The Age of Exploration PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 44
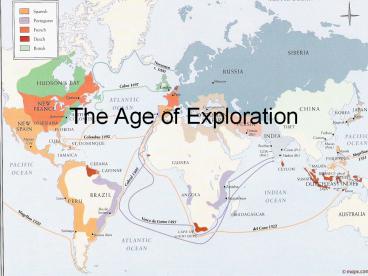
Title: The Age of Exploration
1
The Age of Exploration
2
Life Found on Mars!
Unbelievable but true This recent photo from the
unmanned space exploration to Mars shows
conclusive proof that savage, almost humanlike,
alien life-forms exist among the rich mineral
deposits on the surface of Mars.
3
Barack Obama Wants You Eager to be the first to
make contact with the newly discovered aliens,
the United States Government has sanctioned the
first privately owned space vehicles to make the
journey to Mars. Volunteers are wanted for the
first manned missions to Mars.
4
Would you volunteer for the mission? Yes or No?
___________Why/Why not? _________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
___________________________________What sort of
people do you suppose would volunteer for this
kind of mission?__________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
___________________What would they have to gain?
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________What, if anything could go wrong?
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________What technological advances would have
to occur before this could actually
happen?__________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________________________________________
__________________
5
Exploration and Navigation
http//www.youtube.com/watch?vb3fYF6YvesA
6
The biggest reasons for the Age of Exploration
The 3G Theory
- Desire for spices, and the profit from selling
and trading them. Expanding economies of Europe
and increased trade in Asia, led to the need for
new raw materials. (GOLD) - Competition between European powers. The Desire
to be first to explore and conquer new places for
their country (GLORY) - To diffuse (spread) Christianity Protestantism
(England Holland) Catholicism (Spain, Portugal
France). (GOD)
7
The search for spices
- During the Middle Ages, the Crusaders who fought
the Muslims in the Middle East learned of spices,
and brought them back to Europe. - The Europeans wanted cinnamon, cloves, nutmeg,
and most of all pepper to spice and preserve
meat, make perfume(s). - The chief source of spices was the Moluccas (in
modern day Indonesia) which they called the Spice
Islands.
8
The Muslim Situation
- Europeans wanted spices.
- Following the fall of Constantinople (it became
Istanbul), Europe no longer had their gateway to
the East. - Trading over land was expensive and dangerous.
- Muslims and Italian sailors controlled the trade
by sea. - Other European sailing powers (England, France,
Spain and Portugal) wanted in on the riches of
the spice trade, but had to find a way to get
there.
9
Improved technology leads to better sailing
techniques
- European cartographers (mapmakers) created much
better maps and charts of the sea and its
currents. - Europeans mastered the use of the astrolabe, an
instrument developed by the Greeks and mastered
by the Muslims, to determine their latitude at
sea. - The caravel, a ship that combined European body
styles with Muslim triangular sails and Chinese
rudders, made ships much faster and able to
travel farther.
10
Portugal
- By the 1400s, Portugal was strong enough to
expand into Muslim controlled North Africa. - Prince Henry, known as Henry the Navigator,
hoping to spread Christianity and find Muslim
gold, began a school for cartographers, sailors
and captains at Sagres.
11
Portugal (continued)
- In 1487, Bartolomeu Diaz, rounded the southern
tip of Africa. He ended the myth that the sea
was full of monsters, and it gave hope to those
who wished to sail to India. He named the tip of
Africa the Cape of Good Hope.
12
Bartolomeu Diaz
Cape of Good Hope
13
Portugal (continued)
- In 1497, Vasco da Gama led four ships around the
southern tip of Africa, and on his next voyage,
made it to the port of Calicut, in western India. - The spices he brought back sold at 3000 of the
money he put into it. - His sailors paid a heavy price, they discovered
scurvy, a disease caused by lack of vitamin C.
14
Vasco da Gama
15
Spain
- An Italian sailor from Genoa wished to sail for
Portugal. He had an idea that since the world
was round, a relatively new concept at the time,
that if he sailed westward, that he would reach
India faster. His name was Christopher Columbus. - Portugal refused to sponsor him, so he got help
from the Spanish King Ferdinand and his wife
Isabella, who were famous for expelling the
Muslim Moors from Spain.
16
Ferdinand and Isabella sponsor the voyages of
Columbus.
17
Spain (continued)
- Columbus made two huge errors
- Underestimating the size of the world greatly
- Not knowing that two continents lay in his way
- He had three ships the Nina, the Pinta, and the
Santa Maria. He sailed west and ran into the
islands of the Caribbean. Since he thought he
was in the Indies, he called the people he found
there Indians.
18
Naming the New World
- In 1507 a German cartographer read reports of a
new world written by an Italian sailor named
Amerigo Vespucci. He labeled the region
America after Vespucci. The region that
Columbus had found became known as the West
Indies.
19
The Grande Exchange
- Introduced to the Americas
- 1. DISEASES rapidly devastated human
populations that had no resistance to Old World
Diseases, killing 50-90 of native populations
50 epidemics in Valley of Mexico 1519-1820 often
carried to villages by other natives, arriving
before actual contact with Spanish - smallpox, measles, whooping cough, bubonic
plague, malaria, yellow fever, diphtheria,
influenza - 2. ANIMALS no large mammals in Middle America
introduced new means of transportation/labor
horse became indispensable to plains Indians new
food sources - horses, pigs, sheep, goats, cattle, rats (spread
disease, decimated native small animals) - adapted quickly
- competed with Indians for food
- destroyed vegetation
20
The Grande Exchange (continued)
- Brought to the Americas
- 3. PLANTS
- sugar cane - harmed both man and environment
forbearer of plantation system with slave labor
and the initial assault on tropical rainforests - from 1650 until beginning of 20th century,
Caribbean region was the world's center of cane
sugar worldwide demand - changed ethnic make up of much of Latin America
- grains - wheat, millet, barley, sorghum, rice
adapted well to many areas, enhanced native diets
- chick peas (garbanzos), soybeans
- fruit - peaches, pears, oranges, melons, limes,
bananas - vegetables - onions, radishes, salad greens,
yams, peas, leeks, parsley - European clover, grasses, many other plants
widely used in our modern American landscape - weeds - Kudzu (legume brought for forage from
Japan - has taken over in the Gulf and South
Atlantic US) - 4 INSECTS
- Asian cockroaches, Japanese beetle, Dutch elm
disease, Killer bees, Gypsy moth
21
The Grande Exchange (continued)
- Brought to the Americas
- 5. TECHNOLOGIES
- Alphabet/ writing
- iron-edge tools -didn't shatter like those made
of obsidian by Indians - farming equipment - plow drastically changed
agricultural practices - wheel
- gunpowder
- ranching - changed landscape walled ranches with
tile roofs, adobe brick buildings surrounded by
corrals and pastureland cowboys, gauchos - Other new institutions
- towns - relocated Indians from their land into
villages and towns changed building patterns
that used wood and charcoals led to more
deforestation - government structures/policies encomienda -
system that gave the right to a conquistador to
collect tribute from Indians - religion (Catholic)
- 6. PEOPLE
- Spanish, Portuguese - main colonizers of Middle
and South America - Africans - necessary as native population
decreased worked on plantations eventually
replaced Indians as the dominant ethnic group in
the Caribbean infused much of their culture into
many areas of the Americas - British, Irish, French, Germans, Dutch, Asians,
Indians (from India)
22
The Grande Exchange (continued)
- Brought Back to Europe
- PLANTS
- maize (corn) from Mexico
- introduced in Africa and south of equator as
early as 1550 - fed Africans that provided the manpower for
American plantations - grows where rainfall was sufficient in S. Europe,
especially important to Greeks and Serbs - led to population growth necessary to provide
labor for industrialization - potato from Peru
- basic food for people all over the world no
other single crop has played such a decisive role
- N. Europe potatoes dominated the diet of the poor
in the 19th/20th century. This in turn
contributed to population growth which led to
industrialization of Germany and Russia Maize
(corn) and potatoes had a fundamental advantage
over the different sorts of grain in Europe -
they produced more calories per acre, feeding up
to 4 times as many people. - sweet potatoes
- tomatoes
- adapted well to Mediterranean climate
- vitamin content supplemented diet
- what would Italian food be without tomatoes?
- healing plants
- quinine from Peruvian bark
- Ipecac from Amazon roots
- today some 500 prescription drugs derived from
American herbs, other plants
23
Line of demarcation- The Treaty of Tordesillas
- Portugal and Spain fought over who got what in
the Americas finally Pope Alexander VI stepped
in and ordered both Catholic monarchs to settle
the problem. - On June 7, 1494, the Spanish and the Portuguese
signed a treaty to divide the world in two. The
dividing line ran through the Atlantic with Spain
gaining lands to the west including all the
Americas. Brazil was granted to Portugal. The
eastern half including Africa and India was given
to Portugal.
24
(No Transcript)
25
Circumnavigating the Globe
- In 1519, a minor Portuguese noble named Ferdinand
Magellan set out from Spain with five ships and
hundreds of men. - He discovered the Strait of Magellan, and sailed
into the Pacific he named it because it means
peaceful- Ocean. - He faced several mutinies, and was murdered in
the Philippines. - In1522, one ship and 18 sailors returned to
Spain, and were credited with being the first to
sail all the way around the globe, or
circumnavigate it
26
Voyage of Magellan
27
Spain (continued)Cortez the Killer
- In 1520, Hernan Cortez (also spelled Cortes) and
his conquistadors went to the new world in
search of gold. They found the Aztec Empire in
what is today Mexico. - With the use of guns, and with the help of the
fact that the Aztecs had no immunity to the
diseases (smallpox) the Spaniards carried, the
Aztec Empire was almost completely eliminated.
28
Spain (continued)
29
Spain (continued)
30
Spain (continued)
- Soon after Cortez, Francisco Pizarro followed.
He went to South America to what is now Peru. He
destroyed the Inca culture for their gold. - Spain sent ships back and forth to the new world
to take the gold home and make themselves the
richest nation in the world. These ships came to
be known as the Spanish Armada.
31
Pizarro destroys the Inca Empire
32
Encomienda
33
Encomienda System
- A hierarchical social order emerged with the
Indians and slaves at the bottom, the mestizos
and mulattos in the middle and the Europeans and
their descendants at the top. Royal protection of
the Indian was generally ineffective. Because
Spaniards and creoles looked down on manual
labor, they developed several labor systems to
force Indians to work for Spanish landowners.
34
The English, Dutch, and French in the New World
35
The English, Dutch, and French in the New World
(continued)
- French Captain Jaques Cartier explored the
St. Lawrence River and established
the area now know as Quebec (Canada).
36
Francis Drake
- Eager to get into the race for new land and
glory, Queen Elizabeth sends out explorer Sir
Francis Drake, who becomes the first Englishman
to circumnavigate the globe.
37
Sir Francis Drake (continued)
38
The English, Dutch, and French in the New World
(continued)
- The Northern European countries spread
Protestantism to the New World. - England sent protestants looking for religious
freedom to what is now the U.S. - France settled in the areas founded by Cartier,
most notably, Quebec. - Cash crops
- Mercantilism
What plant is this?
French seaport at the height of Mercantilism in
the 17th century
39
The English, Dutch, and French in the New World
(continued)
- Like the Spanish encomienda system who used the
slave labor of the Aztec and Mestizo people, the
Northern Europeans wished to plant cash crops
which required lots of labor. - Europeans began plantation systems in the
Caribbean and the Americas which has destroyed
the economies of the people who first lived
there, as well as destroyed the enviornment - African slaves were imported (slavery was based
on race). - Both leave behind a rigid class system that lasts
for generations.
40
Trade in Africa
- Made possible by outposts established along the
coast. - Slave ports.
- Trade in slaves, gold, and other products with
peoples of the interior.
41
Triangular Trade
- Linked Europe, Africa, and the Americas.
- Traded in slaves, sugar and rum.
- Europe also mined precious metals (gold and
silver) from the new world to give it wealth and
power like the world has never known.
42
The Middle Passage
43
Trade in Asia
- Colonization was done by small groups of
merchants who obtained the rights from the
monarch. - Dutch East India Company
- British, Portuguese, and Dutch trading companies
invest heavily in trade in the east.
44
The Dutch East India Company
-joint stock company -still exists today