How Does a CFD Code Work PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 20
Title: How Does a CFD Code Work
1
How Does a CFD Code Work
Department of Mechanical Engineering
MEHB463
CFD Chap. 1 Introduction to CFD
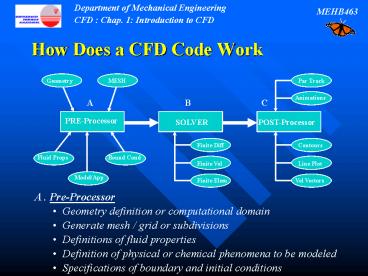
- A . Pre-Processor
- Geometry definition or computational domain
- Generate mesh / grid or subdivisions
- Definitions of fluid properties
- Definition of physical or chemical phenomena to
be modeled - Specifications of boundary and initial
conditions
2
How Does a CFD Code Work .
Department of Mechanical Engineering
MEHB463
CFD Chap. 1 Introduction to CFD
- B. SOLVER
- This is the heart of the code
- Involved applications of the discretized equation
to each of the CV - Basically 3 Steps are Involved -
- Approximation of the unknown flow variables
- Discretization Substitution of approximation
into governing flow equations and subsequent
manipulations - Solution of Algebraic Equation For Each Node
- 3 Methodologies are used Finite Difference,
Finite Volume, Finite Element - Most Commercial Code use FV e.g. FLUENT, CFX,
PHOENICS
3
How Does a CFD Code Work .
Department of Mechanical Engineering
MEHB463
CFD Chap. 1 Introduction to CFD
- B. SOLVER cont
- Finite Volume Method
- Basically 3 Steps are Involved -
- Formal Integration of the Governing Equation For
All CVs - Discretization substitution of FD-type equation
of the Convection, Diffusion and Sources Terms - Solution of Algebraic Equation For Each Node eg
by TDMA, Stone Algorithm, Conjugate Gradient - FVM Mimics the underlying physical conservation
principles. - General Conservation Law
- Rate of change of ? in the CV Convection
Flux of ? into CV Diffusion Flux of ? into
the CV Rate of Source Creation of ? in the CV
4
For example, for general fluids motion the PDE
is called the Navier Stokes equations
5
How Does a CFD Code Work .
Department of Mechanical Engineering
MEHB463
CFD Chap. 1 Introduction to CFD
Small control volume where equations are applied
Structured H-mesh
inlet
periodic
Unstructured adaptive mesh
exit
exit
inlet
6
How Does a CFD Code Work .
Department of Mechanical Engineering
MEHB463
CFD Chap. 1 Introduction to CFD
- Post-Processor
- Graphical Display of the Output Results
- Eg. Contours, Line Plot, Vector Plot, Surface
Plot, Particle Track
7
Introduction to CFD analysis using GAMBIT FLUENT
GAMBIT
FLUENT
8
(No Transcript)
9
(No Transcript)
10
(No Transcript)
11
(No Transcript)
12
(No Transcript)
13
(No Transcript)
14
(No Transcript)
15
(No Transcript)
16
Test case using GAMBIT FLUENT
- Problem Identification and Preprocessing
- Define your modeling goals. ?
- 2. Identify the domain you will model ?
- 3. Design and create the grid ?
- Solver Execution
- 4. Set up the numerical model.
- 5. Compute and monitor the solution.
- Post-Processing
- 6. Examine the results.
- 7. Consider revisions to the model.
17
Pre-Requisites of CFD-User
Department of Mechanical Engineering
MEHB463
CFD Chap. 1 Introduction to CFD
- Aware that the underlying physics are very
complex and results generated is as good as the
physics embedded and as worst as its operator - The knowledge required are -
- Understanding of the Physics of the flow problem
Flow equations physical behaviour, model
embedded, approximation made, fundamental physics
of flow e.g. steady-unsteady, compressibility,
significant factors influencing the flow - Understanding of Numerical Algorithm Basic
concepts of Numerical Method such as convergence,
consistency stability Basics of discretization
scheme such as conservativeness
transportiveness, numerical viscosity, false
convection Effect of grid size, orthogonolity
etc.
18
Scope of This Course
Department of Mechanical Engineering
MEHB463
CFD Chap. 1 Introduction to CFD
- The Objective is to Provide all the Necessary
Pre-Requisites of Good CFD User - This is Achieved by -
- Understanding Basic Governing Equations, Their
Physical Meanings Possible Approximations - Understanding the Finite Volume Methods and
Associated Numerical Discretization Methods as
Applied to Fluid Flow Conservation Equations - Understanding the concept of turbulence and its
importance in CFD. Different types of turbulence
models
19
- End of lecture
20
MEHB463
Department of Mechanical Engineering
CFD Chap. 2 Fluid Flow Governing Equations
Summary of Governing Equations. In
conservation or divergence form
Continuity
x-mom
y-mom
z-mom
- Energy
Equation of state - Thermal eqn
of state p ?RT Caloric eqn of
state e CvT
Back