Myelitis : Overview, causes, types, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Myelitis : Overview, causes, types, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
Description:
Myelitis is a spinal disorder. Myelitis is the infection of the white matter of spinal cord. White matter of spinal cord is a part of the central nervous system that functions as a bridge between the brain and the rest of the body. Myelitis can result in muscle weakness or paralyzing legs and then arms. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:345
Title: Myelitis : Overview, causes, types, symptoms, diagnosis and treatment
1
Myelitis
2
Myelitis
- Myelitis may be a painful and complicated
disease, but in can be treated. And from
diagnosis of the disease to treatment motivation
and will power would be the main strength for a
patient. Overview of myelitisMyelitis involves
the infection or the inflammation of the white
matter or gray matter of the spinal cord which is
a part of the central nervous system that acts as
a bridge between the brain and the rest of the
body. - During an inflammatory response in the spinal
cord, the myelin and axon may get damage which
can cause symptoms such as paralysis and sensory
loss. - Myelitis can be divided into certain types
depended on the area of the cause of
inflammation. - Myelitis mainly occurs in narrow region that can
go and spread to other broad regions.
3
Symptoms of myelitis
- The symptoms of early myelitis can be-
- Pain in your lower back
- Weakness or paralysis in your legs or arms
- Sensitivity to touch to the point where slight
fingertip pressure causes pain - Numbness or a pins-and-needles feeling in your
toes, feet, or legs - Problems controlling your bladder or bowels
- Muscle spasms
- Fever
- Loss of appetite
4
Symptoms of myelitis
Continue
- With the coming of symptoms the symptoms can go
worse within some hours. But in most case, the
symptoms hit peaks in 10 days. - Myelitis is most common in younger people within
the age of 10 to 19 and from 30 to 39 are at
higher risk. Like multiple sclerosis, myelitis is
common in women than men.
5
Types of myelitis
- Poliomyelitis-Disease caused by infection in gray
matter which shows symptoms of muscle paralysis
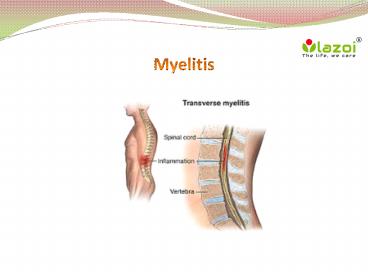
and weakness. - Transverse myelitis-It occurs when both side of
one section of the spinal cord gets damaged. Many
times the covering of the nerve cells, the myelin
gets damaged. - Meningococcal Myelitis (or meningomyelitis)
lesions occurring in the region of meninges and
the spinal cord - Though there are three types of myelitis the most
common myelitis is the transverse myelitis an
doctors, and people often refer to any
inflammatory attack in spinal cord as transverse
myelitis.
6
Causes of myelitis
- The exact reason of myelitis is not known. But
there are certain conditions which can cause
inflammation. They are- - Virus or other infection-Recent infection
in respiratory tract or gastrointestinal
tract can cause myelitis. Mostly myelitis occurs
after infection is over. - Viruses that can infect the spinal cord directly
are herpes viruses, including the one that causes
shingles and chickenpox (zoster), enteroviruses,
and West Nile virus. - Other viruses may trigger an autoimmune reaction
without directly infecting the spinal cord. - Parasites may infect the spinal cord in a rare
condition, and some bacteria such as that of Lyme
disease can cause a painful inflammation in the
nerve roots of the spinal cord. - Multiple sclerosis-It is a disease when the
body's immune system affects the spinal cord
cells. Transverse myelitis can be the first sign
of multiple sclerosis.
7
Causes of myelitis
Continue
- Neuromyelitis optica (Devic's disease) -It is a
condition that causes inflammation and myelin
loss around the spinal cord and the nerve in the
eye. - Transverse myelitis can be associated with
neuromyelitis optica,which can affect both side
of the body and can lead to eye problems even
temporary vision loss. - However people may not have any symptoms of
Neuromyelitis optica, only can show symptoms of
Myelitis. - Autoimmune disease-It can cause myelitis in some
people.As, antibody affection the spinal cord can
sometime lead to transverse myelitis. - Vaccinations -using vaccines for infectious
diseases including hepatitis B,
measles-mumps-rubella and diphtheria-tetanus
vaccines have occasionally been associated as a
possible trigger.
8
Treatments of Myelitis
- Intravenous steroids Steroids are given to
reduce inflammation in the spinal column. - Plasma exchange therapy Patient snot responding
to steroids may be given therapy of plasma
exchange.Here the plasma in bone marrow is
replaced with another fluid. - Antiviral medication. Patients having myelitis
from viral infection can be treated with
medicines against virus. - Therapy against complications
- Pain medication. Chronic pain is a common
complication of transverse myelitis. Medications
that may lessen muscle pain include common pain
relievers, such as acetaminophen (Tylenol,
others), ibuprofen (Advil, Motrin IB, others) and
naproxen sodium (Aleve.) - Nerve pain may be treated with antidepressant
drugs, such as sertraline (Zoloft), and
anticonvulsant drugs, such as gabapentin
(Neurontin, Gralise) or pregabalin (Lyrica).
9
Treatments of Myelitis
Continue
- People who have been diagnosed with antibody
against neuromyelitis optica should undergo
medications for that such as corticosteroids
and/or immunosuppressant, to reduce their chances
of more transverse myelitis attacks or developing
optic neuritis. - Psychotherapy-To deal with anxiety, derpression
and long term complications which may affect the
patient's emotions.
10
Diagnosis of myelitis
- Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) -It uses a
magnetic field and radio waves to create 3-D
images of soft tissues. An MRI can show
inflammation of the spinal cord, and other
potential causes of the symptoms, including
abnormalities affecting the spinal cord or blood
vessels. - Lumbar puncture (spinal tap) -In this technique a
needle is used to draw small amount of
cerebrospinal fluid (CSF), the protective fluid
surrounding the spinal cord and brain. People
with transverse myelitis, show abnormally high
level of white blood cells in CSF or immune
system proteins that indicate inflammation. - Blood tests-Antibody blood tests can be done
which checks for antibodies associated with
neuromyelitis optica.
11
Complications of myelitis
- People with transverse myelitis can experience
complications for further long periods which are - Pain, one of the most common long-term
complications of the disorder. - Stiffness, tightness or painful spasms in the
muscles (muscle spasticity). This is most common
in the hips and legs. - Partial or total paralysis of your arms, legs or
both. This may persist after the first symptoms. - Sexual dysfunction, it can be common complication
for both men and women. - Depression or anxiety, which is common in those
with long-term complications .It is because of
the significant changes in lifestyle, the stress
of chronic pain or disability and the impact of
sexual dysfunction, Overview Diagnosis
12
CONNECT WITH US
- Logon to
- www.lazoi.com
- Like us on Facebook
- https//www.facebook.com/LazoiTheLife
- Follow us on Twitter
- https//www.twitter.com/lazoithelife
- Follow us on Pinterest
- https//www.in.pinterest.com/lazoithelife