Theorem : If two chords intersect inside a circle, the product of the lengths of the segments of one chord equals the product of the lengths of the segments of the other chord. - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 13
Title:
Theorem : If two chords intersect inside a circle, the product of the lengths of the segments of one chord equals the product of the lengths of the segments of the other chord.
Description:
Geometry Segments of Chords and Secants Theorem : If two chords intersect inside a circle, the product of the lengths of the segments of one chord equals the ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:237
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Theorem : If two chords intersect inside a circle, the product of the lengths of the segments of one chord equals the product of the lengths of the segments of the other chord.
1
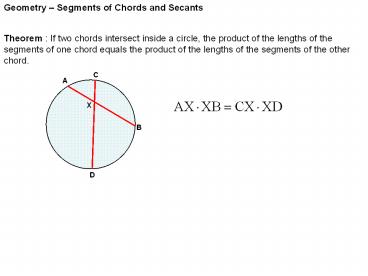
Geometry Segments of Chords and Secants
Theorem If two chords intersect inside a
circle, the product of the lengths of the
segments of one chord equals the product of the
lengths of the segments of the other chord.
C
A
X
B
D
2
Geometry Segments of Chords and Secants
Theorem If two chords intersect inside a
circle, the product of the lengths of the
segments of one chord equals the product of the
lengths of the segments of the other chord.
C
A
2
3
X
6
B
D
EXAMPLE AX 3, XB 6, CX 2. Find XD.
3
Geometry Segments of Chords and Secants
Theorem If two chords intersect inside a
circle, the product of the lengths of the
segments of one chord equals the product of the
lengths of the segments of the other chord.
C
A
2
3
X
6
B
D
EXAMPLE AX 3, XB 6, CX 2. Find XD.
4
Geometry Segments of Chords and Secants
Theorem If two chords intersect inside a
circle, the product of the lengths of the
segments of one chord equals the product of the
lengths of the segments of the other chord.
C
3
A
B
10
X
20
D
EXAMPLE 2 AX 10, XD 20, CX 3. Find XB.
5
Geometry Segments of Chords and Secants
Theorem If two chords intersect inside a
circle, the product of the lengths of the
segments of one chord equals the product of the
lengths of the segments of the other chord.
C
3
A
B
10
X
20
D
EXAMPLE 2 AX 10, XD 20, CX 3. Find XB.
6
Geometry Segments of Chords and Secants
Theorem If two secants form an angle outside a
circle
A
B
X
C
D
7
Geometry Segments of Chords and Secants
Theorem If two secants form an angle outside a
circle
A
9
B
12
X
C
D
24
Example If AB 9, BX 12, DX 24, find CX.
8
Geometry Segments of Chords and Secants
Theorem If two secants form an angle outside a
circle
A
9
B
12
X
C
D
24
Example If AB 9, BX 12, DX 24, find CX.
9
Geometry Segments of Chords and Secants
Theorem If two secants form an angle outside a
circle
A
9
B
12
X
C
D
24
Example If AB 9, BX 12, DX 24, find CX.
10
Geometry Segments of Chords and Secants
Theorem If a secant and a tangent line form an
angle outside a circle
A
B
X
C
11
Geometry Segments of Chords and Secants
Theorem If a secant and a tangent line form an
angle outside a circle
A
12
B
4
X
C
EXAMPLE AB 12, BX 4, find CX.
12
Geometry Segments of Chords and Secants
Theorem If a secant and a tangent line form an
angle outside a circle
A
12
B
4
X
C
EXAMPLE AB 12, BX 4, find CX.
13
Geometry Segments of Chords and Secants
Theorem If a secant and a tangent line form an
angle outside a circle
A
12
B
4
X
C
EXAMPLE AB 12, BX 4, find CX.