Organic Macromolecules - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 33
Title:
Organic Macromolecules
Description:
A macromolecule is a larger molecule (polymer) built by putting together smaller ... as well as other organic macromolecules (amino and fatty acids) ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:17
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Organic Macromolecules
1
Organic Macromolecules
- Carbohydrates
- Lipids
- Proteins
- Nucleic Acids
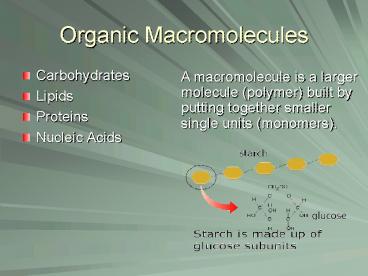
A macromolecule is a larger molecule (polymer)
built by putting together smaller single units
(monomers).
2
(No Transcript)
3
Carbohydrates
- Main source of energy for living things
- Plants and some animals use carbohydrates for
structural purposes
4
Carbohydrates fuel and building material
- Three types
- 1. monosaccharides
- 2. disaccharides
- 3. polysaccharides (macromolecule stage)
- Made up of C, H, and O
- Number of sugar molecules attached determines
category - mono- one
- di- two
- poly- more than two
- Glycosidic bonds attach the sugar monomers
together
5
Monosaccharides
- Are major sources of energy for cells
- Ex. Glucose cellular respiration
- Found in other carbohydrates as well as other
organic macromolecules (amino and fatty acids) - Most common monosaccharides glucose, fructose,
galactose
6
Figure 5.3 The structure and classification of
some monosaccharides
7
Glucose, Fructose, Galactose
- Glucose made during photosynthesis
- main source of energy for plants and
animals - Fructose found naturally in fruits
- is the sweetest of monosaccarides
- Galactose found in milk
- is usually in association with glucose
or fructose
8
Diaccharide
- Disaccharide two monosaccharide bonded
together. - table sugar(sucrose) is made up of glucose and
fructose bonded together, - milk sugar(lactose) is made up of glucose and
galactose
9
Figure 5.5 Examples of disaccharide synthesis
10
Polysaccharide
- Polysaccharide more than two monosaccharide
bonded together by glycosidic bonds - Serve as storage material or building material
- Storage (ex starch, glycogen)
- Structural (ex cellulose, chitin)
- A complex carbohydrate is a polysaccharide with
12 or more monosaccharide units. - Pasta and starches are polysaccharide
- Potatoes are a starch
11
Figure 5.7b,c Starch and cellulose structures
12
Chemical Identification of Carbohydrates
- Benedicts Test Identifies the presence of a
MONOSACCHARIDE by changing from blue to orange in
the presence of heat - Iodine Test Identifies the presence of a
POLYSACCHARIDE by changing from yellow to
purple/black - Process of Elimination If there is no reaction
with either the Benedicts or Iodine Tests, then
a DISACCHARIDE is present.
13
1. What are the three types of carbohydrates?
(give examples of each)2. What are
carbohydrates used for?3. What is a
polymer?4. What kind of bond attaches
carbohydrate monomers together?
14
(No Transcript)
15
Lipids (fats and oils)
- Used to store energy
- Some lipids are important parts of biological
membranes and waterproof coverings
16
Lipid Structure
- Lipid molecules are made up of fatty acids and
glycerol - Unsaturated fat- a fat that contains at least one
carbon-carbon double bond (it is liquid at room
temperature) - Saturated fat- a fat without one carbon-carbon
double bond (solid at room temperature)
17
Saturated fat
Unsaturated fat (oil)
18
5. What is the molecular difference between a
saturated and unsaturated fat? 6. What are
lipids used for?7. What usually makes up a
lipid?
19
(No Transcript)
20
Nucleic Acids
- Store and transmit hereditary or genetic
information - (RNA and DNA)
- RNA- ribonucleic acid
- DNA- deoxyribonucleic acid
- DNA has a double helix structure
DNA
21
Nucleic Acid Structure
- Nucleic Acids are made up of nucleotides bonded
together (phosphodiester bond) - Nucleotides consist of 3 parts
- 5-carbon sugar
- A phosphate group
- And a nitrogenous base
22
8. What are the two types of nucleic acids? 9.
What are nucleic acids used for?10. What makes
up a nucleic acid?
23
(No Transcript)
24
Proteins
- Proteins control the rate of reactions and
regulate cell processes. (enzymes are proteins) - Proteins are used to form bones and muscles
- Proteins transport substances into or out of
cells or help to fight disease
25
Protein Structure
- There are four levels of structure in a protein
- The primary structure of protein
- Proteins are made up of amino acids bonded
together by peptide bonds
Amino acids
26
- Protein Structure
- (1)Primary Structure- amino acid sequence in a
polypeptide chain - (2)Secondary Structure- polypeptide chains
hydrogen bonded into a helix form - (3)Tertiary Structure- one complete protein chain
clumped up - (4)Quaternary Structure- many protein lumps stuck
together
27
Amino Acid
- Amino Acids are compounds with an amino end (NH2
and a carboxyl end (COOH) - 20 different amino acids are commonly found in
proteins
28
11. What makes up a protein? 12. What is the
structure of a protein? 13. What kind of bond
does a protein have?
29
Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
- Chemical Reaction- a process that changes one set
of chemicals into another - CO2 H2O ? C6H12O6 O2
- Energy is usually absorbed or released in a
reaction
Reactants
Products
30
Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
- Activation energy- energy needed to get a
reaction started - Enzymes are proteins that act as biological
catalysts (speed up a reaction)
31
Chemical Reactions and Enzymes
- Enzymes speed up a reaction by lowering the
activation energy of a reaction - Enzymes act as a site of a reaction and are not
used up
32
14. What is a chemical reaction? 15. What is
activation energy?16. What does an enzyme do?
33
Carbon Macromolecules Compounds
include
that consist of
that consist of
that consist of
that consist of
which contain
which contain
which contain
which contain