Paediatric Guidelines for the Management of Acute and Post-operative Pain. - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 2
Title:
Paediatric Guidelines for the Management of Acute and Post-operative Pain.
Description:
Title: Paediatric Guidelines for the management of acute and post-operative pain. Author: IT Department Last modified by: RussellSu Created Date – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:58
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Paediatric Guidelines for the Management of Acute and Post-operative Pain.
1
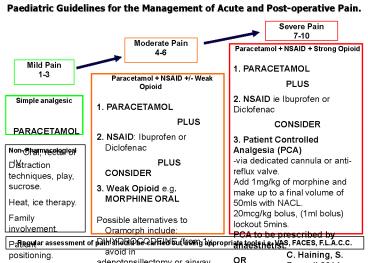
Paediatric Guidelines for the Management of Acute
and Post-operative Pain.
Severe Pain 7-10
Moderate Pain 4-6
Paracetamol NSAID Strong Opioid 1.
PARACETAMOL PLUS 2. NSAID ie Ibuprofen or
Diclofenac CONSIDER 3. Patient Controlled
Analgesia (PCA) -via dedicated cannula or
anti-reflux valve. Add 1mg/kg of morphine and
make up to a final volume of 50mls with
NACL. 20mcg/kg bolus, (1ml bolus) lockout
5mins. PCA to be prescribed by anaesthetist. OR
3. IV Morphine bolus Add 1ml of 10mg/ml morphine
ampoule to 9mls NaCl 0.9. 0-1month
25microgram/kg 1-3months 50microgram/kg gt3months
100microgram/kg Monitor Respiratory rate and
SPO2 for all children receiving IV morphine bolus
or PCA.
Mild Pain 1-3
Paracetamol NSAID /- Weak
Opioid 1. PARACETAMOL
PLUS 2. NSAID
Ibuprofen or Diclofenac
PLUS CONSIDER 3. Weak Opioid e.g. MORPHINE
ORAL Possible alternatives to Oramorph
include DIHYDROCODEINE (from 1y, avoid in
adenotonsillectomy or airway surgery) OR
gt12years CODEINE (Contraindicated in children
lt18years old with obstructive sleep apnoea
undergoing ENT surgery) OR gt12y TRAMADOL
- Simple analgesic
- PARACETAMOL
- Oral, rectal or IV
Non- Pharmacological Distraction techniques,
play, sucrose. Heat, ice therapy. Family
involvement. Patient positioning. Splinting of
fractures.
Regular assessment of pain should be carried out
using appropriate tools i.e. VAS, FACES,
F.L.A.C.C.
C. Haining, S. Russell 2014
2
Paediatric Dosage Guidelines for the Management
of Acute and Post-operative Pain The doses
below apply to short-term use in otherwise
healthy children. See BNF for cautions.
- Weak Opioid
- MORPHINE ORAL
- 0-1month 80 microgram/kg 4hrly.
- 1-3 months 100 microgram./kg 4hly
- 3-6months 150 microgram/kg 4hly
- 6-12 months 200 microgram/kg 4hly
- gt1year 200-300 microgram/kg 2-4hrly, max per dose
10mg. - 100-200 microgram/kg 2-4hly as substitute for
oral codeine - OR
- DIHYDROCODEINE Oral
- 1-4y 0.5 mg/kg (max 30mg) 4hrly
- gt4y 0.5 1 mg/kg (max 30mg) 4hly
- OR
- gt12years CODEINE Oral 1mg/kg (max 60mg) 4hly
- maximum daily dose 240mg in 24 hrs for maximum
3days
- Simple analgesic
- PARACETAMOL
- Oral or Rectal
- gt3months 15mg/kg 4hrly, routinely up to max four
doses per day. Max 75mg/kg/day (max 4g) - Consider loading dose 20mg/kg oral or 30-40mg/kg
pr - gt12y provided gt50kg 1g four times a day (no
loading dose) - IV CONSULTANT PRESCRIPTION ONLY
- 10-50kg 15mg/kg 4-6hrly
- Max daily dose 60mg/kg i.e. four doses per day.
- gt50kg 1gramme 4-6hrly
- Max daily dose 4grammes. No loading dose IV.
- /- NSAID ibuprofen or diclofenac
- IBUPROFEN Oral
- 1-6months 5mg/kg 6hrly.
C. Haining, S. Russell 2014