Position: - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 9
Title: Position:
1
Position (your seat ).. Your
Name Last, First Name of
Workshop Instructor Last, First.. Exam
(2) Date March 22nd,
2005
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
9
10
11
12
Q12 (C, E, F) are for bonus points.
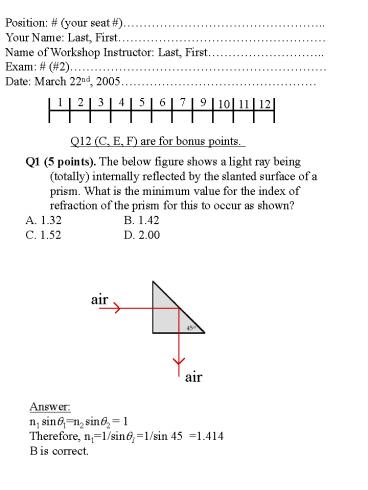
Q1 (5 points). The below figure shows a light ray
being (totally) internally reflected by the
slanted surface of a prism. What is the minimum
value for the index of refraction of the prism
for this to occur as shown? A. 1.32 B. 1.42 C.
1.52 D. 2.00
air
air
Answer n1 sin?1n2 sin?2 1 Therefore,
n11/sin?11/sin 451.414 B is correct.
2
Q2 (6 points). If an object is placed 8 cm in
front of a converging lens with a focal length of
2 cm, its image is at a location, relative to the
lens center A. 2.67 cm B. 5.3 cm C. 8 cm D. -4
cm Answer
1/f (1/d0) (1/di) Therefore, (1/di) 1/f
- (1/do)0.5 0.125 0.375 di 2.67 cm
Q3 (4 points). The image in Question 2 is A.
real and erect B. real and inverted C. virtual
and erect D. virtual and inverted Answer B is
correct (see Lecture 12, Slides 21, 22)
3
Q4 (3 points). A light ray is incident on a
mirror, and is reflected from the mirror. The
incident light ray is drawn below. What is the
reflected ray? Please explain your answer.
D
C
A
B
Incident ray
mirror
Answer A is correct. The reflected ray does not
go beyond the mirror, such as in B, C, and D.
Q5 (8 points). I had trouble with the reading of
a CD. I realized that the surface had some
fingerprints. Please explain in a brief verbal
argument what happened. How does a CD
work? Answer The compact disc, although
appearing to be stationary in the textbook,
should actually be envisioned as rotating at high
speed. A beam is emitted by the laser and
directed onto a single track on the disc by the
prism/beamsplitter. As the disc rotates, the beam
encounters a series of pits and landings that
determine whether the beam is reflected back into
the detector (from a landing) or scattered (a
pit).
4
Q6 (5 points). A light ray strikes a horizontal
mirror and is reflected onto a vertical mirror.
If ? 32 degrees and d 1.85 meters, what to
the nearest degree is f?
Answer The first mirror the incidence angle ?
is equal to the reflected angle. The second
mirror The incidence angle is equal to the
reflected angle ?. The sum of ? and ? is
90?. Therefore, ? 58?.
Q7 (7 points). If do 15.6 cm and f 6.6 cm,
what is the image distance to the nearest tenth
of a cm?
Answer 1/f (1/d0) (1/di) Therefore,
(1/di) 1/f - (1/do)(1/6.6) (1/15.6)
0.1515-0.06410.0874 di 11.4 cm
5
Q8 (3 points). The speed of light is often listed
as equaling 3.00 x 108 m/s. Does light always
travel at that speed, or can it travel faster?
Can it travel slower? Why do you believe this is
so?
Answer 1. No. 2. Yes, it can travel slower.
This happens, as the light interacts with the
atoms of the material through which it goes
through.
Q9 (5 points). Light strikes a flat piece of
glass (n1.50) at an incident angle of 60. What
is the angle of refraction in the glass? What is
the angle with which the ray emerges from the
glass? Answer The incidence angle is equal to
the reflected angle. Therefore, the reflected
angle is 60. Snells law is n1 sin ?1 n2 sin
?2 sin ?2(n1/n2)sin ?1(1/1.5)sin
600.6660.8660.576 ?235.1?.
6
Q10 (3 points). Red light and blue light impact
on retina of your eye, with roughly equal
intensity. Then, your eye-brain system perceives
the color of A. White B. Black C. Cyan D.
Yellow E. Magenta Answer E. Magenta
Q11 (3 points). At 600 K, the value of the
wavelength for which the intensity is peaked is
5,000 nm. If the temperature is tripled (reaching
1800 K), then the wavelength for which the
intensity of radiation is peaked is now A.
40,000 nm B. 2,500 nm C. 20,000 nm D. 1,667
nm E. 5,000 nm Answer ?pTconstant 5000600
nm K ?p 1800 nm K ?p 1,667 nm
7
Q12. A beam of light travels from water into a
piece of diamond in the shape of a triangle, as
shown in the diagram. Step-by-step, follow the
beam until it emerges from the piece of diamond.
A (5 points). How fast is the light traveling
inside the piece of diamond?
Answer The speed can be calculated from the
index of refraction
8
B (5 points). What is ?2, the angle between the
normal and the beam of light inside the diamond
at the water-diamond interface?
Answer A diagram helps for this. In fact, let's
look at the complete diagram of the whole path,
and use this for the rest of the questions. The
angle we need can be found from Snell's law
C (7 points). The beam travels up to the
air-diamond interface. What is ?3, the angle
between the normal and the beam of light inside
the diamond at the air-diamond interface?
Answer This is found using a bit of geometry.
All you need to know is that the sum of the
three angles inside a triangle is 180. If
is 24.9, this means that the third angle in that
triangle must be 25.1. So
9
D (5 points). What is the critical angle for the
diamond-air interface? Answer
E (5 points). What happens to the light at the
diamond-air interface?
Answer Because the angle of incidence (64.9)
is larger than the critical angle, the light is
totally reflected internally.
F (5 points). The light is reflected off the
interface, obeying the law of reflection. It
then strikes the diamond-water interface. What
happens to it here? Answer
Again, the place to start is by determining the
angle of incidence, ?4. A little geometry shows
that
The critical angle at this interface is
Because the angle of incidence is less than the
critical angle, the beam will escape from the
piece of diamond here. The angle of refraction
can be found from Snell's law