DNA vaccine induces TH1 response' - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 31
Title:
DNA vaccine induces TH1 response'
Description:
DNA vaccine is preferred for inducing immunity against intracellular infection. ... Live RSV vaccine: balanced TH1/TH2. Formalin inactivated RSV: TH2 response ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:337
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: DNA vaccine induces TH1 response'
1
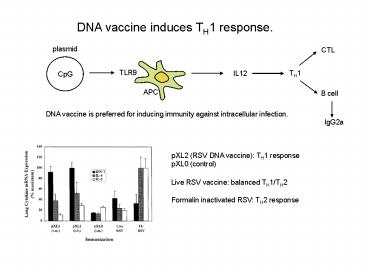
DNA vaccine induces TH1 response.
plasmid
CTL
TLR9
TH1
IL12
CpG
APC
B cell
DNA vaccine is preferred for inducing immunity
against intracellular infection.
IgG2a
pXL2 (RSV DNA vaccine) TH1 response pXL0
(control)
Live RSV vaccine balanced TH1/TH2
Formalin inactivated RSV TH2 response
2
(No Transcript)
3
DNA vaccine expressing multiple antigens
DNA vaccine priming / boosting with other vaccines
4
Mucosal vaccine
Mucosal surface is the major site of pathogen
entry.
Mucosal vaccine induces both mucosal and systemic
immunity. Injected vaccines are poor inducers of
mucosal immunity.
M
DC
B
T
T
GC
Plasma cells, memory B cells
TH cells, CTL
5
Mucosal lymphocytes home to mucosal tissues.
Common mucosal immune system
Inductive site
Peyers patch
Effector site
Effector site
Other mucosal tissues
Other mucosal tissues
Plasma cells, CTL, TH cells Memory cells
Lymph node
Blood circulation
Blood circulation
6
Lymphocyte homing to mucosal tissue
Mucosal tissue-specific adhesion molecules and
chemokine/chemokine receptors
Mucosal effector site
a4b7 integrin
MADCAM1 (addressin)
Endothelial cells of venules in intestine
plasma cells
Epithelial cells of intestine and other mucosal
tissues
CCR10
CCL28
Mucosal induction site
a4b7 integrin
MADCAM1 (addressin)
Endothelial cells of venules in intestine
Effector T cells
Epithelial cells of intestine and other mucosal
tissues
CCR9
CCL25
7
Mucosal immunization also induces systemic
immunity.
M
Mucosal immunity
DC
B
T
T
GC
Mucosal lymphoid tissue
Lymph node
Systemic immunity
8
Mucosal plasma cells produce IgA.
Neutralization
Mucus
Dimeric IgA
Epithelial cells
IgA gt IgG
IgA
CTL
IgG
TH
Mucosal plasma cells
Blood circulation
Mucosal effector T and B cells
Blood circulation
Systemic immunity (lymph nodes, spleen)
IgG gt IgA
9
Preferential localization of mucosal immunity to
induction site
10
Challenges in mucosal vaccine
Degradation, dilution on mucosal surface
Live attenuated pathogen (polio vaccine, S. typhi
vaccine)
Use as recombinant vectors vaccines
Prevent tolerance
Mucosal adjuvant to induce danger signal
(activate DCs)
Mutated enterotoxins of bacteria (e.g. cholera
toxin)
PAMPs (e.g. CpG, flagellin)
11
Cancer vaccine
Immune response against tumor
Tumor Ag
Tumor cells
Mature DCs
Uptake of Tumor Ag By immature DCs
Kill tumor cells
MHC I and II-antigen
CTL
B7
Lymph node
CD4 T
CTL
CD8 T
12
Boosting Immune response against tumor
Immunization with Tumor Ag
Loading DCs with Tumor Ag (DC vaccine)
Tumor cells
Tumor Ag
Mature DCs
Uptake of Tumor Ag By immature DCs
Kill tumor cells
MHC I and II-antigen
CTL
B7
Lymph node
CD4 T
CTL
CD8 T
Cytokine stimulation
In vitro activation of anti-tumor T
cells Adoptive transfer
13
Dendritic cell vaccine
patient
monocytes
CD34 HSC
Direct isolation
DC loaded with tumor Ag
cytokines
cytokines
Immature DCs
Peptides or proteins (tumor Ag)
Tumor cell lysate
Cytokines
Mature DCs
14
Cancer vaccine trials
Peptide vaccines alone or with IL-12 or GM-CSF
Recombinant virus expressing tumor antigens
Irradiated autologous tumor cells or tumor cell
lysates
Dendritic cells loaded with peptides, proteins,
or tumor lysates, etc.
15
Immunosuppression mechanisms of tumor
Inhibition of DC maturation
Peripheral tissues
Mf
activation
iMC
CMP
HSC
Immature Myeloid cells
Mature DC
Immature DC
Bone marrow
myeloid DCs
granulocyte
16
Immature DCs capture antigens.
Mature DCs activate T cells.
CD4 T
TH
Immature DC
Mature DC
2o lymphoid tissues
MHC I
MHC I
MHC II
MHC II-
CTL
B7-
B7
Antigen capture
CD8 T
Antigen presentation
T cell tolerance
T cell activation
17
Tumors inhibit DC maturation.
VEGF (vascular endothelial growth factor)
Tumor cells
M-CSF (macrophage colony-stimulating factor)
Cyclooxygenase-2 (COX2) produces prostaglandin
E2, PGE2)
Tumor microenvironment
VEGF
IL10
Mature DC
Immature DC
TGF-b
M-CSF
IL6
gangliosides
PGE2
MHC I
MHC I
MHC II
MHC II-
B7
B7-
18
Reduced number of DCs in cancer patients
Clinical Cancer Research 6, 1755-1766 (2000)
HNSCC head and neck cancer
19
Defective DC function in cancer patients
Proliferation (3H incorporation)
CD4 T cells
DCs (mismatched class II MHC)
20
Cancer patients have higher proportions of
Immature DCs.
Immature DCs HLA-DR- (class II MHC)
B7-
CD40-
21
Surgery removal of tumor reduces immature DCs.
5 patients
Proportion of immature DCs
22
Reduction of immature DCs after chemotherapy and
Anti-VEGF antibody treatment.
23
Tumors induce the expression of B7-H1, H4 in APCs.
Some tumor cells express B7-H1,B7-H4.
B7-H1,B7-H4
Tumor microenvironment
B7-H1, H4
B7-H1, B7-H4 inhibit T cell activation
(co-inhibitory molecules)
Normal maturation
B7.1(CD80), B7.2(CD86)
T cell activation
24
Cancer patients have higher levels of Treg cells.
CD4CD25FoxP3 T cells (5-10 of peripheral CD4
T cells)
Inhibit T cell response.
25
Depletion of CD25 cells increases tumor
rejection.
26
Depletion of Treg cells by DAB389IL-2
(denileukin diftitox, ONTAK)
High affinity IL2 receptor
Low affinity IL2 receptor
?
?
?
?
?
IL2R? CD25
Effector T cell CD4CD25Treg
Naive T cell
DAB389IL-2
Diphtheria toxin
IL2
CD25- T cell
CD25 T cell
DAB389IL-2 preferentially kill CD25 T cells.
27
DAB preferentially kills CD25high Treg cells.
J. Clinical Investigation 115, 3623-3633 (2005)
CD4CD25int
CD4CD25neg
CD4CD25neg T cells naïve resting T cells
CD4CD25high
CD4CD25int T cells activated T cells
CD4CD25high T cells Treg cells (FoxP3)
Cancer patients have highly levels of CD25Treg
cells (FoxP3)
RCC Renal cell carcinoma
Donor healthy control
28
Depletion of CD25Treg cells enhances T cell
response against tumor.
Determine the frequency of CD8 T cells that
express IFN-? in response to tumor.
Vaccinated with DC vaccine against RCC
patient
Treat with DAB
Patient
29
Treatment with CTLA4-specific antibody
CD4CD25Treg cells constitutively express CTLA4.
CTLA4 antibodies improve tumor rejection, but
cause autoimmunity.
30
Adoptive transfer of anti-tumor T cells
Science 298, 850-854 (2002)
13 Cancer Patients
Cyclophosphamide fludarabine
(metastatic melanoma)
Tumor cells
Melanoma
Lymphodepleted patients
TIL (tumor infiltrating Lymphocyte)
6/13 responded
5/13 have autoimmune melanocyte destruction
Infusion of anti-tumor T cell with IL2
Anti-CD3IL2
Expansion of TIL in cell culture
These T cells can be activated By tumor antigens
in self-MHC
Tumor regression after a few month
31
Relevant part in book
Cancer vaccine and therapy page 511-520