Remember Vector Algebra PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Remember Vector Algebra
1
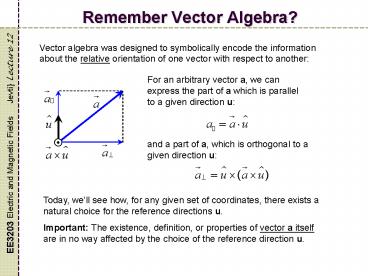
Remember Vector Algebra?
Vector algebra was designed to symbolically
encode the information about the relative
orientation of one vector with respect to
another
For an arbitrary vector a, we can express the
part of a which is parallel to a given direction
u
and a part of a, which is orthogonal to a given
direction u
Today, well see how, for any given set of
coordinates, there exists a natural choice for
the reference directions u. Important The
existence, definition, or properties of vector a
itself are in no way affected by the choice of
the reference direction u.
2
Consider Cartesian Coordinates
If the y coordinate of the point P(x,y,z) is
changed by dy, the point P is displaced to a new
point P(x,ydy,z). Think of PP as a vector
obtained by changing the y coordinate alone.
Clearly, vector PP points in the y-direction
Similarly for other 2 directions. We see that
this is a procedure that allows us to find the
local coordinate direction at any point of a
Cartesian system.
Can this line of reasoning be extended to
curvilinear coordinates?
3
Curvilinear Coordinates
Let us assign a set of three coordinates
to each point in space.
could be any of
,
Starting from a point P whose coordinates are
we obtain a new point P by an infinitesimal
change of only one of the coordinates, say
.
The vector
singles out a direction in space, at point P,
which well label as a unit vector
If this process is repeated for the other two
coordinates we obtain three unit vectors
which specify three directions at point
P.
The directions are called
coordinate induced basis and can be used as
reference directions for specifying an arbitrary
vector at the point P.
4
Prescription
- Given a) Coordinate system
- b) Point in space
- How to find the coordinate induced basis at the
point? - For each of 3 coordinates
- Increase the coordinate by an infinitesimal
positive amount. - See in which direction the point moves.
- Youve just found the induced direction for that
coordinate.
5
Cartesian Coordinates
6
Cylindrical Coordinates
7
Spherical Coordinates
8
Summary
Spherical
Cylindrical
Cartesian
Coordinates
Basis vectors
Lamé coefficients
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics, the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.