Determine the limiting reactant and the mass of product when 1.20mol of Sb and 2.40mol I2 mixed? PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Determine the limiting reactant and the mass of product when 1.20mol of Sb and 2.40mol I2 mixed?
1
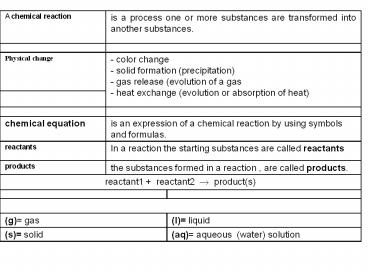
A chemical reaction is a process one or more substances are transformed into another substances. is a process one or more substances are transformed into another substances.
Physical change - color change - solid formation (precipitation) - gas release (evolution of a gas - heat exchange (evolution or absorption of heat) - color change - solid formation (precipitation) - gas release (evolution of a gas - heat exchange (evolution or absorption of heat)
- color change - solid formation (precipitation) - gas release (evolution of a gas - heat exchange (evolution or absorption of heat) - color change - solid formation (precipitation) - gas release (evolution of a gas - heat exchange (evolution or absorption of heat)
chemical equation is an expression of a chemical reaction by using symbols and formulas. is an expression of a chemical reaction by using symbols and formulas.
reactants In a reaction the starting substances are called reactants In a reaction the starting substances are called reactants
products the substances formed in a reaction , are called products. the substances formed in a reaction , are called products.
reactant1 reactant2 ? product(s) reactant1 reactant2 ? product(s) reactant1 reactant2 ? product(s)
(g) gas (g) gas (I) liquid
(s) solid (s) solid (aq) aqueous (water) solution
2
Balancing Chemical Reaction Balancing Chemical Reaction
Because atoms are neither created nor destroyed in any reaction, a chemical equation must have equal number of atoms of each elements on each side of the arrow. Stoichiometric balancing of a chemical reaction means adjusting the coefficients for the reactants and products in equation. Because atoms are neither created nor destroyed in any reaction, a chemical equation must have equal number of atoms of each elements on each side of the arrow. Stoichiometric balancing of a chemical reaction means adjusting the coefficients for the reactants and products in equation.
CH4 O2 ? CO2 H2O Stoichiometric coefficients are the numbers placed in front of formulas in a chemical equation. CH4 O2 ? CO2 H2O Stoichiometric coefficients are the numbers placed in front of formulas in a chemical equation.
The balanced reaction is, CH4 2 O2 ? CO2 2 H2O.
Left side contains Right side contains
1 C 1 C
4 H 2 H
2 O 3 O
3
2 H2 (g) O2 (g) ? 2 H2O (s) 2 H2 (g) O2 (g) ? 2 H2O (s)
2 molecules H2 1molecules O2 2 molecules H2O 2 molecules H2 1molecules O2 2 molecules H2O
two moles of H2 reacts with one mole O2 and two moles H2O is produced. two moles of H2 reacts with one mole O2 and two moles H2O is produced.
4 grams of H2 reacts with 32 g O2 and 36 g H2O is produced. 4 grams of H2 reacts with 32 g O2 and 36 g H2O is produced.
4
how many moles and grams of H2O are produced by burning 2.72 moles H2 a) in an excess of O2 b) with 1 mol O2
5
Ballance the following reactions
N2H4 N2O4 ? N2 H2O
NaOH CO2 ? Na2CO3 H2O
CaO P4O10 ? Ca3(PO4)2
6
limiting reactant
In a chemical reaction one reactant is completely consumed while some amount of the other reactant/s) remains. The amount of products is limited by that reactant consumed. The reactant that is completely consumed in a chemical reaction limits the amounts of products formed, is called limiting reactant or limiting reagent.
7
- Determine the limiting reactant and the mass of
product when 1.20mol of Sb and 2.40mol I2 mixed? - Sb I2 ? SbI3 Sb243
I127.0
8
- what mass of AgBr is formed when a solution
containing 3.45 g of KBr is mixed with a solution
containing 7.28 g AgNO3? - KBr AgNO3 ? AgBr K NO3-
9
Consider the following reaction
Na3PO4 (aq) Ba(NO3)2(aq) ?
Ba3(PO4)2(s) NaNO3 (aq)Suppose that a
solution containing 3.50 grams of Na3PO4 is mixed
with a solution containing 6.40 grams of
Ba(NO3)2. How many grams of Ba3(PO4)2 can be
formed?
10
Yields of chemical reactions Yields of chemical reactions
theoretical yield. The quantity of product that is calculated to form when all of the limiting reactant is consumed in a reaction is called the theoretical yield.
actual yield. The amount of product actually obtained is called the actual yield.
The percent yields The percent yields is the ratio actual yield to the theoretical yield times 100
11
Soru Fe O2 ? Fe2O3 Reaksiyonunda 11.2g Fe yeteri kadar oksijenle reaksiyona girdiginde 10.0g Fe2O3 olusuyor. Reaksiyonun teorik verimi, gerçek verimi ve yüzde verimini hesaplayiniz. Fe 56 O16 Fe O2 ? Fe2O3 Reaksiyonunda 11.2g Fe yeteri kadar oksijenle reaksiyona girdiginde 10.0g Fe2O3 olusuyor. Reaksiyonun teorik verimi, gerçek verimi ve yüzde verimini hesaplayiniz. Fe 56 O16
12
Methyl tert-butyl ether (MTBE, ), a substance
used as an octane booster ingasoline, can be
made by reaction of isobutylene with methanol.
What is the percent yield of the reaction if 32.8
g of methyl tert-butyl ether is obtained from
reaction of 26.3 g of isobutylene with sufficient
methanol?
13
Na3PO4 (aq) Ba(NO3)2(aq) ? Ba3(PO4)2(k) NaNO3 (aq) When 3.50 Na3PO4 reacts ewith 6.40 gram Ba(NO3)2 how many grams of Ba3(PO4)2 will produce?
14
- Soru 3,00g etilenamin CH3NH2, 0,100g H ile
reaksiyona girdiginde 2,60g CH3NH3 olustuguna
göre reaksiyonun gerçek verimi ve yüzde verimini
hesaplayiniz. - CH3NH2, H ? CH3NH3 CH3NH2,
31,06 -
CH3NH3 32,07
15
Reactions in Aqueous Solution Reactions in Aqueous Solution Reactions in Aqueous Solution
Precipitation Reactions Acids, Bases, and Neutralization Reactions OxidationReduction (Redox) Reactions
16
Çözelti Homogeneous mixtures are called solutions Homogeneous mixtures are called solutions Homogeneous mixtures are called solutions
solvent solvent solvent solvent solute
nonelectrolyte nonelectrolyte nonelectrolyte Substances such as sucrose or ethyl alcohol, which do not produce ions in aqueous solution, are called nonelectrolytes. Substances such as sucrose or ethyl alcohol, which do not produce ions in aqueous solution, are called nonelectrolytes.
electrolytes Substances such as NaCl or KBr, which dissolve in water to produce conducting solutions of ions, are called electrolytes. Substances such as NaCl or KBr, which dissolve in water to produce conducting solutions of ions, are called electrolytes.
strong electrolytes, strong electrolytes, strong electrolytes, strong electrolytes, weak electrolytes.
Compounds that dissociate to a large extent (100) into ions when dissolved in water are said to be strong electrolytes, Compounds that dissociate to a large extent (100) into ions when dissolved in water are said to be strong electrolytes, Compounds that dissociate to a large extent (100) into ions when dissolved in water are said to be strong electrolytes, Compounds that dissociate to a large extent (100) into ions when dissolved in water are said to be strong electrolytes, compounds that dissociate to only a small extent are weak electrolytes.
17
(No Transcript)
18
Mol number m n --------- MA
Molarity n M ------- mol/L V
density m d ---------- gr/mL V
19
Diluting Concentrated Solutions Diluting Concentrated Solutions
Minitial x Vinitial mol number Mfinal x Vfinal Minitial x Vinitial Mfinal x Vfinal
20
Find the molarity of a solution that 23.4g of Na2SO4 was dissolved in water and diluted to 250.0ml Na2SO4 142
calculate the molarity of H2SO4 solution when we dilute 50.0 mL of a solution of 2.00 M H2SO4 to a volume of 200.0 mL.
21
Q1 How can you prepare 500ml 0.10 M H2SO4 solution from 3.0M H2SO4?
Q2 How would you prepare 500.0 mL of 0.2500 M NaOH solution starting from a concentration of 1.000 M?
Q3 What is the final concentration if 75.0 mL of a 3.50 M glucose solution is diluted to a volume of 400.0 mL?
22
Reactions in Aqueous Solution Reactions in Aqueous Solution Reactions in Aqueous Solution
Precipitation reactions Are the reactions, an insoluble solid is formed, the solid product is called as a precipitate. Are the reactions, an insoluble solid is formed, the solid product is called as a precipitate.
Ag(aq) Cl-(aq) ? AgCl(s) Ag(aq) Cl-(aq) ? AgCl(s) Ag(aq) Cl-(aq) ? AgCl(s)
23
solubility rules
Soluble salts
salts of 1A groups (Na, K, Li,) and NH4 are soluble all nitrates, acetates and perchlorates are soluble NO3 (Nitrat), CHCOO- (asetat) ,ClO4 (perklorat) all chlorides (halogens) are soluble except (AgCl, Hg2Cl2, PbCl2) most sulfates (SO42 ) are soluble except (Sr SO4, Ca SO4 , Ba SO4 , Pb SO4 )
Cl-, Br-, I- SO42- Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs NH4 NO3- ClO4- CH3CO2-
24
solubility rules
Slightly soluble
all OH- hydroxides are insoluble except those of 1A group (Na, K, Li,) and NH4 all sulfides S2- are insoluble except those of 1A group (Na, K, Li,) and NH4 all carbonates are insoluble except those of 1A group (Na, K, Li,) and NH4 All PO43- are insoluble except those of 1A group (Na, K, Li,) and NH4
CO32-, PO43- OH-, S2-
25
(No Transcript)
26
- What will happen if Na2CO3 and CaCl2 solutions
are mixed ? - What will happen if CuSO4 and NaNO3 solutions are
mixed ?
27
(No Transcript)
28
Acids and Bases Acids and Bases
Asit Baz
Have a sour taste, dissolve metals such as zinc and carbonate minerals change color of litmus to red -Have a bitter taste, -Have a slippery feel -change color of litmus to blue, -React with dissolved metal to form prepiciate
29
Asit ve Bazlar
Asit- Baz Tanimlari
Arrhenius Acid-Base Definition (1884) An acid is a substance that contains hydrogen and dissociates to produce Hydrogen ion in water H HCl(aq) ? H(aq) Cl-(aq) A base is a substance that contains the hydroxyl group and dissociates to produce Hydroxide ion OH NaOH (aq) ? Na (aq) OH -(aq) Neutralization is the reaction of an H ion from the acid and the OH - ion from the base to form water, H2O H(aq) OH-(aq) ltgt H2O(l)
30
Asit ve Bazlar
Asit- Baz Tanimlari
Brønsted-Lowry Acid-Base Definition (1923) An acid is a species having a tendency to donate an H ion. HCl H2O ? Cl H3O A base is a species having tendency to accept an H ion. NH3 H2O ? NH4 OH- In the Brønsted-Lowry perspective, one species donates a proton and another species accepts it an acid-base reaction is a proton transfer process.
31
Asit ve Bazlar
The Lewis acid-base definition A base is any species that donates an electron pair An acid is any species that accepts an electron pair. B H ? B - H
32
Asit ve bazlarin Kuvvetliligi Asit ve bazlarin Kuvvetliligi
Kuvvetli Asit Zayif Asitler
Strong Acids An acid that completely ionized in water, is called as a strong acid Weak acid is an acid that partly ionized in water.
HCl ?H Cl- CH3COOH H2O? CH3COO- H3O
HCl, HBr, ve HI HNO3, H2SO4, HClO4 gibi Oksiasitler HF . HCN , H2S HClO, HNO2, ve H3PO4 Organik asitler (RCOOH), CH3COOH C6H5COOH
33
Asit ve bazlarin Kuvvetliligi Asit ve bazlarin Kuvvetliligi
Kuvvetli baz Zayif baz
A base that completely ionized in water, is called as a strong base A weak base is a base that partly ionized in water.
NaOH? Na OH - NH3 H20 ? NH4 OH -
M2O or MOH, M 1A(1) metalleri (Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs) MO or M(OH)2, M Group 2A metalleri (Ca, Sr, Ba) MgO and Mg(OH)2 Amonyak (NH3) Aminler (RNH2, R2NH, R3N), CH3CH2NH2, (CH3)2NH, (C3H7)3N, C5H5N
34
(No Transcript)
35
- pH
- The pH is defined as the negative logarithm in
base 10, of the hydronium ion concentration - pH - logH3O
- The pOH is defined as the negative logarithm in
base 10, of the hydroxyl ion concentration - pOH - logOH-
- pH of a neutral solution 7.00
- pH of an acidic solution lt 7.00
- pH of a basic solution gt 7.00
36
Oxidation reduction reactions
- Chemical reactions which involve involve electron
transfers from one atom to another, are called
oxidation-reduction or redox reactions. - Oxidation is the process in which the oxidation
number of atoms increase, - Reduction is the process in which the oxidation
number of atoms is decreased - Oxidation is the loss of electrons by an atom
reduction is the gain of electrons
Fe3 --- metallic iron
CO(g)---- Carbon diokside
37
- Fe3 Cu ? Fe2 Cu2
- Fe3 e- ? Fe2
- Cu ? Cu2 e-
38
Oxidation states
- Oxidation states (oxidation numbers) reflect, in
general way, how electros are involved in
compound formation. - the oxidation state(O.S) of an atom in the pure
(uncombined) element is 0. - The total (sum) of the oxidation state of all
the atoms in a molecule or formula unit is 0. - For an ion total of the oxidation state is equal
to the charge on the ion. - In their compounds the alkali metals (1a groups
Li, Na, K, Rb, Cs, Fr) have an 1 oxidation
number. 2A group metals 2. - In its compounds, the oxidation state of hydrogen
is 1. but in NaH BeH2 it has OS of -1 - O.S. of fluorine is 1. halogens have generally
O.S of -1 when they combine with H and metals. - In its compounds oxygen has an oxidation state of
2.
39
(No Transcript)
40
(No Transcript)
41
(No Transcript)
42
Balancing Redox reactions
- 1- Split the equation into two half equation
- 2- Balance the two half equation same number of
electrons must appears in each half equation - balance the atoms of element being oxidized or
reduced - balanve oxidation number by adding electrons
- balance charge in acidic solutions add H add
OH in basic solutions - balance hydrogen by adding H2O
- 3- combine the two half equation eliminate
electrons
43
- Soru Fe2 MnO4- ? Fe 3 Mn2
balance in acidic medium - Soru Cl2 Cr(OH)3 ? Cl- CrO42-
balance in basic medium - Soru C2H5OH Ce4 ? CO2 Ce3 balance
in acidic medium
44
Titrasyon
- Titration is a procedure for determining the
concentration of a solution by allowing a
carefully measured volume to react with a
standard solution of another substance, whose
concentration is known. By finding the volume of
the standard solution that reacts with the
measured volume of the first solution, the
oncentration of the first solution can be
calculated. - equivalent point
- The point that all reactants are consumed,
Stoichiometric mol numbers of both reactants are
equal. - an indicator a compound that change its color
around equivalent point. such as phenolphthalein,
is colorless in acidic solution but turns pink in
basic solution.
45
(No Transcript)
46
(No Transcript)
47
- Soru antiasit ilaç tabletlerinin anabileseni
CaCO3 tür. 0.542 gr olarak tartilan bir tablet
HCl ile titre edildiginde, reaksiyonun
tamamlanmasi için 38.5 ml 0.200M HCl harcandigina
göre tablet içindeki CaCO3 yüzdesi nedir? - CaCO3 HCl ? Ca2 CO2
Cl- H2O
48
- Konsantrasyou bilinmeyen bir permanganat
çözeltisinin 28,97ml si 0,1058g okzalik asit ile
tamamen reaksiyona girdigine göre permanganat
çözeltisinin konsantrasyonunu hesaplayiniz. - MnO4- H2C2O4 ? Mn2 CO2
- 2 MnO4- 5 H2C2O4 6 H? 2 Mn2 10 CO2 8H2O
49
- A 25.0 mL sample of vinegar (dilute acetic acid,
) is titrated and found to react with 94.7 mL of
0.200 M NaOH. What is the molarity of the acetic
acid solution?