Protein Synthesis - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 14
Title:
Protein Synthesis
Description:
Lysine. Nucleus. Translation. Section 12-3. mRNA. Go to ... Lysine. tRNA. tRNA. Ribosome. Growing polypeptide chain. mRNA. Translation (continued) Section 12-3 ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:32
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Protein Synthesis
1
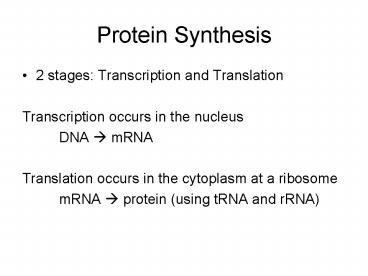
Protein Synthesis
- 2 stages Transcription and Translation
- Transcription occurs in the nucleus
- DNA ? mRNA
- Translation occurs in the cytoplasm at a ribosome
- mRNA ? protein (using tRNA and rRNA)
2
Nucleic Acids
- Exist as 2 types DNA and RNA
- DNA -- double stranded (entire code)
- sugar is deoxyribose
- never leaves nucleus
- bases are A,T,C,G
- involved in replication and protein
synthesis - RNA -- single stranded (partial code)
- sugar is ribose
- mobile nucleus and cytoplasm
- bases are A,U,C,G ( Uracil replaces
Thymine) - involved in Protein Synthesis
3
Figure 5.28 DNA? RNA ? protein a diagrammatic
overview of information flow in a cell
4
Figure 17.3 The triplet code
5
RNA and Protein Synthesis
- Types of RNA
- Messenger RNA (mRNA) carries information from
DNA in the nucleus to the ribosomes where the
proteins are assembled. - It is read 3 bases at a time codon.
- 2. Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) found in ribosomes and
helps in the attachment of mRNA and in the
assembly of proteins. - 3. Transfer RNA (tRNA) transfers the needed
amino acids from the cytoplasm to the ribosome so
the proteins coded by the mRNA can be assembled.
(The three exposed bases are complementary to the
mRNA and are called the anticodon)
6
Transcription
Section 12-3
Adenine (DNA and RNA) Cystosine (DNA and
RNA) Guanine(DNA and RNA) Thymine (DNA
only) Uracil (RNA only)
Step 1 Area of DNA need to copy opens up
(helicase) Step 2 RNA nucleotides floating
in the nucleoplasm float in and pair up with the
complementary base on the DNA strand to make a
single-stranded mRNA (RNA polymerase) Step 3
The newly made mRNA strand leave the nucleus
through a pore and enters the cytoplasm
RNApolymerase
DNA
RNA
Note after the mRNA is made, the DNA molecule
will reform and retwist (DNA polymerase and
gyrase)
Go to Section
7
Translation
- Step 1
- The mRNA strand travels to a ribosome rRNA
anchors the mRNA strand in position on the small
part of the ribosome a ribosome cap locks the
strand in place - Step 2
- The mRNA strand begins to feed through the
ribosome as codons reach the decoding sites,
anticodons on tRNA molecules pair up with the
mRNA strand and deliver the appropriate amino
acid - Step 3
- When 2 codons are occupying the decoding sites, a
covalent bond called a PEPTIDE BOND is formed
between the amino acids being delivered - Step 4
- After the amino acids are bonded, the ribosome
moves down one decoding site to allow the next
codon to be read again, the complementary tRNA
delivers the amino acid, a bond forms, and the
process repeats
8
Translation
Section 12-3
Nucleus
Messenger RNA Messenger RNA is transcribed in
the nucleus.
mRNA
Lysine
Phenylalanine
tRNA
Transfer RNA The mRNA then enters the cytoplasm
and attaches to a ribosome. Translation begins at
AUG, the start codon. Each transfer RNA has an
anticodon whose bases are complementary to a
codon on the mRNA strand. The ribosome positions
the start codon to attract its anticodon, which
is part of the tRNA that binds methionine. The
ribosome also binds the next codon and its
anticodon.
Methionine
Ribosome
Start codon
mRNA
Go to Section
9
Translation (continued)
Section 12-3
Growing polypeptide chain
Ribosome
tRNA
Lysine
tRNA
mRNA
mRNA
Translation direction
Ribosome
Go to Section
10
Start and Stop Codons
- NOTE
- A start amino acid is found at the beginning of
most proteins methionine. The codon for this
is AUG. - A stop codon DOES NOT CODE FOR ANY AMINO ACID
it is the signal that the protein is complete and
can be released
11
Figure 17.4 The dictionary of the genetic code
12
The Genetic Code
Section 12-3
Go to Section
13
Working with the Code use the box from your
textbook
- Given TACGGGCCCCAAACT
- a. what is the mRNA made?
- b. what is the tRNA needed for translation?
- c. what is the protein made?
- (amino acid chain)
- 2. Given TACGCACATAATACT
- do a, b, and c as above
14
So, what is a gene?
- Functional definition a DNA sequence coding for
a specific polypeptide chain