KINGDOM ANIMALIA: PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: KINGDOM ANIMALIA:
1
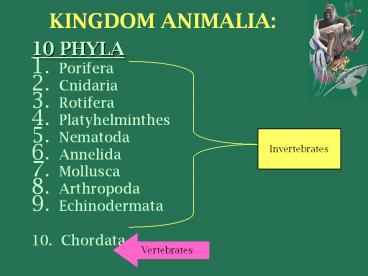
KINGDOM ANIMALIA
- 10 PHYLA
- Porifera
- Cnidaria
- Rotifera
- Platyhelminthes
- Nematoda
- Annelida
- Mollusca
- Arthropoda
- Echinodermata
- 10. Chordata
Invertebrates
Vertebrates
2
(No Transcript)
3
Phylum Porifera
- Sponges
- Very primitive, no true tissues
- Supported by spongin (protein fibers) or spicules
(mineral crystals) - Sessile animals live attached to rocks.
- Get food/ oxygen from water that is pumped
through their hollow bodies by cells with
flagella - Filter feeders
- Reproduce through budding and sperm/eggs
4
Phylum Porifera
5
- Flagellated choanocytes - Filter food / O2 from
the water passing through the porous body
6
Phylum Cnidaria
- Have true tissue no organs
- Have a simple skeletal system
- Excretion through same opening used to pump food/
water through - Free-floating or sessile
- 2 stages of life cycle- medusa/polyp
- Budding/sexual reproduction
7
Polyp stage
Medusa stage
- Cnidaria
- Corals, Jellyfish, Sea Anemones
8
- Cnidarians have a gastrovascular cavity and
cnidocytes on tentacles that sting prey
9
PHYLUM ROTIFERA
- Very small size and mostly soft bodies
- Microscopic, mostly aquatic-found in many
freshwater and moist soil - Complete digestive tract with mouth and anus
- Body cavities that are partially lined by
mesoderm- coelomates. - Crown of cilia around the mouth of the rotifer
that makes them appear to whirl like a wheel - Tiny mouths primarily omnivorous, unicellular
algae and other phytoplankton - Sexual reproduction
10
Phylum Rotifera
11
Phylum Platyhelminthes
- Flatworms (tapeworms, Planaria)
- 3 cell layers- Acoelomates
- Bilaterally symmetrical
- No respiratory or circulatory systems
gastrovascular cavity and organized response
mechanisms - Thin flat bodies absorb oxygen and release CO2
and wasted directly in the surrounding water. - Reproduce by splitting in 2
- Some parasitic, they live in the digestive
systems of other animals.
12
- A planarian has a gastrovascular cavity and a
simple ner vous system
13
- Flukes and tapeworms are parasitic flatworms
Figure 18.7B
14
Phylum Nematoda
- Roundworms
- Less than 1 mm long Live in soil and water.
- Sexual reproduction- male sperm/female egg
- Some are decomposers, others are parasites of
animals or plants - Pseudocoelom complete digestive system
- Pinworms and hookworms in soil burrow into the
skin of people who go barefoot outdoors Trichina
worms infest people who eat undercooked pork or
wild game. (cause Elephantitis- swelling of
appendages due to blocking of fluid movement in
blood vessels by worms)
15
Phylum Nematoda
16
Phylum Annelida
- Earthworms, leeches- segmented worms
- Each segment is separated from the next by a
membrane - Closed circulatory system with blood vessels that
run the length of the animal. - Has a complete excretory and digestive system
where food travels through in one direction from
anterior to posterior. - Branches of the main nerves and clusters of nerve
cells at the anterior end serves as a simple
brain. - Live in water or damp soil Bilateral sym
- Reproduction occurs by splitting or by mutual
fertilization (hermaphrodites)
17
- Ear thworms and Their Relatives
- Eat their way through soil
- Have a closed circulatory system
Figure 18.10A
18
Phylum Annelida (cont.)
- Leeches were once used to suck out peoples
excess blood and reduce harmful high blood
pressure - Leeches are uses today to produce
anti-blood-clotting medicines, to suck blood from
bruises, and to stimulate blood circulation in
severed limbs that have been surgically
reattached..
19
Phylum Mollusca
- Includes snails, clams, slugs, squid, and their
relatives. - Bilateral sym. coelomates
- Radula- scrapes up food complete digestive tract
- Separate sexes sexual reprod.
- Mollusks have soft bodies with 3 parts
- A visceral mass that contains most of the organs
- A muscular foot that is used in movement
- A thick flap called a mantle, which covers the
body and in most species produces a heavy shell
of calcium compounds.
20
Phylum Mollusca (cont.)
- Mollusks pump water through gills- both for
oxygen and food for clams and oysters. - Squid and octopi use the pump for jet propulsion
through the water in search of prey.
21
Phylum Mollusca
22
- Diverse mollusks are variations on a common body
plan - All mollusks have a muscular foot and a mantle,
which may secrete a shell that encloses the
visceral mass - Many mollusks feed with a rasping radula
23
- Gastropods
- The largest group of mollusks and include the
snails and slugs
24
- Bivalves
- Have shells divided into 2 halves and include
clams, oysters, mussels, and scallops
25
- Cephalopods
- Adapted to be agile predators and
- include squids and octopi