The eye and sight PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: The eye and sight
1
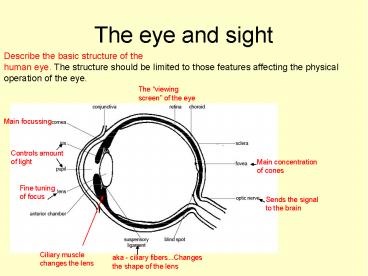
The eye and sight
Describe the basic structure of the human eye.
The structure should be limited to those features
affecting the physical operation of the eye.
The viewing screen of the eye
Main focussing
Controls amount of light
Main concentration of cones
Fine tuning of focus
Sends the signal to the brain
Ciliary muscle changes the lens
aka - ciliary fibers...Changes the shape of the
lens
2
State and explain the process of depth of vision
and accommodation.
The near point and the far point of the eye for
normal vision are also included.
(Closest distance without straining) near point
(25cm)
far point
3
Hyperlink
Accommodation is the process by which the eye
increases its optical power to maintain a clear
image (focus) on an object as it draws near the
eye.
4
(No Transcript)
5
State that the retina contains rods and cones,
and describe the variation in density across the
surface of the retina.
6
Describe the function of the rods and of the
cones in photopic (cones) and scotopic (rods)
vision.
Students should be able to sketch and interpret
spectral response graphs and give an explanation
for colour blindness.
S,M,L short, medium and long wavelengths of
cones R rods
Scotopic vision is the monochromatic vision of
the eye in low light. Since the cone cells are
nonfunctional in low light, scotopic vision is
produced exclusively through the rod cells so
therefore there is no colour perception.
Photopic vision is the vision of the eye under
well-lit conditions. In humans and many animals,
photopic vision allows colour perception,
mediated by the cone cells.
7
Scotopic and photopic vision
The sensitivity of the cones in your eye is known
as the photopic response and refers to colour
vision and the perception of fine detail.
The sensitivity of the rods in your eye is known
as the scotopic response and refers to vision
under conditions of low level light intensity
so called night vision.
8
Colour blindness
Hyperlink
Hyperlink
Cones and Colour There are "red," "blue," and
"green" cones, which are sensitive to those
colors and combinations of them. You need all
three types to see colours properly. When your
cones don't work properly, or you don't have the
right combination, your brain doesn't get the
right message about which colours you're seeing.
9
Describe colour mixing of light byaddition and
subtraction.
Students should be able to identify primary and
secondary colours.
Hyperlinks
10
Hyperlink
11
Questions
E.g. Shining white light on a yellow book.
12
1. The graph below shows the overall relative
light absorption curve for the light-sensitive
cells involved in scotopic vision. The relative
light absorption is expressed as a percentage of
the maximum.
wavelength / nm
(a) State the name of the cells involved in
scotopic vision. .................................
..................................................
................................................ (
1) (b) (i) On the axes above, sketch a relative
light absorption curve for a cell involved in
photopic vision. (2) (ii) State the colour to
which the cell is most sensitive. ................
..................................................
..................................................
..... (1) (c) Outline how colour blindness may
arise from defects in the retinas light
sensitive cells. .................................
..................................................
................................................ .
..................................................
..................................................
.............................. ...................
..................................................
..................................................
............ .....................................
..................................................
............................................ .....
..................................................
..................................................
.......................... (3) (Total 7 marks)
13
Discuss the effect of light and dark, and colour,
on the perception of objects.
Students should consider architectural effects
of light and shadow (for example, deep shadow
gives the impression of massiveness). Glow can be
used to give an impression of warmth (for
example, blue tints are cold) or to change the
perceived size of a room (for example,
light-coloured ceilings heighten the room). TOK
This can contribute to a discussion on perception.