Elementary Vector Analysis PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 58
Title: Elementary Vector Analysis
1
(No Transcript)
2
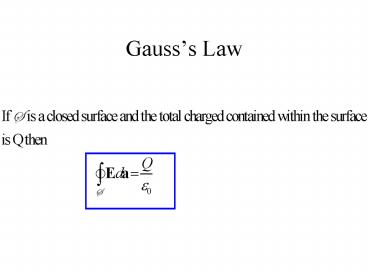
V
3
Gausss Law in differential form
4
(No Transcript)
5
.
6
(No Transcript)
7
(No Transcript)
8
(No Transcript)
9
(No Transcript)
10
(No Transcript)
11
- But this precisely the potential due to q
- At the center of the sphere.
- By the superposition principle for any collection
of charges outside the sphere the - Potential at the center of the sphere is equal
- to the their average potential over the
surface of the sphere.
12
(No Transcript)
13
- Earnshaws theorem follows immediately
- i.e. A charged particle can not be held in
equilbrium by electrostatic forces alone.
14
(No Transcript)
15
Question 6
16
(No Transcript)
17
Depends only on x
Depends only on y
18
(No Transcript)
19
(No Transcript)
20
Spherical Symmetry
Function of ? only
Function of r only
21
(No Transcript)
22
(No Transcript)
23
(No Transcript)
24
- An uncharged metal sphere of radius R is placed
in a uniform field EEk. Find the potential in
the region outside the sphere.
25
(No Transcript)
26
(No Transcript)
27
(No Transcript)
28
(No Transcript)
29
- Earnshaws theorem follows immediately
- i.e. A charged particle can not be held in
equilbrium by electrostatic forces alone.
30
Electric dipole
31
(No Transcript)
32
(No Transcript)
33
A dipole in an electric field
34
The tendency of the electric field to align the
dipole moment with itself is confirmed by the
potential energy formula. The potential energy is
lowest when the dipole moment is aligned with the
field and highest when the two are anti-aligned.
35
Water is a polar molecule
36
Bonds between atoms
- Different types of bonds between atoms
37
(No Transcript)
38
An insulator
- Suppose we place a pitcher of water in a electric
field - As we have seen the water molecule is polar so
the container looks like a random collection of
dipoles. - When the field is applied the dipoles will try to
align themselves to oppose the field
39
- To do this hydrogen bonds need to be brokenthe
stronger the field the more the dipoles can align
40
(No Transcript)
41
- Even for amolecule which is not naturally polar.
- The application of an electric field induces a
polarization.
42
(No Transcript)
43
(No Transcript)
44
(No Transcript)
45
- A material which is not a conductor we will
describe as a dielectric - A pure insulator is a dielectric where there is
no free charges
46
(No Transcript)
47
(No Transcript)
48
- For many materials the polarization is
proportional to the field
49
(No Transcript)
50
51
Magnetostatics
52
(No Transcript)
53
(No Transcript)
54
(No Transcript)
55
(No Transcript)
56
(No Transcript)
57
(No Transcript)
58
(No Transcript)