Frequency analysis: why? PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 25
Title: Frequency analysis: why?
1
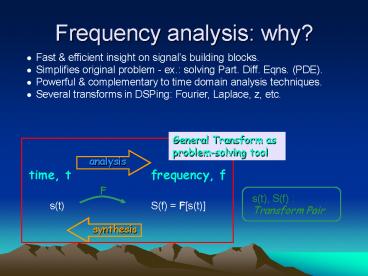
Frequency analysis why?
- Fast efficient insight on signals building
blocks. - Simplifies original problem - ex. solving Part.
Diff. Eqns. (PDE). - Powerful complementary to time domain analysis
techniques. - Several transforms in DSPing Fourier, Laplace,
z, etc.
2
Fourier analysis - applications
- Applications wide ranging and ever present in
modern life - Telecomms - GSM/cellular phones,
- Electronics/IT - most DSP-based applications,
- Entertainment - music, audio, multimedia,
- Imaging, image processing,
- Industry/research - X-ray spectrometry, chemical
analysis (FT spectrometry), radar design, - Medical - EGG, heart malfunction diagnosis,
- Speech analysis (voice activated devices,
biometry, ).
3
Fourier analysis - tools
Input Time Signal Frequency spectrum
4
Fourier Series (FS)
synthesis
analysis
Note cos(k?t), sin(k?t) k form orthogonal
base of function space.
5
FS synthesis
Square wave reconstruction from spectral terms
Convergence may be slow (1/k) - ideally need
infinite terms. Practically, series truncated
when remainder below computer tolerance (?
error). BUT Gibbs Phenomenon.
6
Gibbs phenomenon
Overshoot exist _at_ each discontinuity
7
Fourier Integral (FI)
Fourier analysis tools for aperiodic signals.
8
FT - example
FT of 2?-wide square window
9
Digital data formats
Positional number system with base b
.. a2 a1 a0 . a-1 a-2 .. b .. a2 b 2 a1
b 1 a0 b 0 a-1 b -1 a-2 b -2 ..
Important bases 10 (decimal), 2 (binary), 8
(octal), 16 (hexadecimal).
10
Fixed-point binary
Represent integer or fractional binary numbers.
NB Constant gap between numbers.
11
Floating-point binary - 2
IEEE 754 standard
12
Finite word-length effects
13
DSP Devices Architectures
- Selecting a DSP several choices
- Fixed-point
- Floating point
- Application-specific devices(e.g. FFT
processors, speech recognizers,etc.). - Main DSP Manufacturers
- Texas Instruments (http//www.ti.com)
- Motorola (http//www.motorola.com)
- Analog Devices (http//www.analog.com)
14
Typical DSP Operations
- Filtering
- Energy of Signal
- Frequency transforms
15
Traditional DSP Architecture
X RAM
Y RAM
a
x(n-i)
Multiply/Accumulate
Accumulator
y(n)
Most modern DSPs have more advanced features.
16
TIs DSP Portfolio
C6000 (C62x, C67x)
- Power Efficient Performance
- Wireless Telephones/IADs
- Modems / Telephony
- VoIP
- .32ma/MIPS to sub 1V parts
- 5 / 100 MIPS
C3x C4x C8x
- Control Efficient
- Storage
- Brushless Motor Control
- Flash Memory
- A/D
- PWM Generators
- High Performance
- Multi-Channel / Function
- Comm Infrastructure
- xDSL
- Imaging, Video
- VLIW architecture
- 2400 MIPS
- Roadmap to 1 GHZ
17
Personal and Portable Applications
18
(No Transcript)
19
C67x Architecture
20
(No Transcript)
21
(No Transcript)
22
(No Transcript)
23
DSP STARTER KIT (DSK)
24
C6711 DSK OVERVIEW
25
(No Transcript)