Breast Cancer : Overview of symptoms, causes, diagnosis, risk factor and treatment - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Breast Cancer : Overview of symptoms, causes, diagnosis, risk factor and treatment
Description:
Breast cancer is a disorder in women, which starts in the inner lining of milk ducts or the lobules that supply them milk. Breast cancer may include lump in the breast, a change in breast or red scaly patch on skin. Breast cancer usually builds up with the age or it can be genetics. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:252
Title: Breast Cancer : Overview of symptoms, causes, diagnosis, risk factor and treatment
1
Breast Cancer
2
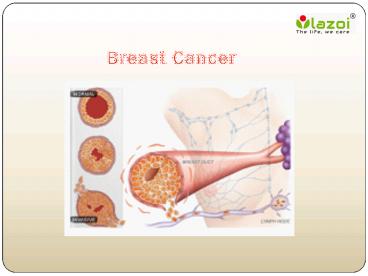
Breast Cancer
- Breast cancer starts when cells in the breast
begin to grow out of control. These cells usually
form a tumor that can often be seen on an x-ray
or felt as a lump. The tumor is malignant
(cancer) if the cells can grow into
(invade) Overview of breast cancer-Breast
cancer occurs when cell of breast began to grow
out of control often from a tumor which can start
from a lump. - The tumor occurs malignant when the cells grow in
the surrounding tissue, i.e spread in the
different parts of the body. - The cancer can start in all part of the breast,
but most cancers start in the inner lining of the
milk ducts or globules that supply them with
milk, rarely cancer start is the tissue of the
breast. - Breast cancer is the most common cause of cancer
in women, men can also have breast cancer but
it's rare (2000 new cases registered every year
in US). - It accounts for 16 of all female cancers, and
22.4 of invasive cancer worldwide, and 18.2 of
all cancer deaths worldwide. One in every eight
women in US has breast cancer.
3
Symptoms of breast cancer
- Any women having certain symptoms mentioned
below should be consulted with a doctor
immediately - A lump in a breast
- A pain in the armpits or breast that does not
seem to be related to the woman's menstrual
period - Pitting or redness of the skin of the breast like
the skin of an orange - A rash around (or on) one of the nipples
- A swelling (lump) in one of the armpits
- An area of thickened tissue in a breast
- One of the nipples has a discharge sometimes it
may contain blood - The nipple changes in appearance it may become
sunken or inverted - The size or the shape of the breast changes
- The nipple-skin or breast-skin may have started
to peel, scale or flake
4
Causes of breast cancer
- The cause of breast cancer is still not known.
- In breast cancer, the normal cells become
cancerous through the mutation of cell DNA
although some can be inherited but most cases
occur that DNA changes related to breasts cancer
occur during one's lifetime. - Proto-oncogenes can also help, if these cells
mutate the growth of any cell goes out of
control.So, it can lead to cancer.
5
Risk factors of breast cancer
- Though the causes of breast cancer is not known
there are some factors which can increase the
chance of getting breast cancer such as - Age The chances of getting breast
cancer increases with the age of a person. - Family history The risk of breast cancer is
higher among women who have relatives with the
disease. Having a close relative increases the
risk to double. - Personal history Women who had a breast cancer
before, even a non-invasive one has a higher
chance of getting breast cancer in the other
breast. - Menstruation Women who started their menstrual
cycle at a younger age (before 12) or went
through menopause later (after 55) have a
slightly increased risk. - Breast tissue Women with dense breast tissue (as
documented by mammogram) have a higher risk of
getting breast cancer. - Race White women have a higher risk of
developing breast cancer. But African-American
women have more proliferative and invasive tumors
when they have them.
6
Risk factors of breast cancer
Continue
- Radiation-Exposure to previous chest radiation or
use of diethylstilbestrol increases the risk of
breast cancer. - Having no children or the first child after age
30 increases the risk of breast cancer. - Breastfeeding for one and a half to two years
might slightly lower the risk of breast cancer. - Being overweight or obese increases the risk of
breast cancer. - High sugar intake can increase the risk of
breasts cancer. - Use of oral contraceptives in the last 10 years
increases the risk of breast cancer. - Using combined hormone therapy after menopause
increases the risk of breast cancer. - Alcohol use increases the risk of breast cancer.
- Genetic risk factors The most common causes are
mutations in the BRCA1 and BRCA2 genes (breast
cancer genes). Inheriting a mutated gene from a
parent means that one has a significantly higher
risk of developing breast cancer.
7
Diagnosis of breast cancer
- Mammogram-Mammogram is the X-ray of breast which
is used to detect any abnormalities or changes in
the breast. Women of higher age i.e. above 45
should undergo mammogram annually to detect any
risk, or women of lower that age and higher that
age must undergo mammogram to fall out the risk. - Breast test-A test is done by the physician who
looks for lump or any abnormalities in the breast
which can indicate cancer. - Ultrasound of breast-Ultrasound of a breast is
done to look for dense breast tissues, or certain
changes in the breast which can be felt but not
seen in mammogram. - MRI of breast-This technique is useful for women
who had already detected with breast cancer. It
helps to measure the size of the cancer, other
tumors in breast and check for tumor in other
breast. - Breast biopsy-Biopsy of the breast is done, by
taking a small tissue sample from the breast and
studies it to find any abnormal or different
cells in the breast tissue.
8
Treatments of breast cancer
- Treatments of breast cancer-
- The treatment of breast cancer take into account
several factors of patient before starting the
treatment such as the stage of the cancer, the
health of the patient, the age of the patient
and also the type of the breast cancer. - Surgery
- Breast-conserving surgery (lumpectomy) - Only the
part of the breast containing the cancer is
removed along with some surrounding tissue. The
removal of the breast tissue size depends on the
size and location of the tumor. - Mastectomy -In this surgery the entire breast is
removed, including all of the breast tissue and
sometimes other nearby tissues. Some women may
also get a double mastectomy, in which both
breasts are removed.
9
Treatments of breast cancer
Continue
- If the cancer has passed on to the nearby lymph
nodes than certain lymph node surgery is needed
for the removal. - Sentinel lymph node biopsy (SLNB) - In this
method only the lymph nodes under the arm to
which the cancer would likely to spread is
removed. - Axillary lymph node dissection (ALND) -In this
method anywhere from about 10 to 40 (though
usually less than 20) lymph nodes from under the
arm. This technique is avoided as removal of such
many lymph nodes can cause serious side effects. - Radiation therapy
- Breast radiation therapy - after a lumpectomy,
radiation is administered to the remaining breast
tissue to ensure no return of cancer. - Chest wall radiation therapy - this is applied
after a mastectomy to the chest walls or places
where any drains which excited the body after
surgery. - Breast boost - a high-dose of radiation therapy
is given after lumpectomy to the whole breast.
10
Treatments of breast cancer
Continue
- Lymph nodes radiation therapy - the radiation is
aimed at the axilla (armpit) and surrounding area
to destroy cancer cells that have reached the
lymph nodes - Breast Brachytheraphy-
- All the previous radiation methods are external
methos, i.e a radiation is provided from outside
the body. - In brachytherapy small device containing
radioactive pellets is placed in the breast
tissue for few minutes a radiation is given
internally. - They ensure targeted radiation to specific cancer
cells and removal of them. - Side effects of any radiation therapy may include
irritation in breast region, redness, infection,
fatigue and darkening of breast skin. - Chemotherapy
- Chemotherapy treatment can be given before or
after radiation. Before radiation it is given to
shrink the cancer size so less or no radiation is
required. And after surgery it is given to remove
any cancer cells which are remained back.
11
Treatments of breast cancer
Continue
- Drugs used are
- Anthracyclines, such as doxorubicin (Adriamycin)
and epirubicin (Ellence) - Taxanes, such as paclitaxel (Taxol) and docetaxel
(Taxotere) - 5-fluorouracil (5-FU)
- Cyclophosphamide (Cytoxan)
- Carboplatin (Paraplatin)
- Most often combination of two or three drugs is
used. - Advanced cancer-Patients with cancer which has
spread beyond breast and lymph nodes can be given
advanced chemotherapy treatment. Drugs used are- - Docetaxel
- Paclitaxel
- Platinum agents (cisplatin, carboplatin)
12
Treatments of breast cancer
Continue
- Vinorelbine (Navelbine)
- Capecitabine (Xeloda)
- Liposomal doxorubicin (Doxil)
- Gemcitabine (Gemzar)
- Mitoxantrone (Novantrone)
- Ixabepilone (Ixempra)
- Albumin-bound paclitaxel (nab-paclitaxel or
Abraxane) - Eribulin (Halaven)
- Targeted therapy-
- Trastuzumab (Herceptin) - this monoclonal
antibody targets and destroys cancer cells that
are HER2-positive. (HER2 is the gene that gets
mutated in breast cancer). Possible side effects
may include skin rashes, headaches, and/or heart
damage.
13
Treatments of breast cancer
Continue
- Lapatinib (Tykerb) - this drug targets the HER2
protein. It is also used for the treatment of
advanced metastatic breast cancer. Tykerb is used
on patients who did not respond well to
Herceptin. Side effects include painful hands,
painful feet, skin rashes, mouth sores, extreme
tiredness, diarrhea, vomiting, and nausea. - Breast cancer can be prevented by preventing all
the certain risk factors which can increase the
rate of this particular cancer.
14
CONNECT WITH US
- Logon to
- www.lazoi.com
- Like us on Facebook
- https//www.facebook.com/LazoiTheLife
- Follow us on Twitter
- https//www.twitter.com/lazoithelife
- Follow us on Pinterest
- https//www.in.pinterest.com/lazoithelife