Human Evolution PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 23
Title: Human Evolution
1
(No Transcript)
2
(No Transcript)
3
Human Evolution
- Primate Adaptations
- 1. Primate evolution provides a context for
understanding human origins - a. Most primates have hands and feet adapted for
grasping - b. Relative to other mammals, they have large
brains and short jaws.
4
- c. They have flat nails on their digits, rather
than narrow claws for increased manipulative
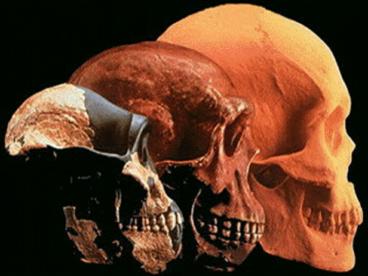
sensitivity - d. Well-developed parental care and complex
social behavior - e. Visual acuity-(stereoscopic (3D with color)
5
(No Transcript)
6
- 2. In addition to monkeys, the anthropoid
suborder also includes four genera of apes
Hylobates (gibbons), Pongo (orangutans), Gorilla
(gorillas), and Pan (chimpanzees and bonobos). - a. Modern apes are confined to the tropical
regions of the old world.
7
- b. they evolved from old world monkeys about
25-30 million years ago. - c. with the exception of gibbons, modern apes
are larger than monkeys, with relatively long
arms and short legs, and no tails.
8
- d. Although all apes are capable of brachiating,
only gibbons and orangutans are primarily
arboreal. - e. Social organization varies, with gorillas and
chimpanzees highly social - f. Apes have relatively larger brains than
monkeys, and their behavior is more flexible
9
- B. Humanity is one very young twig on the
vertebrate tree - 1. In the continuity of life spanning over 3.5
billion years, humans and apes have shared
ancestry for all but the last few million years
10
- 2. Paleoanthropology is the study of human
origins and evolution. Paleoanthropologists use
two words that are easy to confuse but which have
distinct meanings. - a. Hominoid is a term referring to great apes
and humans collectively
11
- b. Hominid has a narrow meaning, referencing the
part of the evolutionary tree that is more
closely related to us than to any other living
species.
12
- c. There are two main groups of hominids the
australopithecines which came first and are all
extinct, and members of the genus homo, with all
species extinct except one Homo Sapiens
13
- 3. Paleoanthropology has a history with many
misconceptions about human evolution generated
during the early part of the twentieth century
that still persist in the minds of the general
public, long after these myths have been debunked
by fossil discoveries
14
- a. First, our ancestors were not chimpanzees or
any other modern apes - b. Chimpanzees and humans represent two
divergent branches of the hominoid tree that
evolved from a common ancestor that was neither a
chimpanzee nor a human
15
- c. Second, human evolution did not occur as a
ladder with a series of steps leading directly
from an ancestral hominoid to Homo Sapiens. - d. Human phylogeny is more like a multi-branched
bush with our species as the tip of the only
surviving twig.
16
- e. Third, the various human characteristics, such
as upright posture and enlarged brain, did not
evolve in unison. They evolved at different
rates called mosaic evolution. - f. There are still many questions about our
ancestry,
17
C. Human evolution is marked by the evolution of
several major features
- 1. Brain size based on skull measurements,
researchers have estimated that brain size in
hominoids tripled over the past 6 million years. - a. it increased from 400-500cm3 in hominoids
(and modern chimpanzees) to about 1,300cm3 in
modern humans.
18
- b. This allowed for greater language development
and cultural complexity. - 2. Jaw shape our hominoid ancestors had longer
jaws (prognathic jaws) than modern humans - a. this resulted in a flatter face and more
pronounced chins
19
- 3. Changes in dentition based on dietary shifts
- 4. Bipedal Posture based on fossil skeletons, it
is clear that hominoid ancestors walked on all 4
limbs when on the ground, like modern apes. - a. the evolution of bipedal posture is
associated with key skeletal modifications seen
in early hominid fossils
20
- b. this modification was helpful for tool use,
it allowed humans to better view their
surroundings, provided more flexibility and
agility for posturing and movement. - 5. Reduced size differences between the sexes
- a. male gorillas are 2x heavier than females,
male chimps are 1.35X heavier and male humans are
1.2X heavier.
21
6. Key changes in family Structure
- a. Insights into social behavior are derived
from comparisons between humans and extinct
hominoids - b. In contrast to most ape species, monogamy or
long term pair bonding prevails in most human
cultures.
22
- c. Newborn infants are exceptionally dependent
on their mothers, the duration of parental care
and opportunities for enhanced learning is longer
in humans than other hominoids.
23
7.Cultural Evolution
- Tool use is more sophisticated
- Use of fire
- Cave paintings
- Introduction of language
- Agricultural advances
- Skills learned from teaching and communication