TCA mechanisms of Toxicity PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 32
Title: TCA mechanisms of Toxicity
1
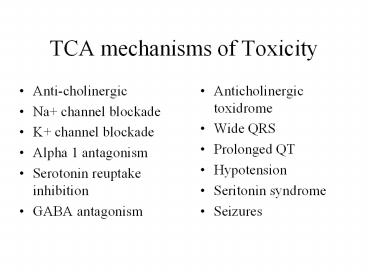
TCA mechanisms of Toxicity
- Anti-cholinergic
- Na channel blockade
- K channel blockade
- Alpha 1 antagonism
- Serotonin reuptake inhibition
- GABA antagonism
- Anticholinergic toxidrome
- Wide QRS
- Prolonged QT
- Hypotension
- Seritonin syndrome
- Seizures
2
Anticholinergic Toxidrome
- Agitation/altered LOC
- Red, hot, dry skin
- Tachycardia
- Dilated pupils
- No bowel sounds
- Urinary retension
- Mild hyperthermia
- Mild hyperreflexia
3
Case of the day!
- After you intubate, patient has a generalized
seizure - Why?
- Anticholinergic effect
- Gaba antagonism
- Hypotension
- Why are seizures so bad?
- Management?
4
TCA overdoses and seizures
Acidosis
Seizure
Cardiac toxicity
DEATH
Shock
5
TCA toxicity and Seizures
- Management
- First line benzodiazepines
- Second line phenobarbital
- Third line agents propofol
- Avoid dilantin (Na channel blockade)
- Should you give bicarb? Yes
6
Flumazenil
- Why is flumazenil contraindicated in a patient
with BZD TCA overdose? - Will precipitate seizures ----gt acidosis, cardiac
toxicity, death, call CMPA - Flumazenil is generally not indicated in the
overdose setting for this reason - One exception may be a pediatric ingestion of BZD
with absolutely no suspicion of coingestant
7
Case of the day!
- HR 120, BP 80/50
- What is your management?
- Why?
8
TCAs and Hypotension
- Fluids, go early to pressors
- Norepinephrine is the pressor of choice
- If you are going to use dopamine, titrate up to
alpha range (15 - 20 ug/kg/min) - Why is norepinephrine better than dopamine?
9
TCAs and Hypotension
- Dopamine is a precursor to norepinephrine
- Dopamine stimulates the release of stored
norepinephrine - Dopamine stimulates adrenergic receptors
10
TCAs and Hypotension
11
TCAs and Hypotension
12
TCAs and Hypotension
- Extreme options!
- ECMO
- Cardiac bypass
- IABP
13
Case of the day!Interpretation?Will she have a
bad outcome?
14
TCA toxicity and the ECG
- Sinus tachycardia
- Prolonged QT
- Wide QRS
- Wide complex tachycardia SVT with aberrancy or
Vtach - Right BBB
- Tall R wave in aVR
- R/S ration in aVR gt
- Terminal 40 msec right axis
15
TCA toxicity and the ECG
- Tall R in aVR, R/S ratio in aVR gt 0.7
16
TCA toxicity and the ECG
- Terminal 40 msec right axis
17
TCA toxicity and the ECG
- Terminal 40 msec right axis
18
TCA toxicity and the ECG
- What ECG features are predictive of TCA toxicity?
- QRS width
- Tall R in aVR
- R/S ratio in aVR
- Terminal 40 msec right axis
- Which are the most sensitive/specific for TCA
toxicity?
19
QRS width
20
aVR tall R wave and R/S ratio
21
Terminal 40 msec right axis
22
What is the differential dx of wide QRS in the
overdose setting?
23
ECG and Toxicology
- Wide QRS (Na channel blockade)
- TCAs
- Gravol, bendadryl
- Cocaine and other sympathomimetics
- Haldol and other neuroleptics
- Celexa
- Carbemezepine?
- kdjflfjljletc
- Prolonged QTc
- TCA
- Haldol etc
- Ia
- Ic
- dfjkl
24
Case of the day!
- Vtach
- Management?
25
TCA and Sodium Bicarbonate
- Sodium Bicarbonate is the treatment of choice for
cardiac toxicity - Dose 1-2 mEq/kg iv bolus q10 min prn
- End points no indication, pH 7.50 - 7.55
- Monitor response with repeat ECGs
26
TCA and Sodium Bicarbonate How does it work?
- Increases protein binding
- TCAs are albumin bound which is pH sensitive
minor role b/c large Vd and lipophilic thus most
TCA is in tissue not serum - Alkalosis
- the TCA to Elevated pH decreases the binding of
the voltage gated sodium channel - Sodium loading
- Na load with bicarb creates a larger gradient
across the Na channel
27
TCA and Sodium Bicarbonate What are the
indications?
- Hypotension
- Wide complex tachycardia
- Conduction blocks
- QRS gt 100 msec (or gt 120 msec)
- New/unexplained RBBB
- R in aVR gt 3mm, R/S ratio gt 0.7, or terminal 40
msec right axis - ? Which are goldfranks recommendations
- ? seizures
28
TCA and Sodium Bicarbonate Bolus versus
infusion?
- Boluses are preferred for initial indications
Why? - All studies showing effect of bicarb have used a
bolus - Probably better b/c big Na load with bolus
overcomes Na blockade Na load likely more
important than pH change - Repeat boluses vs infusion never directly studied
- Bicarb infusion resonable for patient requiring
repeat boluses
29
Could Fab fragments be the cure for the TCA
overdose??
30
Case of the day!
- ICU resident order serum TCA level and urine TCA
screen ------gt what do you say?
31
TCA and lab testing
- Urine TCA screen
- Dip stick screen, immunoassay
- HORRIBLE specificity thus the lab doesnt even do
it
- Serum TCA levels
- Do NOT correlate with toxicity
- False ves
- Benadryl
- Gravol
- Flexeril
- dfldjf
- fldljfkl
32
TCA overdose and disposition
- Toxicity develops within 6 hrs
- Monitored for 6hrs NO seizures, hypotension,
arrythmias, no bicarb Rx - Can d/c home or to psych
- ICU for seizures, hypotension, arrythmias,
decreased LOC - Telemetry for prolonged QTc
- Duration of cardiac monitoring
- 24hrs after normalization of BP, off
alkalinization/antidysrhythmics/pressors