cardiac valve stenosis : Symptoms, Types, Causes, Treatment and Diagnosis (1) - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
cardiac valve stenosis : Symptoms, Types, Causes, Treatment and Diagnosis (1)
Description:
All forms of cardiac valve disease are greater not unusual with age, despite the fact that a few may be caused by congenital heart defects. As an example, a sort of malformed aortic valve may be a bicuspid aortic valve. About 1.4 percentage of the population is born with a bicuspid valve abnormality which means that alternatively of having three flaps that open for blood drift, are fused collectively. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:60
Title: cardiac valve stenosis : Symptoms, Types, Causes, Treatment and Diagnosis (1)
1
Cardiac Valve Stenosis
2
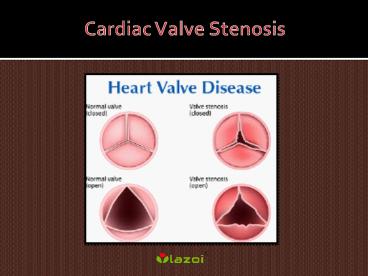
Cardiac Valve Stenosis
- Stenosis is the term for a valve that doesn't
open properly. The flaps of a valve thicken,
stiffen, or fuse together. As a result, the valve
can't completely open. Thus, the heart has to
work harder to pump blood through the valve, and
the body may suffer from a reduced supply of
oxygen.
3
Symptoms
- Symptoms of cardiac valve stenosis
- Aortic stenosis Certain symptoms for aortic
stenosis may include - Chest pain or pressure (angina). Feeling heavy,
tight feeling in the heart. - Feeling dizzy or faint.
- Feeling tired and being short of breath.
- A feeling that heart is pounding, racing, or
beating unevenly (palpitations). - Tricuspid stenosis Certain symptoms may include
- Tired and lethargic
- Fragility
- A quivering feeling in the neck
- A rapid, irregular heartbeat called a
palpitation, or both. - Pain in the upper right part of the abdomen which
may be caused by an enlarged, congested liver.
4
Symptoms
Continue
- Pulmonary stenosis Certain symptoms may include
- Shortness of breath (dyspnea)
- Chest pain (angina)
- Fainting (syncope)
- Cyanosis (blueness)
- Mitral stenosis Certain symptoms may include
- Cough, with or without blood
- Chest pain, or chest discomfort
- Fatigue
- Swelling in ankles and/or feet
- Respiratory infections
- Plum-colored cheeks
5
Types of stenosis may include
- Aortic stenosis Aortic valve stenosis is the
narrowing of the aortic valve. The aortic valve
allows blood to flow from the heart's lower left
chamber (ventricle) into the aorta and to the
body. Stenosis keeps the valve from opening
appropriately, forcing the heart to work harder
to pump blood through the valve. This causes
pressure to build up in the left ventricle and
thickens the heart muscle. - Tricuspid stenosis Tricuspid stenosis is a
narrowing of the tricuspid valve opening.
Tricuspid stenosis confines blood flow between
the upper and lower part of the right side of the
heart, or from the right atrium (higher right
chamber) to the right ventricle (higher left
chamber). - Pulmonary stenosis Pulmonary stenosis is a
condition caused by a narrowing of the pulmonary
valve opening. Pulmonary stenosis restricts blood
flow from the lower right chamber (right
ventricle) to the pulmonary arteries, which
delivers blood to the lungs. - Mitral stenosis Mitral stenosis is a narrowing
of the mitral valve opening. Mitral stenosis
restricts blood flow from the left atrium (lower
right chamber) to the left ventricle (lower left
chamber).
6
Causes of different stenosis
- Aortic stenosis There may be certain causes,
which include - Calcium buildup on the aortic valve. With
increasing age, calcium can build up on the
valve, making it hard and thick. This buildup
happens over time, so symptoms usually don't
appear until after age 65. - A heart defect a person is born with
(congenital). - Rheumatic fever or endocarditis, These infections
can damage the valve. - Tricuspid stenosis This stenosis can be caused
by - It mostly develop due to rheumatic fever in
childhood, which is caused by streptococcus
bacteria - The second rare case may be due to tumour or
connective tissue disease - And there may be person born with a heart defect
(congenital)
7
Causes of different stenosis
Continue
- Pulmonary stenosis Pulmonary stenosis can be
developed due to - It is most commonly result of congenital birth
defect (present from birth). - Certain infections can cause it in adult, which
include rheaumatic fever and carcinoid tumours. - Mitral stenosis There may be some causes which
include - It mostly develop due to rheumatic fever in
childhood, which is caused by streptococcus
bacteria - The other rare cause may involve calcium buildup
in the valve. - Other causes may include tumours, blood clot,
radiation treatment, and congenital heart
diseases.
8
Treatment
- Treatments of cardiac valve stenosis
- Aortic stenosis Treatments may include
- Monitoring In case of mild stenosis, doctors
might advise to have regular heart check-ups, so
if the stenosis becomes severe it can be traced. - Medications No medications can release blockage
in stenosis, but there may be some medicines
which can give relieve to different symptoms such
as fast heart beat, chest pain etc. - Surgery In case of severe stenosis, surgery may
be the final option. Replacement of the aortic
valve may be the option to release a person from
stenosis. - Tricuspid stenosis Treatments may include
- Monitoring In case of mild stenosis, doctors
might advise to have regular heart check-ups, so
if the stenosis becomes severe it can be traced.
9
Treatment
Continue
- Medications No medications can release blockage
in stenosis, but there may be some medicines
which can give relieve to different symptoms such
as fast heart beat, chest pain etc. - Surgery In case of severe stenosis, surgery may
be the final option. Replacement of the damaged
valve with biological or mechanical devices may
be the option to release a person from stenosis. - Pulmonary stenosis Treatments may include
- Monitoring In case of mild stenosis, doctors
might advise to have regular heart check-ups, so
if the stenosis becomes severe it can be traced. - Medications No medications can release blockage
in stenosis, but there may be some medicines
which can give relieve to different symptoms such
as fast heart beat, chest pain etc.
10
Treatment
Continue
- Surgery In case of severe stenosis, surgery may
be the final option. Surgical procedure known as
a valvuloplastycan stretch the pulmonary valve's
walls, enlarging it to improve blood flow. Or in
some cases replacing the pulmonary valve may be
the option to release a person from stenosis. - Mitral stenosis Certain treatments may include
- Monitoring In case of mild stenosis, doctors
might advise to have regular heart check-ups, so
if the stenosis becomes severe it can be traced. - Medications No medications can release blockage
in stenosis, but there may be some medicines
which can give relieve to different symptoms such
as fast heart beat, chest pain etc. - Surgery In case of severe stenosis, surgery may
be the final option. Replacement of the existing
mitral valves with new ones, or repairing the
existing mitral valves may be the option to
release a person from stenosis
11
Diagnosis of cardiac valve stenosis
- Aortic stenosis Certain diagnosis tests may
include - Physical test which may e done to hear a heart
murmur, click or heart sound using stethoscope. - Stress test to follow the heart beat during
exercise. - Echocardiogram, which shows moving pictures of
the heart - Electrocardiogram, which measures the electric
activity of the heart - Left cardiac catheterization, passage of thin
tube in the left side of the heart to diagnose
and treat certain problems. - Transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE), which
produces pictures of the heart. - Tricuspid stenosis Certain diagnose may include
- Physical test which may e done to hear a heart
murmur, click or heart sound using stethoscope. - Stress test to follow the heart beat during
exercise.
12
Diagnosis of cardiac valve stenosis
Continue
- Echocardiogram, which shows moving pictures of
the heart - Electrocardiogram, which measures the electric
activity of the heart - Cardiac catheterization, passage of thin tube
inside the heart to diagnose and treat certain
problems. - Transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE), which
produces pictures of the heart - Pulmonary stenosis Certain diagnose may include
- Physical test which may e done to hear a heart
murmur, click or heart sound using stethoscope. - Stress test to follow the heart beat during
exercise. - Chest X-ray
- Echocardiogram, which shows moving pictures of
the heart - Cardiac catheterization, passage of thin tube
inside the heart to diagnose and treat certain
problems.
13
Diagnosis of cardiac valve stenosis
Continue
- Transesophageal echocardiogram (TEE), which
produces pictures of the heart - Mitral stenosis Certain diagnose test may
include - Physical test which may e done to hear a heart
murmur, click or heart sound using stethoscope. - Stress test to follow the heart beat during
exercise. - Echocardiogram, which shows moving pictures of
the heart - Electrocardiogram, which measures the electric
activity of the heart - Cardiac catheterization, passage of thin tube
inside the heart to diagnose and treat certain
problems.
14
CONNECT WITH US
- Logon to
- www.lazoi.com
- Like us on Facebook
- https//www.facebook.com/LazoiTheLife
- Follow us on Twitter
- https//www.twitter.com/lazoithelife
- Follow us on Pinterest
- https//www.in.pinterest.com/lazoithelife