Chap' 23' Memory systems PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 34
Title: Chap' 23' Memory systems
1
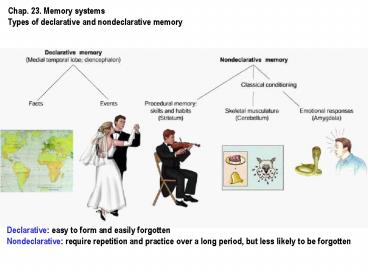
Chap. 23. Memory systems Types of declarative and
nondeclarative memory
Declarative easy to form and easily
forgotten Nondeclarative require repetition and
practice over a long period, but less likely to
be forgotten
2
Short-term (seconds to hours) and long-term memory
3
Amnesia retrograde and anterograde Transient
global amnesia caused by reduced cerebral blood
flow
4
The effects of cortical lesions on maze
performance
5
Hebbs cell assembly and memory storage Engram
(?? ??(??)
Donald O. Hebb. (1904-1985) Father of Cognitive
Psychobiology
Hebb
6
Responses to faces in inferotemporal (IT) cortex
7
Processing or memory?
8
The brain lesion in the patient H. M.
9
(No Transcript)
10
(No Transcript)
11
Information flow through the medial temporal
lobe
12
The Brain Memory (the case of Jeremy)
13
The DNMS (Delayed non-match to sample)
task Recognition memory
Delay Seconds to 10 min
14
Medial temporal (contains hippocampus) lesions
and DNMS performance (working memory)
15
Components of the diencephalon involved in memory
- Fornix?Mammilary body in the hypothalamus?Anteri
or nucleus in the thalamus?Cingulate cortex -
Lesion in the left dorsomedial thalamus?severe
retro and antero amnesia
16
Hippocampus and working memory Radial arm
maze Disrupted by hippocampal lesion.
17
Place cells in the hippocampus
10 min
10 min
10 min
18
Are place cells related to where the animal think
it is?
NW
No visual cues (i.e. light off)?
SE
19
Place cells in the human brain? Figure 24.18.
Activity in human brain related to spatial
navigation Maguire et al. Knowing where and
getting there a human navigation
network.Science. 1998 May 8280(5365)921-4. PET
studies Difference between the navigation and
directed navigation hippocampus
20
Caudate may reflect movement planning Hippocampu
s place cells? Similar hippocampal activity
from imagination of navigation in experienced
taxi drivers Reasons for the asymmetry is not
clear
21
Spatial map vs. Relational memory
Spatial map hippocampal place fields organized
as the locations in space, much like the
retinotopy in the visual cortex. Relational
memory ball A is below cone B would be one
memory.
22
Hippocampal activity for nonspatial targets An
odor discrimination experiment to study
relational memory
Some neurons in the hippocampus are selectively
responsive to a pair of odors (even selective to
the relative position of odors)
23
Nature Reviews Neuroscience 5, 361 -372 (2004)
NMDA RECEPTORS, PLACE CELLS AND HIPPOCAMPAL
SPATIAL MEMORY Kazu Nakazawa, Matthew A. Wilson
Susumu Tonegawa -NMDARs in area CA1 of the
hippocampus in spatial memory acquisition. -Uniqu
e role of NMDARs in area CA3 in the rapid
acquisition and associative retrieval of spatial
information. -In vivo hippocampal recording
studies that indicate that the activity of
hippocampal place cells during behaviour is an
expression of a memory trace. -Approaches
spatio-temporal targeting of NMDAR.
24
Striatum and procedural memory (association
between two events) Striatum caudate nucleus
putamen. Radial arm maze (standard version)
requires declarative memory Radial arm maze
(light version) requires procedural memory
(simple association) Differential effects of
hippocampal and striatal lesions in these two
assays.
25
Changing responses in rat striatum during the
learning of a habit
Low tone High tone
Formation of a habit?
26
Memory of amnesiac and Parkinsons
patients Whether prediction test association
between cards and weather
Declarative memory
Associational procedural memory
27
The neocortex and working memory
28
(No Transcript)
29
Prefrontal cortex and working memory The
Wisconsin card-sorting test (should figure out
the current sorting category!) See Figure
24.25 Patients with prefrontal lesions have
difficulty on this task!! ? Prefrontal cortex
involved in the working memory
30
Prefrontal cortex and working memory Neural
responses in monkey prefrontal cortex Delayed
response test (monkey cannot see the food during
the delay)
31
Lateral intraparietal cortex (LIP area) and
working memory
32
Parietal cortex and working memory The
delayed-saccade task and the response of a LIP
neuron
33
Novel or unexpected events or stimuli draw our
attention and are more easily remembered than
predictable or familiar ones. How? Neural
mechanisms for detecting and remembering novel
events.Nat Rev Neurosci. 2003 Mar4(3)193-202.
Review.
34
Box 2 Brain regions implicated in novelty
processing