India and Pakistan - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 33
Title:
India and Pakistan
Description:
'A moment comes, which comes but rarely in history, when we step out from the old ... The Karakoram Range of Central Asia, one of the highest mountain systems in the ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:13070
Avg rating:5.0/5.0
Title: India and Pakistan
1
India and Pakistan
2
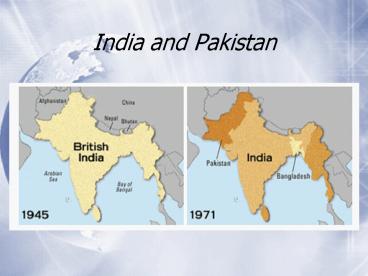
The Partition of India
- "A moment comes, which comes but rarely in
history, when we step out from the old to the
new, when an age ends, and when the soul of a
nation, long suppressed, finds utterance." - -Jawarhalal Nehru
3
- August 14th, 1947, saw the birth of the new
Islamic Republic of Pakistan. At midnight the
next day India won its freedom from colonial
rule, ending nearly 350 years of British presence
in India. - The British left India divided in two. The two
countries were founded on the basis of religion,
with Pakistan as an Islamic state and India as a
secular one.
4
History India and Pakistan
- India and Pakistan have a long and complicated
history with each other. - These two countries were supposed to be divided
into two parts. Subject to the local leaders
approval each area consisting of 75 or more
Muslims were to become Pakistan and the rest of
the territory India. - One region hesitated to declare their choice.
5
Kashmir
- After the Prince in this region hesitated to
chose Pakistan attacked hoping to force the
Prince into submission, instead he turned to
India for help - Today approximately 1/3 of Kashmir went to
Pakistan while the remaining 2/3 became apart of
India - Pakistan was left with territory that was thinly
populated, relatively inaccessible, and
economically underdeveloped. - The largest Muslim group lay in
Indian-administered territory and joined India
6
Why are India and Pakistan in conflict today?
Despite Kashmir being 77 Muslim their Prince
hesitated to join Pakistan. This disputed
territory has remained an issue for these two
countries for over 50 years.
7
What is India Today?
- On one hand, India is the world's biggest
democracy, almost 970 million people representing
a myriad religions and ethnicities. - Home to a burgeoning middle-class estimated at
250 million, nearly equal to the entire
population of the United States. - India's military strength is impressive and its
space program is unparalleled in the developing
world. - On the other hand, India remains one of the
world's poorest nations. Half of its people are
illiterate. Disease continues to take a toll. An
ever-growing population threatens to overwhelm
progress.
8
What is Pakistan Today?
- Muhammad Ali Jinnah dreamed of an egalitarian
state. Jinnah led India's Muslims out of
colonialism to independence from both Britain and
its cultural sibling India. - Jinnah had a vision of a Pakistan built on
"character, courage, integrity and perseverance."
- But with his death in 1948 barely 13 months
after the creation of Pakistan the
confederation of competing Muslim interests was
left leaderless.
9
Background Information Pakistan 1
- Government Islamic Republic
- President Pervez Musharraf
10
Pakistan 2
- Population 167,762,040
- Life Expectancy
- Male 63.07 years
- Female 65.24 years
- Religion
- Muslim 97 (Sunni 77, Shi'a 20)
- Other (includes Christian and Hindu) 3
11
Side Note
The star and crescent is a well-known symbol of
Islam. It features prominently on the flags of
many countries in the Islamic world, notably
Turkey and Pakistan. The crescent and star are
often said to be Islamic symbols, but historians
say that they were the insignia of the Ottoman
Empire, not of Islam as a whole. The Ottoman
Turks used the crescent moon and star symbol on
their flag. It has since become associated with
Islam. Islam has few traditional symbols. The
crescent moon and star are not ones that are
recognized as traditional symbols by Muslims.
12
Pakistan 3
- Land Use
- Arable land 24.44
- Permanent crops 0.84
- Other 74.72 (2005)
- Climate
- mostly hot, dry desert temperate in northwest
arctic in north
Pakistan Farm
The Karakoram Range of Central Asia, one of the
highest mountain systems in the world, extends
into northern Pakistan.
13
Pakistan 4
14
Background Information India
- Government Democracy
- President Pratibha Patil
15
India 2
- Population
- 1,147,995,898
- Life Expectancy
- male 66.87 years
- female 71.9 years
- Religion
- Hindu 80.5
- Muslim 13.4
- Christian 2.3, Sikh 1.9, other 1.8,
unspecified 0.1
16
India 3
17
Islam 1
The word Islam means 'submission to the will of
God'. Islam is the second largest religion in
the world with over 1 billion followers. There
are several different groups of Muslims, but all
of them, in every country and community, regard
their faith as a bond between them, and as a
major part of their identity.
18
Islam 2
- Islam was revealed over 1400 years ago in Mecca,
Arabia. - Followers of Islam are called Muslims.
- Muslims believe that there is only One God.
- The Arabic word for God is Allah.
- According to Muslims, God sent a number of
prophets to mankind to teach them how to live
according to His law. Jesus, Moses and Abraham
are respected as prophets of God. - They believe that the final Prophet was Muhammad
- Muslims believe that Islam has always existed,
but for practical purposes, date their religion
from the time of the migration of Muhammad. - Muslims base their laws on their holy book the
Qur'an, and the Sunnah. - The Sunnah is the practical example of Prophet
Muhammad. - There are five basic Pillars of Islam
- 1. declaration of faith,
- 2. praying five times a day
- 3. giving money to charity
- 4. fasting
- 5. a once in a lifetime pilgrimage to Mecca.
19
Islam 3
Muslims have six main beliefs. 1 Belief in
Allah as the one and only God 2 Belief in
angels 3 Belief in the holy books 4
Belief in the Prophets... o e.g. Adam,
Ibrahim (Abraham), Musa (Moses), Dawud (David),
Isa (Jesus). o Muhammad (peace be upon
him) is the final prophet. 5 Belief in the
Day of Judgement... o The day when the
life of every human being will be assessed to
decide whether they go to heaven or hell. 6
Belief in Predestination... o That
Allah has already decided what will happen.
o Muslims believe that this doesn't stop
human beings making free choices.
20
Understanding a Commonly Misunderstood
IssueSunni and Shia
Often when you read stories about the Muslim
world you will see these two words but few people
know what they mean. If you want to understand
the Muslim world it is important you understand
the difference between these two terms.
21
Sunni and Shia 2
The division between Sunnis and the Shia is the
largest and the oldest in the history of Islam.
When the Prophet Muhammad died in the early 7th
century the question of who should succeed him
left an Islamic state in the Arabian Peninsula
divided. The larger group elected Abu Bakr as the
next caliph (leader) A smaller group believed
that Muhammads son-in-law Ali should become the
caliph
22
Sunni and Shia 3
The Sunnis believed that because Abu Bakr lead
the congregational prayers as Muhammad lay on his
deathbed that this meant he should succeed
Muhammad
The Shias take the evidence that Muhammad stood
up in front of hundreds of his companions on his
way back from Hajj and proclaimed that his family
would never be led astray and other reports that
claim Muhammad took Alis hand and said that his
supporters should follow Ali to mean Ali was the
true successor to Muhammad
Both believe that Muhammad was the final
prophet
23
Sunni and Shia 4
Ali delayed pledging his loyalty to Abu Bakr.
After a few months, however, Ali pledged
allegiance to Abu. Over the next 2 decades 2 men
succeeded as the 2nd and 3rd caliphs. The 3rd
caliph, Uthman, was murdered and Ali was elected
as the 4th caliph. Aisha, wife of the Prophet
Muhammad, was upset with Ali because she believed
that Ali was lax in bringing Uthmans killers to
justice and Aisha opposed Alis appointment as
caliph. This lead to the Battle of the Camel in
656. Aisha was defeated, despite the defeat and
Aishas later apology to Ali, this clash
strengthened any opposition to Alis rule.
24
Sunni and Shia 5
Sunni means one who follows the Sunna Sunna
what the Prophet said, did, agreed to or condemned
Shia is a contraction of the phrase Shiat Ali
meaning the partisans of Ali (partisan
supporter of a person, group, party)
Remarkably Muhammad had predicted the very
outcome that occurred where hereditary and not
elections determined the future caliphs the
caliphate will remain in my nation after me for
thirty years. Then, it will be a monarchy after
that.
25
Sunni and Shia 6
Differences Initially the difference was merely
who should lead the Muslim community. The Hadith
(the traditional account of things said or done
by Muhammad or his companions) is interpreted
differently. Sunni Muslims tend to follow the
opinion of the 1st and 2nd Century scholars
Hanbali, Hanafi, Maliki, and Shaafii The Shia
believe only a living scholar must be
followed Sunni Muslims pray 5 times a day Shia
Muslims can combine prayers to pray 3 times a day
26
Hinduism 1
Hinduism is based on the concept that human and
animal spirits reincarnate, or come back to earth
to live many times in different forms. Souls move
up and down an infinite hierarchy depending on
the behaviors they practiced in their life For
certain Hindus charity towards others is unheard
of because each individual deserves to be in the
social class they were born in. A person is born
into the highest class because they behaved well
in a past life, and a person is born into poverty
and shame because of misbehaviors in a past
life. Central to Hinduism are the concepts of
reincarnation, the caste system, merging with
brahman (or the ultimate reality), finding
morality, and reaching Moksha (the peaceful
escape from the cycle of reincarnation).
27
Hinduism 2
- The triumvirate consists of three gods who are
responsible for the creation, upkeep and
destruction of the world. - Brahma is the creator of the universe and Shiva
is the destroyer. Vishnu is the preserver and
protector of the universe.
28
Hinduism Brahma
- Brahma's job was to create the world and all
creatures. - Brahma is the least worshipped god in Hinduism
today. There are only two temples in India
devoted to him, compared with the many thousands
devoted to the other two. - What does Brahma look like?
- Brahma has four heads and it is believed that
from these heads came the four Vedas (the most
ancient religious texts for Hindus). Some also
believe that the caste system, or four varnas,
came from different part of Brahma's body.
29
Hinduism Vishnu
- His role is to return to the earth in troubled
times and restore the balance of good and evil. - Vishnu's worshippers, usually called Vaishnava,
consider him the greatest god. - What does Vishnu look like?
- Vishnu is represented with a human body, often
with blue colored skin and with four arms. His
hands always carry four objects in them,
representing the things he is responsible for.
The objects symbolize many more meanings than is
presented here - The conch the sound this produces 'Om',
represents the primeval sound of creation - The chakra, or discus symbolizes the mind
- The lotus flower an example of glorious
existence and liberation - The mace represents mental and physical strength
- Vishnu is usually represented in two positions.
- Standing upright on a lotus flower with Lakshmi,
his consort, close by him - Reclining on the coils of a serpent, with Lakshmi
massaging his feet. They are surrounded by the
Milky Ocean.
30
Hinduism Shiva
- Hindus believe Shivas powers of destruction and
recreation are used to destroy the illusions and
imperfections of this world, paving the way for
beneficial change. - According to Hindu belief, this destruction is
not arbitrary, but constructive. Shiva is
therefore seen as the source of both good and
evil and is regarded as the one who combines many
contradictory elements. - Shiva's relationship with his wife, Parvati,
brings him balance. - Hindus who worship Shiva as their primary god are
members of the Shaivism sect. - Lord of the dance
- Dance is an important art form in India, and
Shiva is believed to be the master of it. He is
often called the Lord of Dance. The rhythm of
dance is a metaphor for the balance in the
universe which Shiva is believed to hold so
masterfully.
31
Hinduism Shiva
- What does Shiva look like?
- In his representations as a man, Shiva always has
a blue face and throat. Strictly speaking his
body is white, but images often show him with a
blue body too. Shiva is sometimes represented as
half man, half woman. - Shiva is represented with the following features
- A third eye
- The extra eye represents the wisdom and insight
that Shiva has. - A cobra necklace
- This signifies Shiva's power over the most
dangerous creatures in the world.. - The vibhuti
- The vibhuti are three lines drawn horizontally
across the forehead in white ash. They represent
Shiva's all pervading nature, his superhuman
power and wealth. Also, they cover up his
powerful third eye. Members of Shaivism often
draw vibhuti lines across their forehead. - The trident
- The three pronged trident represents the three
functions of the Hindu triumvirate.
32
Additional CommentsPossible Nuclear War?
- Three wars have occurred between Pakistan and
India involving the Kashmir region since 1947. - Kashmir remains the site of the world's largest
and most militarized territorial dispute with
portions under the de facto administration of
China (Aksai Chin), India (Jammu and Kashmir),
and Pakistan (Azad Kashmir and Northern Areas) - New York Times Article
33
Additional CommentsGandhi
- Gandhi was a leader during the revolution in
India for independence. - He sought an independent India, yet, did not
believe their was a need for a separate India and
Pakistan. - Gandhi practiced non-violence
- Gandhi used religious rhetoric (language),
orchestrated large marches, other displays of
disobedience, fasting (hunger strikes) - Gandhi believed India needed to become
self-sufficient (he sewed his own cothes) - Gandhi inspired many future leaders (Martin
Luther King Jr. in particular)