5.2 Probability and Heredity - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 5
Title:
5.2 Probability and Heredity
Description:
5.2 Probability and Heredity A. Punnett Squares 1. It is used to show a. all possible _____combinations of the offspring that result from a mating for a particular ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:82
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: 5.2 Probability and Heredity
1
- 5.2 Probability and Heredity
- A. Punnett Squares
- 1. It is used to show
- a. all possible ___________combinations of the
offspring that result from a mating for a
particular trait - b. ______________of each allele combination
showing up in the offspring - each square inside the punnett square equals
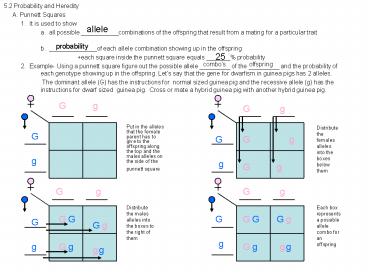
_______ probability - 2. Example- Using a punnett square
figure out the possible allele _________ of the
_________ and the probability of each
genotype showing up in the offspring. Lets say
that the gene for dwarfism in guinea pigs has 2
alleles. - The dominant allele (G) has the instructions
for normal sized guinea pig and the recessive
allele (g) has the instructions for dwarf sized
guinea pig. Cross or mate a hybrid guinea pig
with another hybrid guinea pig.
allele
probability
25
combos
offspring
G
g
G
g
Distribute the females alleles into the boxes
below them
Put in the alleles that the female parent has to
give to the offspring along the top and the males
alleles on the side of the punnett square
G
G
G
g
g
g
G
g
G
G
g
g
Distribute the males alleles into the boxes to
the right of them
Each box represents a possible allele combo for
an offspring
G
G
G
G
G
G
g
G
G
g
g
g
g
G
G
g
g
g
g
g
2
- Lets do a couple of things using the results of
the punnett square - a. First we can list the genotypes and
phenotypes of the possible offspring for that
given trait- dwarfism - b. Now we can figure the probabilities of
each of the offspring
Genotypes
Phenotypes
Probability
GG
Normal
25
Gg
Normal
50
gg
Dwarf
25
4. Codominance or incomplete dominance
3
- More incomplete dominance or codominance visuals
x
4
- B. Pedigrees
- 1. Family tree that tracks the movement of a
__________________ within a family - female male Male carrier of
trait - Female w/trait
marriage children - C. Diagnosing Genetic Disorders
- 1. Amniocentisis- removing of ________________
that surrounds a developing baby - a. How is it done?
trait
fluid
Needle is inserted into the abdomen of pregnant
mother then into amniotic sac
Genetic disorder
cells
chromosomes
Karyotype
5
- Try This Activity- text page 164.
- Comparing a coin toss to percentages of what
Mendel found in his resulting offspring s