals for people and for animals.
- He built new roads so it was easier to trade and
put shelters and shade trees along roads where
travelers could rest. - He sent Buddhist teachers through India and the
rest of Asia to carry the religion to new
believers. - He had laborers build thousands of stupas, or
Buddhist shrines that have the shape of a dome or
mound.
7
Asokas Legacy
- Asoka allowed his Hindu subjects to practice
their religion and such tolerance was unusual at
this time. - With a good road system and a strong ruler, the
empire prospered. - India became the center of a huge trade network
that stretched to the Mediterranean Sea.
8
The Fall of the Mauryan Empire
- Asoka died in 232 BC, and the kings who followed
him were not good leaders. - They made bad decisions that turned the people
against them. - They forced the merchants to pay heavy taxes and
seized peasants crops for themselves. - Things were so bad that in 183 BC, the last
Mauryan ruler was killed by one of his own
generals.
9
The Gupta Empire
- For 500 years, India had no strong ruler. Once
again, small kingdoms fought with one another and
made life miserable for their subjects. - Then, in 320 AD, one prince in the Ganges River
valley grew more powerful than the others. - His name was also Chanragupta and he chose to
rule from the old capital of the Mauryan
empirePataliputra.
10
Gupta Dynasty
- Chandragupta founded the Gupta dynasty.
- When he died, his son, Samudragupta, took over
the throne and expanded the Gupta empire in
northern India. - Soon, the new kingdom dominated almost all of
northern India. The Guptas ruled for about 200
years. - Gupta rulers had one advantage over the earlier
Mauryan kings. The empire was smaller and that
made it easier to manage.
11
(No Transcript)
12
Gupta Wealth
- The Gupta empire grew wealthy from trade.
- Salt, cloth, and iron were common goods traded in
India. Indian merchants also traded with China
and with kingdoms in southeast Asia and the
Mediterranean. - The Gupta rulers controlled much of the trade and
became very wealthy. - They owned silver and gold mines and large
estates.
13
Pilgrimages
- Trade created jobs for people in India and made
many people and cities prosperous. - Cities grew up along the trade routes, and many
people traveled. Some people called pilgrims,
often used the trade routes to travel to a
religious shrine or site. - Just as cities today make money from tourism,
Indian cities that were famous for their temples
became wealthy from visiting pilgrims.
14
Indian Literature
- During the Mauryan and Gupta empires, art,
literature, architecture, and science also began
to develop. - The Vedas of India are ancient hymns and prayers
for religious ceremonies. - Two epics are very famous in India. The
Mahabaharata and the Ramayana both tell the long
poems tell about brave warriors and their heroic
deeds.
15
Mahabharata
- The Mahabharata is the longest poem in any
written languageabout 88,000 verses. - Historians think several different authors wrote
it around 100 BC. - It describes a great war for control of an Indian
kingdom about 1,000 years earlier. - In the section titled the Bhagavad Gita, the god
Krishna preaches a sermon before a battle. He
explains how noble it is to do ones duty even
when it is difficult and painful.
16
(No Transcript)
17
Ramayana
- The Ramayana is another long poem.
- It tells the story of a great king Rama and his
queen Sita. - Ramas enemies have him banished from the
kingdom. He is forced to live as a hermit in the
forest. - Later, he fights and defeats the demon Ravana,
who had kidnapped Sita. - As many Indian epics, they live happily ever
after.
18
(No Transcript)
19
Ramayana
- The Ramayana contains many moral and religious
lessons. - Rama is the perfect hero, king, and son.
- Sita is the perfect, faithful wife.
- Like adventure movies today, these poems told
thrilling stories about great heroes.
20
Kalidasa
- One of Indias best-known authors was Kalidasa.
- He lived during the Gupta dyanasty.
- He wrote plays, poems, love stories, and
comedies. - His poem The Cloud Messenger is one of the most
popular Sanskrit poems. - It is a love story that also contains beautiful
descriptions of the mountains, forests, and
rivers of northern India.
21
Indian Math and Science
- Indian mathematicians, especially in the Gupta
period, made important contributions. - Aryabhata was the leading mathematician of the
Gupta empire. - He was one of the first scientists known to have
used algebra. - Indian mathematicians developed the idea of zero
and a symbol to represent it. - They also explained the concept of
infinitysomething without an end.
22
Mathematics
- Gupta mathematicians created the symbols for the
numbers 1 to 9 that we use today. - These number symbols, or numerals, were adopted
by Arab traders in the 700s AD. - European traders borrowed them from the Arabs.
Use of these numbers spread through Europe and
replacing Roman numerals. - Today, this system of number symbols is known as
the Indian-Arabic numerical system.
23
Algorithms
- Early Indians also invented mathematical
algorithms. - An algorithm is a series of steps that solve a
problem. - If you follow the steps you get the right answer.
- Computer programmers today often use algorithms
to tell computers what to do.
24
Astronomy
- Ancient Indians followed and mapped movements of
planets and stars. - They understood that the Earth was round and
revolved around the sun. - They also seemed to have understood gravity.
- Indians developed ideas about what the universe
was made of. As early as the 500s BC, Indian
thinkers believed that the universe was made up
of many tiny particles. They came up with the
idea of Atoms before the Greeks in the West did.
25
Medicine
- Gupta doctors were very advanced for their time.
- They could set broken bones and perform
operations. - They also invented many medical tools.
- Indian doctors used herbs to treat illnesses.
- They also believed it was important to remove the
causes of a disease and not just cure the disease
itself.