Buses PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 22
Title: Buses
1
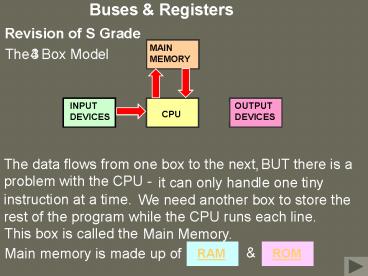
Buses Registers
Revision of S Grade
MAIN MEMORY
The Box Model
3
4
INPUT DEVICES
OUTPUT DEVICES
CPU
The data flows from one box to the next,
BUT there is a problem with the
CPU -
it can
only handle one tiny instruction at a time.
We need another
box to store the rest of the program while the
CPU runs each line.
This box is called the
Main Memory.
Main memory is made up of
2
Buses Registers
Revision of S Grade
RAM
Random Access Memory
- The user can make changes to the RAM.
- The user can wipe the RAM
- The RAM is temporary.
Any interruption of the power supply will wipe
the RAM
5 box model
thats why we need the
Different Kinds of RAM (Higher)
3
Buses Registers
Revision of S Grade
ROM
Read Only Memory
- The user cant make changes to the ROM.
- The user cant wipe the ROM
- The ROM is permanent.
The ROM is programmed permanently in the factory
with things like the meaning of the keys on the
keyboard (the ).
character set
Different Kinds of ROM (Higher)
4
Buses Registers
Revision of S Grade
MAIN MEMORY
The Box Model
4
5
INPUT DEVICES
OUTPUT DEVICES
CPU
Because the RAM is temporary, we need a storage
method that doesnt need electricity.
This is called Backing Storage.
5
Buses Registers
Revision of S Grade
H Grade
MAIN MEMORY
Buses
INPUT DEVICES
OUTPUT DEVICES
CPU
Lets concentrate on the links between the main
memory and the CPU.
6
Buses Registers
H Grade
MAIN MEMORY
Buses
CPU
Lets concentrate on the links between the main
memory and the CPU.
Actually, we can ignore the ROM for the moment.
7
Buses Registers
H Grade
MAIN MEMORY
Buses
CPU
are actually conducting lines
that make up the Bus.
These links
The DATA bus can
read from memory locations, as well as write to
them, so its called a
bus.
DATA
bi-directional
8
Buses Registers
H Grade
MAIN MEMORY
Buses
CPU
The data bus in this example has 8 lines,
so the CPU can handle an 8 bit
instruction at one time.
We say that the memory word
size is 8 bits.
Its an 8 bit computer.
9
Buses Registers
H Grade
MAIN MEMORY
Buses
CPU
Of course, we need to tell the RAM which of its
memory locations to open up.
We do this using the
Bus.
ADDRESS
10
Buses Registers
H Grade
MAIN MEMORY
Buses
CPU
Lets think about how we could use the address
bus to uniquely identify memory locations
11
Buses Registers
H Grade
MAIN MEMORY
Buses
0
1
0
1
CPU
so either memory location 0 or
memory location 1 can be identified -
A single line can either carry a 0
or a 1,
NO OTHERS.
12
Buses Registers
H Grade
MAIN MEMORY
Buses
00
01
10
11
10
00
01
11
CPU
Two lines could either identify memory location
00,
NO OTHERS.
or 11 -
or 10,
or 01,
13
Buses Registers
H Grade
MAIN MEMORY
Buses
000
110
001
111
010
100
011
101
CPU
Three lines could identify the memory locations
shown -
NO OTHERS.
14
Buses Registers
H Grade
MAIN MEMORY
Buses
000
110
001
111
010
100
011
101
CPU
THE NUMBER OF ADDRESSABLE (USABLE) MEMORY
LOCATIONS
number of lines in the address bus
2
15
Buses Registers
H Grade
MAIN MEMORY
Buses
000
110
001
111
010
100
011
101
CPU
So far, we have only looked at things that happen
within the Arithmetic Logic Unit (ALU) of the
CPU.
The ALU contains the
electronic circuits that handle calculations and
simple decisions.
16
Buses Registers
H Grade
MAIN MEMORY
Buses
000
110
001
111
010
100
011
101
CPU
The CU
communicates with the ALU to move data from
register to register,
We also need to know about the Control Unit (CU).
and it controls various other
functions around the computer, using different
lines of the
Bus.
CONTROL
17
Buses Registers
H Grade
MAIN MEMORY
Buses
000
110
001
111
010
100
011
101
CPU
Lines of the Control Bus
1 Read/Write
A signal on this lines tells the memory to open
either for reading or writing.
2 Clock
Sends regular pulses around the computer to make
sure that processes happen at the correct times.
3 Interrupt
This line tells the CPU to pause what its doing
and deal with the interruption,
(perhaps from a printer thats out of paper).
Software can be used to
ignore (mask) trivial interrupts.
4 Non Maskable Interrupt (NMI)
This can not be ignored. Used for things like
fire alarms.
5 Reset
Resets all the registers to zero.
18
Buses Registers
H Grade
MAIN MEMORY
Buses
Registers
000
110
001
111
010
100
Registers are small areas of temporary storage
within the CPU.
011
101
CPU
Holds the instruction after transfer from the RAM
or before transfer to it via the data bus.
Memory Data Register (MDR)
Instruction Register (IR)
Instructions are often fetched in 2 parts. The
first part can go to the IR, and be decoded later.
Memory Address Register (MAR)
Holds the address of the memory location to be
opened, before transferring it to the address bus.
Program Counter (PC)
Automatically advances to the address of the next
memory location, to pass it onto the MAR.
19
Buses Registers
H Grade
MAIN MEMORY
Registers
000
110
001
111
010
100
Registers are small areas of temporary storage
within the CPU.
011
101
CPU
General Purpose Registers (for example the
Accumulator (A), X, Y,. Are used for things
like the intermediate results of calculations.
20
MEMORY
RAM
Two main types of RAM chip are available
1 Dynamic RAM (DRAM)
DRAM must have a circuit to constantly refresh
its contents.
DRAM is cheaper to produce than SRAM, so most of
the memory in a computer is DRAM.
21
2 Static RAM (SRAM)
SRAM does not need a refreshing circuit, but it
still needs to have power constantly applied.
SRAM is more expensive than DRAM, but its much
faster than DRAM. For this reason, its used in
the processors memory.
cache
SRAM is used to hold the computers date and time
settings. It uses a small battery to keep this
information when the computer is switched off.
22
ROM
- ROM (Read Only Memory). No changes at all can
be made to a ROM chip.
2 PROM (Programmable ROM). The blank chip can
be programmed once only.
- EPROM (Erasable PROM). The blank chip can be
programmed, then wiped using ultra violet light.
4 EEPROM (Electronically EPROM). The blank chip
can be programmed, then wiped by an electronic
signal.