References - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 1
Title:
References
Description:
Cystic Fibrosis isolates. Soleimanian S 1, Bean DC 2, Genberg C 3 , Savage PB 4, ... Cystic fibrosis (CF) is the commonest autosomal recessive disorder amongst ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:90
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: References
1
In-vitro Activity of the Novel
Ceragenin CSA 13 vs UK Pseudomonas aeruginosa
Cystic Fibrosis isolatesSoleimanian S 1, Bean
DC 2, Genberg C 3 , Savage PB 4, Wareham DW
1,21 2Centre for Infectious Disease, Institute
of Cell and Molecular Science, Barts and The
London, Queen Marys School of Medicine and
Dentistry, London, UK 2Department of Medical
Microbiology, Barts and The London NHS Trust,
London, UK 3 Ceragenix, Denver, CO, USA 4Brigham
Young University, Provo, UT
F1-1656
d.w.wareham_at_qmul.ac.uk
Abstract
Methods
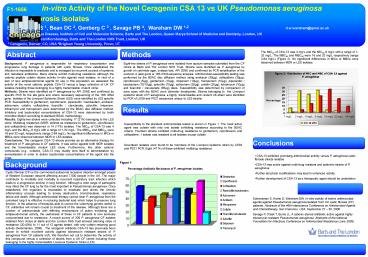
The MIC50 of CSA-13 was 4 mg/L and the MIC90 8
mg/L with a range of 1-32 mg/L. The MBC50 and
MBC90 were 16 and 32 mg/L respectively (range
2-64 mg/L) (Figure 2). No significant differences
in MICs or MBCs were observed between MDR or LES
isolates.
Background P. aeruginosa is responsible for
respiratory exacerbation and progressive lung
damage in patients with cystic fibrosis. Once
established the infection is impossible to
eradicate and is managed by recurrent courses of
systemic and nebulised antibiotics. Many strains
exhibit multi-drug resistance although the
cationic peptide colistin retains activity
in-vitro against most isolates. In view of a lack
of new antipseudomonal agents for use in this
population we assessed the activity of the novel
cationic peptide CSA-13 versus a large collection
of UK CF isolates including those belonging to a
highly transmissible virulent clone. Methods
Strains were identified as P. aeruginosa by API
20NE and confirmed by specific PCR for the eta
gene and where necessary sequencing of the 16S
rDNA gene. Isolates of the Liverpool Epidemic
Strain (LES) were identified by LES specific PCR.
Susceptibility to gentamicin, ciprofloxacin,
piperacillin / tazobactam, amikacin, aztreonam,
colistin, ceftazidime, ticarcillin / clavulanate,
azlocillin, imipenem, tobramycin and meropenem
were determined by the BSAC disc diffusion
method. Inhibitory and bactericidal
concentrations of CSA-13 were determined by broth
microtitre dilution according to standard BSAC
methodology. Results Eighty-two strains were
collected including 17 (21) belonging to the LES
clone. Multidrug resistance (MDR defined as
resistance to gentamicin, ciprofloxacin and
ceftazidime) was observed in 14 (17) isolates.
The MIC50 of CSA-13 was 4 mg/L and the MIC90 8
mg/L with a range of 1-32 mg/L. The MBC50 and
MBC90 were 16 and 32 mg/L respectively (range
2-64 mg/L). No significant differences in MICs or
MBCs were observed between MDR or LES
isolates. Conclusions The ceragenin CSA-13 shows
promise as an alternative therapy for treatment
of P. aeruginosa in CF patients. It was active
against both MDR isolates and the transmissible
virulent LES clone. Furthermore, like other
cationic compounds (e.g., colisitin), CSA-13 may
readily lend itself to administration by
aerosolisation in order to deliver bactericidal
concentrations of the agent into the lungs.
Eight-two strains of P. aeruginosa were isolated
from sputum samples submitted from the CF clinics
at Barts and The London NHS Trust. Strains were
identified as P. aeruginosa by growth on
cetrimide agar, oxidase test, API 20NE and
confirmed by PCR amplification of the exotoxin A
(eta) gene or 16S rDNA sequence analysis.
Antimicrobial susceptibility testing was
performed by the BSAC disc diffusion method using
amikacin (30µg), ceftazidime (30µg),
ciprofloxacin (5µg), gentamicin (10µg), imipenem
(10µg), meropenem (10µg), piperacillin /
tazobactam (75/10µg), azlocillin (75µg),
aztreonam (30µg), colistin (25µg), tobramycin
(10µg) and ticarcillin / clavulanate (85µg)
discs. Susceptibility was determined by
comparison of zone sizes with the BSAC zone
diameter breakpoints. Strains belonging to the
Liverpool epidemic strain of P. aeruginosa, a
highly transmissible and virulent UK strain were
identified by PCR of LES9 and PS21 sequences
unique to LES strains.
Results
1 mg/L
2 mg/L
4 mg/L
8 mg/L
16 mg/L
32 mg/L
64 mg/L
Susceptibility to the standard antimicrobials
tested is shown in Figure 1. The most active
agent was colistin with only one isolate
exhibiting resistance according to the BSAC
criteria. Fourteen strains exhibted multi-drug
resistance to gentamicin, ciprofloxacin and
ceftazidime, 1 isolate was resistant to all
isolates except colistin. Seventeen isolates
were found to be members of the Liverpool
epidemic strain by LES9 and PS21 PCR. Eight (47
) of these exhibited multidrug resistance
- CSA-13 exhibited promising antimicrobial
activity versus P. aeruginosa cystic fibrosis
clinical isolates - CSA-13 was active against multi-drug resistant
and epidemic strains of P. aeruginosa - Further structural modifications may lead to
enhanced activity - Further development of CSA-13 as a therapeutic
agent should be undertaken
Background
Figure 1
Cystic fibrosis (CF) is the commonest autosomal
recessive disorder amongst people of Western
European descent affecting around 7,500 people in
the UK. The major contributor to morbidity and
mortality is recurrent respiratory tract
infection which leads to a progressive decline in
lung function. Although a wide range of pathogens
may infect the CF lung by far the most important
is Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Once established, the
organism is impossible to eradicate and drives
the chronic inflammatory process leading to
airway destruction, bronchiectasis, respiratory
failure and death. Although antimicrobial therapy
cannot clear P. aeruginosa from the colonised
lung it is effective in reducing bacterial load
which helps to preserve lung function. In the
absence of therapies able to correct the
underlying genetic defect in CF, antibiotics will
remain crucial to treatment of the disease.
Although there are a number of antimicrobials
with differing mechanisms of action exhibiting
good antipseudomonal activity, the usefulness of
these in CF patients is now seriously compromised
due to resistance. A recent survey of 326 P.
aeruginosa CF isolates obtained from clinics at
Barts and the London NHS trust showed alarming
rates of resistance (20-40) to 11 out of 12
agents tested, with only colistin retaining good
activity (Soleimanian, 2006). The ceragenin
antibiotic CSA-13 has previously been shown to
exhibit excellent activity against tobramycin
resistant strains of P. aeruginosa from CF
patients (ref). We therefore set out to determine
the activity of this compound versus a collection
of strains from a UK CF centre including those
belonging to the highly transmissible Liverpool
Epidemic Strain (LES)
References
Soleimanian S, Krahe D, Wareham DW. In-vitro
activity of twelve antimicrobial agents against
Pseudomonas aeruginosa isolated from UK cystic
fibrosis (CF) patients. Abstracts of the 46th
Interscience Conference on Antimicrobial Agents
and Chemotherapy. San Francisco, USA. September
27 30, 2006 Savage P, Orsak T, Burns JL. A
cationic steroid antibiotic active against highly
tobramycin-resistant Pseusomonas aeruginosa.
Abstracts of the National Foundation for
Infectious Conference on Antimicrobial Resistance
(June 2005)