World War One: Casualties - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 20
Title:
World War One: Casualties
Description:
I. Open covenants of peace, openly arrived at, after which there shall be no ... The Turkish portion of the present Ottoman Empire should be assured a secure ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:44
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: World War One: Casualties
1
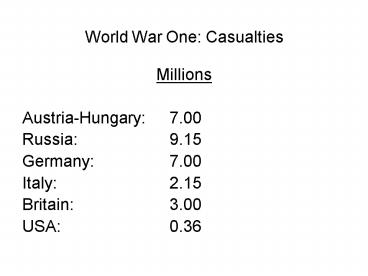
World War One Casualties
- Millions
- Austria-Hungary 7.00
- Russia 9.15
- Germany 7.00
- Italy 2.15
- Britain 3.00
- USA 0.36
2
Woodrow WilsonFourteen Points
3
The 14 Points January 8, 1918
- I. Open covenants of peace, openly arrived at,
after which there shall be no private
international understandings of any kind but
diplomacy shall proceed always frankly and in the
public view. - II. Absolute freedom of navigation upon the seas,
outside territorial waters, alike in peace and in
war. - III. The removal, so far as possible, of all
economic barriers and the establishment of an
equality of trade conditions among all the
nations consenting to the peace and associating
themselves for its maintenance. - IV. Adequate guarantees given and taken that
national armaments will be reduced to the lowest
point consistent with domestic safety. - V. A free, open-minded, and absolutely impartial
adjustment of all colonial claims, based upon a
strict observance of the principle that in
determining all such questions of sovereignty the
interests of the populations concerned must have
equal weight with the equitable claims of the
government whose title is to be determined. - VI. The evacuation of all Russian territory and
such a settlement of all questions affecting
Russia as will secure the best and freest
cooperation of the other nations of the world in
obtaining for her an unhampered and unembarrassed
opportunity for the independent determination of
her own political development and national policy
and assure her of a sincere welcome into the
society of free nations under institutions of her
own choosing..
4
The 14 Points
- VII. Belgium, the whole world will agree, must be
evacuated and restored, without any attempt to
limit the sovereignty which she enjoys in common
with all other free nations - VIII. All French territory should be freed and
the invaded portions restored, and the wrong done
to France by Prussia in 1871 in the matter of
Alsace-Lorraine, which has unsettled the peace of
the world for nearly fifty years, should be
righted, in order that peace may once more be
made secure in the interest of all. - IX. A readjustment of the frontiers of Italy
should be effected along clearly recognizable
lines of nationality. - X. The peoples of Austria-Hungary, whose place
among the nations we wish to see safeguarded and
assured, should be accorded the freest
opportunity to autonomous development. - XI. Rumania, Serbia, and Montenegro should be
evacuated occupied territories restored Serbia
accorded free and secure access to the sea. - XII. The Turkish portion of the present Ottoman
Empire should be assured a secure sovereignty,
but the other nationalities which are now under
Turkish rule should be assured an undoubted
security of life and an absolutely unmolested
opportunity of autonomous development. - XIII. An independent Polish state should be
erected which should include the territories
inhabited by indisputably Polish populations,
which should be assured a free and secure access
to the sea, and whose political and economic
independence and territorial integrity should be
guaranteed by international covenant. - XIV. A general association of nations must be
formed under specific covenants for the purpose
of affording mutual guarantees of political
independence and territorial integrity to great
and small states alike.
5
The Peace Settlement 1919The Big Four in Paris
6
Tiger ClemenceauThe Welsh WizardDavid Lloyd
George
7
Germanys Losses
8
German Reaction to Peace Terms
- Leader of the German Peace Delegation Count von
Brockdorff-Rantzau's Letter to Paris Peace
Conference President Georges Clemenceau on the
Subject of Peace Terms, May 1919 - Mr. President
- I have the honour to transmit to you herewith the
observations of the German delegation on the
draft treaty of peace. - We came to Versailles in the expectation of
receiving a peace proposal based on the agreed
principles. We were firmly resolved to do
everything in our power with a view of fulfilling
the grave obligations which we had undertaken.
We hoped for the peace of justice which had been
promised to us. - We were aghast when we read in documents the
demands made upon us, the victorious violence of
our enemies. The more deeply we penetrate into
the spirit of this treaty, the more convinced we
become of the impossibility of carrying it out.
The exactions of this treaty are more than the
German people can bear. - With a view to the re-establishment of the Polish
State we must renounce indisputably German
territory - nearly the whole of the Province of
West Prussia, which is preponderantly German of
Pomerania Danzig, which is German to the core
we must let that ancient Hanse town be
transformed into a free State under Polish
suzerainty..
9
German Reaction
- . We must agree that East Prussia shall be
amputated from the body of the State, condemned
to a lingering death, and robbed of its northern
portion, including Memel, which is purely German. - We must renounce Upper Silesia for the benefit of
Poland and Czecho-Slovakia, although it has been
in close political connection with Germany for
more than 750 years, is instinct with German
life, and forms the very foundation of industrial
life throughout East Germany. - Preponderantly German circles (Kreise) must be
ceded to Belgium, without sufficient guarantees
that the plebiscite, which is only to take place
afterward, will be independent. The purely
German district of the Saar must be detached from
our empire, and the way must be paved for its
subsequent annexation to France, although we owe
her debts in coal only, not in men. - For fifteen years Rhenish territory must be
occupied, and after those fifteen years the
Allies have power to refuse the restoration of
the country in the interval the Allies can take
every measure to sever the economic and moral
links with the mother country, and finally to
misrepresent the wishes of the indigenous
population. - Although the exaction of the cost of the war has
been expressly renounced, yet Germany, thus cut
in pieces and weakened, must declare herself
ready in principle to bear all the war expenses
of her enemies, which would exceed many times
over the total amount of German State and private
assets.
10
The Economic Consequences of the Peace
- If the European Civil war is to end with France
and Italy abusing their momentary victorious
power to destroy Germany and Austria-Hungary now
prostrate, they invite their own destruction
also, being so deeply and inextricably
intertwined with their victims by hidden psychic
and economic bonds. (p. 3) - J.M. Keynes (1920)
11
Nazi PropagandaThe territories weve lost
thanks to Versailles
12
The End of Austria-Hungary
13
New Leaders Masaryk and Paderewski
14
Meanwhile in RussiaFrom Tsarism to Kerensky
15
From Kerensky to Lenin.to Bela Kun
16
Josef Pilsudski and Poland
17
Greece and TurkeyVenizelos and Ataturk
18
The Middle East in 1920
19
The League of Nations
20
The Locarno Pact 1925Aristide Briand Gustav
Stresemann