GAP Analysis Data and Information PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 4
Title: GAP Analysis Data and Information
1
GAP Analysis Data and Information
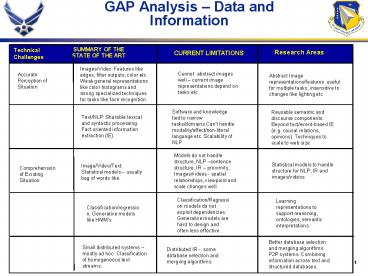
Technical Challenges
SUMMARY OF THE STATE OF THE ART
Research Areas
CURRENT LIMITATIONS
Images/Video Features like edges, filter
outputs, color etc. Weak general representations
like color histograms and strong specialized
techniques for tasks like face recognition.
Cannot abstract images well current image
representations depend on tasks etc.
Accurate Perception of Situation
Abstract Image representations/features useful
for multiple tasks, insensitive to changes like
lighting etc
Software and knowledge tied to narrow
tasks/domains.Cant handle modality/affect/non-lit
eral language etc. Scalability of NLP
Reusable semantic and discourse components.
Beyond fact/event-based IE (e.g. causal
relations, opinions). Techniques to scale to web
size.
Text/NLP Sharable lexical and syntactic
processing. Fact oriented information extraction
(IE).
Models do not handle structure, NLP sentence
structure, IR proximity, Images/videos -
spatial relationships, viewpoint and scale
changes well.
Statistical models to handle structure for NLP,
IR and images/videos.
Image/Video/Text Statistical models usually
bag of words like.
Comprehension of Existing Situation
Classification/Regression models do not exploit
dependencies. Generative models are hard to
design and often less effective.
Learning representations to support reasoning,
ontologies, semantic interpretations.
Classification/regression. Generative models like
HMMs
Better database selection and mergiing
algorithms. P2P systems. Combining information
across text and structured databases.
Small distributed systems mostly ad hoc.
Classification of homogeneous text streams.
Distributed IR - some database selection and
mergiing algorithms.
2
GAP Analysis Data and Information
Technical Challenges
SUMMARY OF THE STATE OF THE ART
Research Areas
CURRENT LIMITATIONS
Long term models for ecommerce (e.g. recommender
systems) but little for IR.
Current methods restricted to high quality,
homogeneous data. Lack of good user models.
Models of Users. Interactive Retrieval. Better
use of implicit feedback. Privacy concerns.
Semi-supervised learning not robust. Too much
high effort. Cant be applied to tasks with
limited data.
Supervised systems require lots of data.
Semi-supervised learning. Learning from small
amounts of data.
3
Technical Challenge AreasData and Information
Panel
- Reduce human effort
- semi-supervised learning
- Learning from small data amounts of data
- Performance Metrics
- Evaluation and testbeds
- How to evaluate complex processes/solutions
- Beyond classification and regression
- E.g., Using geospatial data as input
- E.g., learning semantic structures (ontologies)
- Machine Learning lifecycle
- context of models may change of time
- Maintenance, update, formatting of data
- Managing multiple learning models
- E..g, Portfolio of models each model serves a
different purpose - E.g. ensembles, model correlation, model
disagreement
4
- Trust in going from data to interpretation
- E..g, Pedigree/reliability of data source
- Explaining conclusions
- Modeling Spatial RelationshipsX
- Better image/video features X
- Incorporating user guidance
- Defining search space
- Complex search criteria
- Beyond Syntactic Analysis X
- NLP components for deep semantic interpretation
- Non-factual NLP
- Scalable NLP/information extractionX
- Beyond bag-of-words techniques for IRX
- Incorporating output of information extraction
systems, text categorization systems