remember from chapter 6 (alkyne chapter): PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 54
Title: remember from chapter 6 (alkyne chapter):
1
(No Transcript)
2
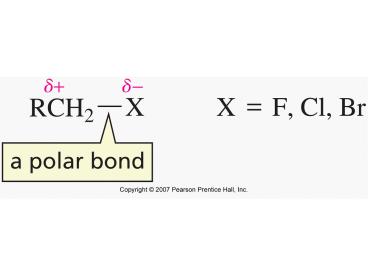
remember from chapter 6 (alkyne chapter)
3
Two possible mechanistic pictures for SN
displacement
The SN2 mechanism
4
The SN1 mechanism
5
- Which mechanism? Depends on
- structure of electrophile (alkyl halide)
- structure, concentration of nucleophile
- solvent
6
example of an SN2
7
SN2 has second order kinetics rds is collision
between two molecules
8
Structure of the alkyl halide less hindered
faster
9
(No Transcript)
10
(No Transcript)
11
(demonstrate with models)
12
SN2 results in inversion of configuration
13
Rate of SN2 reaction influenced by leaving
group weak base good leaving group
14
. . .but not so fast!
15
polarizability also is a factor!
16
which factor predominates? depends on the solvent
17
protic solvent shields nucleophile, stronger
solvent interactions with stronger bases
18
in protic sovent, polarizability determines
nucleophilicity
19
polar, aprotic solvent solvates nucleophiles, but
with less shielding. base strength determines
nucleophilicity These solvents used for SN2
20
less hindered nucleophiles are better nucleophiles
quiz why is tert-butoxide stronger base? (pKa of
alcohols 18 vs. 15.9)
21
(No Transcript)
22
The SN1 reaction
first order rate expression rds is
unimolecular rate kbromide H2O does not
influence rate
23
(No Transcript)
24
(No Transcript)
25
(No Transcript)
26
think about stability of carbocation intermediate!
27
SN1 results in racemization of asymmetric center
28
(No Transcript)
29
Again, weaker bases are better LG
Notice reactivity of Nu does NOT influence rate
of SN1 rxn Solvent effect more polar solvents
better at stabilizing carbocation, so polar
solvents used in SN1 reactions (solvolysis
solvent is nucleophile)
30
SN1 reactions can undergo carbocation
rearrangements!
31
not always 5050 mix why?
32
intimate ion pair influences stereochemical
outcome
33
Benzylic and allylic alkyl halides primary can
undergo SN1, because stable intermediate
34
can get mixed products (compare to 1,2 vs 1,4
addition)
35
vinylic, aryl halides do not undergo SN reactions
36
(No Transcript)
37
SN1 or SN2? methyl, primary SN2 only secondary
both primary and secondary allylic/benzylic
both tertiary SN1 only vinylic/benzylic neither
When both are possible high concentration of
good Nu, polar aprotic solvent favors SN2 poor
Nu, polar solvent favors SN1 (typically
solvolysis)
38
SN2!
39
SN1
40
Which is likely to occur? Depends on
concentration of reactant, ring size
41
5,6-membered rings intra favored
tethering entropy!
42
(No Transcript)
43
(No Transcript)
44
(No Transcript)
45
(No Transcript)
46
(No Transcript)
47
(No Transcript)
48
(No Transcript)
49
(No Transcript)
50
(No Transcript)
51
(No Transcript)
52
(No Transcript)
53
(No Transcript)
54
(No Transcript)