Joint Venture: PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title: Joint Venture:
1
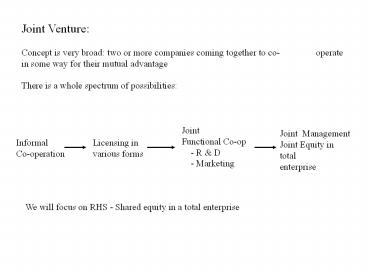
Joint Venture Concept is very broad two or
more companies coming together to co- operate in
some way for their mutual advantage There is a
whole spectrum of possibilities
Joint Functional Co-op - R D - Marketing
Joint Management Joint Equity in total enterprise
Informal Co-operation
Licensing in various forms
We will focus on RHS - Shared equity in a total
enterprise
2
Paradox There are more and more JVs, but
experience says they are hard to manage and
economic theory says they dont make sense -
cheaper when costs are internalized - moral
hazard of partner going on his own - benefits
unequally distributed
3
Motivation for JV
To take existing products into foreign markets
To diversify into new businesses
New Markets
To bring new (foreign) products into existing
markets
To strengthen existing business
Existing Markets
New Products
Existing Products
4
Operating questions that arise - Who does
product design? - Which technology should be
used? Who gets benefits of any improvements
made within the JV? - Which markets should be
served? Local? Export? - Which suppliers should
be used? - Buy from parent(s)? At what
price (transfer price) - Buy on open market?
(real price) How to handle management problems
arising from different cultures? - national -
corporate
5
JV will have to create/define patterns of
interpersonal relationships at all levels and
in all directions The dominant parent,
especially if it is foreign, may - misread local
culture and politics - misread markets -
generate resentments in its partner Problem of
tyranny of the majority
6
Functional JVs (mostly associated with
Existing/Existing) 1. Marketing - - share sales
force - share distribution network - e.g. Air
alliances Problem lose brand identity Possible
answer create a super brand e.g. airlines
Star Alliance Can work pretty well 2.
RD Problems - quality of inputs (researchers,
technicians, scientists, equipment - how to
share benefits of outputs? Note the
contradiction here to the usual approach to
patenting Possible solution joint licensing of
results
7
3. Production (a) Get economies of scale which
would not otherwise be possible Problem
unstable as market grows one or more will become
big enough to want to go it alone (b) Get
access to technology and management
know-how Problem again it is inherently unstable
partner may go it alone once technology is
mastered 4. Other In general to reduce
financial risk, e.g. -joint oil/mining
exploration, - some banking arrangements such
as syndicated loans
8
Existing Product / New Market Use JV as a way of
testing the market. Implication is we will
establish a wholly owned subsidiary when the
market is proven (Is this fair to our
partner?) 1. Follow customers to markets -
Japanese auto parts suppliers to US - US and
European accounting, consulting and legal firms
to SE Asia and China 2. Investing in Future
growth 3. Overcome government regulation - may
require foreign investor to take a local
partner - may have limits on FDI - may have
limitations on foreign employment - may have
limitations on capital transfer 3 (a) Overcome
political connections barriers
9
New Product / Existing Market In some ways this
is the mirror image of the previous 1. Improve
production capacity utilization 2. Broaden the
product line 3. If existing market is in LDC,
foreign partner can be a source of hard
currency - from sales and profits - from
management fees 4. May generate tax
advantages Future problems - Question of
market growth- will we go from marketing to
assembly to full scale production? - New
product means a need for more capital, more
management, more commitment - Question of
source of supply of product - parent
companies? Third party?
10
New Products / New Markets Most diversification
acquisitions or JVs do not succeed
Not a good bet!!
11
Requirements for Success 1. Strategic logic -
is there a market? - is a partnership the best
way to go? - is it a balanced partnership? -
what are the costs benefits for the local
partner? For the foreign partner? 2. Is
there a fit between the partners? - goals -time
horizon - measurement of success? -
compatibility ? - do respective capabilities
fill the gaps? - comfort quotient - with
partner - with environment 3. Shape and
Design of JV - strategic freedom of JV Note
that this will likely change over time - be ready
for it! - develop cadre of managers committed to
JV and not to one or other parent
12
4. Payoffs balanced? - trading profits of the
parents - selling prices, especially transfer
prices - management fees - dividends 5.
Management roles and authorities of each partner
defined and understood? -dispute resolution by
using legal authority or by negotiation? Problem
Can arrive at a decision making
stalemate! Possible answer have one dominant
partner, which in practice usually means the
foreign partner. However this can lead to -
misreading the local culture - misreading
political environment - misreading the
market - generate resentment which will further
impede co-operation
Key Issue is TRUST
13
Doing the Deal What counts is the relationship,
not the contract But contract is important - I
like the books suggestion of a shotgun divorce
clause -I name the price - You decide whether
to buy or sell Maturation problems 1. A
successful JV will develop growing autonomy from
both parents 2. The parents goals will change
over time Therefore need to have a
willingness to recognize changed circumstances
and to re-negotiate arrangements
14
Some results from JV research in
Bahrain Dominant motivation is market access -
both local and export Costs not dominant so long
as critical resources are reasonably
available Government involvement is relatively
unimportant -subsidies - tax breaks -
promotion JV must make sense on its own
merits Needs to be an attractive environment for
foreign staff - schools - health - social
life
15
Most important factor in partner selection was
prior experience with him and his local
reputation Recommendations from third parties -
banks, governments, not significant factor in
partner selection Companies that are in their
first JV place more emphasis on cost Companies
and managers with prior JV experience are more
laid back in their assessment of
success Critical variable for success - getting
managers with prior overseas JV experience Total
years of management experience is not the same
thing as JV experience