Comparison of Resin Types - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 30
Title:
Comparison of Resin Types
Description:
Palladium Catalyst & Scavenger. Slide 3. Polymer-Supported Acids and Bases ... Low palladium level in products ( 100 ppm) Slide 33 ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:1058
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
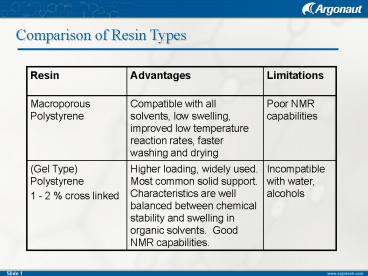
Title: Comparison of Resin Types
1
Comparison of Resin Types
2
Bound Reagent Development Strategy
- Major classes and important reactions
- Acids and Bases
- Scavengers
- Reductive Amination
- Common Reagents for Amide Synthesis
- Oxidizing agents
- Palladium Catalyst Scavenger
3
Polymer-Supported Acids and Bases
4
General Acid Resin MP-TsOH - Example
- Resin-bound toluenesulfonic acid equivalent
- high-loaded 3.5 4.5 mmol/g
- Cation exchange resin
- Macroporous backbone
- Scavenges amines, basic compounds
- Purification via Catch and Release purification
5
Catch and Release Purification
- Sulfonic acid media
- Catch amines/ amine salts - afford product as
free amine - Flow-through process facilitated in cartridges.
Release with NH3/MeOH
Protocol 1. Condition cartridge with THF or
DCM 2. Apply sample solution 3. Wash cartridge
with organic solvent 4. Elute product with 2M NH3
/ MeOH solution
1
2
3
Catch amine
Non basic impurities
4
6
PS-TBD Polymer Supported Base
- Polymer-supported bicyclic guanidine (1,5,7-
triazabicyclo 4.4.0dec-5-ene) - Stronger base than PS-DIEA, PS-NMM - pKa approx.
13 15 - Deprotonates moderately acidic hydrogens
- PS-TBD applications include Alkylation,
esterification and de-halogenation
7
PS-TBD- Resin Bound Base
Catch and Release
8
Polymer-Bound Reagents Schematic
- Remove spent and excess reagent by filtration
- Perform one-pot multi-step reactions
- Mix incompatible functionalities
- Eliminate problems with small molecule reagents
- Toxicity, byproducts difficult to eliminate, odor
9
Argonaut Polymeric Reagents
0020821n.ppt
10
Reductive Amination
- Reductive amination of carbonyl compounds is a
very powerful tool in synthesizing diverse series
of amines - Resin-bound reagents and scavengers simplify
purification of product amine - Excess substrate and reaction byproducts are
removed by filtration - Excellent for lead generation, validation, 25 of
compounds in the drug database are amines or
amine derivatives1 - Borohydride-based reducing agents are most
popular- MP-(OAc)3BH, MP-CNBH3, MP-BH4 (with
PS-DEAM scavenger)
1.Brown, A. R. Rees, D. C. Rankovic, Z.
Morphy, J. R. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1997, 119, 3288.
11
Resins for Reductive Amination
MP-Triacetoxyborohydride
MP-Borohydride
- Macroporous resin
- Inert scaffold for the chemical reagent
- Efficient reagent delivery
- Removed by simple filtration
- Limited swelling
- Ease of use and handling
- Stable to storage
12
Reductive Amination Summary
- MP-BH(OAc)3
- Tolerates acid-sensitive groups ketals, acetals
- Secondary amines isolated as acetate
- Tertiary amines as free base
- MP-BH3CN
- Requires acetic acid
- Similar reactivity and scope
- MP-BH4 /Ti(iOPr)4
- Suppresses over-alkylation with reactive
carbonyls - Enables use of
- sterically hindered carbonyls e.g. adamantyl
ketones - enolizable ketones including acetophenone
- Titanium isopropoxide scavenged by PS-DEAM
13
Bound Coupling Reagents / Amide synthesis
- Polymer-supported reagents for coupling / amide
synthesis - Simplify purification - exploit polymer-bound
intermediates - Combine diverse sets of carboxylic acids with
amines - Excellent for lead generation, validation,
analogue series - PS-DMAP - General Acylation catalyst,
Acylation/Sulfonation via catch and release - PS-Carbodiimide One-step amide synthesis
- Scavenging may be required
- Active ester resins Two-step process
- PS-HOBt (HL), RGT-ACTU/ PS-HOBt (HL)
- Amine used as limiting reagent -gt amides in
high purity - Reactive intermediate can be stored
14
Amide Synthesis PS-Carbodiimide
- Coupling agent
- Bound variant of DCC
- Tether to polystyrene backbone increases
activity - Stable
15
Active Ester Resins
PS-HOBt(HL)
- Two-step synthesis
- Couple acid with the resin to make the bound
active ester - Amine acylation
- Approach
- Both steps in a single reactor, or
- Prepare active ester in bulk and split out
- Synthesize a series of amides from one bound
active ester
16
Synthesis of Amides with PS-HOBt (HL)
- Remove byproducts from active ester preparation
by filtration, solvent washing - Generate pure product with amine as limiting
reagent
17
Amides From PS-HOBt Complex Molecules
Used aminoester hydrochlorides Kulkarni, B.A.
Roth, G.P. Lobkovsky, E. Porco,Jr. J.A. J.
Comb. Chem. 2002, 4, 56.
18
ACTU A New Coupling Agent
ACTU (2-Chloro-1,1,3,3-tetramethyluronium
hexachloroantimonate)
- Precursor to PS-HBTU
- Stable, crystalline solid
- Forms active ester yields in 100 DMF
19
Amide Synthesis with PS-HOBt(HL) and ACTU
- Remove byproducts and DMF from bound active ester
by filtration and solvent washing - Generate pure product with amine as limiting
reagent
20
Racemization Study Comparison
Coupling of (L)cbz-Phenylglycine with (L)-Valine
methyl ester
The reactions were carried out at 0 C in DCMDMF
(91)
Carpino, L.A. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 1993, 115, 4397
21
Amide Synthesis Reagent Comparison
- PS-Carbodiimide - Coupling Agent
- One-step amide synthesis
- Scavenging may be required
- Rearrangement to acylisourea can be problematic
- Active Esters (PS-HOBt)
- Two-step process
- Amine limiting reagent in acylation, affords
high purity amides - Storable reactive intermediate
22
PS-Carbodiimide Coupling vs. Acylurea Formation
- In some cases, acylisourea rearranges to
unreactive acylurea - HOBt additive converts acylisourea to reactive
HOBt ester prior to rearrangement
2 equiv PS-Carbodiimide, 1.5 equiv acid, 1.7
equiv HOBt stirred in DCM 10 min, r.t. Add 1
equiv amine, stir r.t. 16 h. Scavenge HOBt with 5
equiv PS-Trisamine or MP-Carbonate 2h, filter.
23
Oxidizing Agent for Alcohols
- Selective reagent for alcohol oxidation with
simple protocol for product purification - Aldehydes and ketones are versatile building
blocks - Sometimes unstable in storage
- Synthesize reactive carbonyls for use in
multi-step syntheses - Current methods with bound reagents have
drawbacks - Reagents leach toxic heavy metals e.g., chromium,
osmium, lead - Perruthenate resins have low loading
24
Bound Oxidizing Agent MP-TsO-TEMPO
- MP-TsO-TEMPO is a bound oxoammonium sulfonate
- Oxidation of benzylic, allylic, acetylenic and
cyclic secondary alcohols - Stable
- Resin is a mixture of active oxoammonium and
reduced hydroxylammonium species
25
Activation of MP-TsO-TEMPO
- Simple, rapid procedure
- Oxidation of the hydroxylammonium species by
DCDMH - Chlorine-based oxidant removed by washing before
use - Contains only the active oxoammonium species
- Capacity 1.0 mmol/g
26
MP-TsO-TEMPO Oxidation of Activated Alcohols
- Reactions in ACN or DCM
- 2 equiv of MP- TsO-TEMPO at rt
- No liquid liquid extraction or column
chromatography
27
Traditional Chemistry PS-Triphenylphosphine
Mitsunobu Reaction
Wittig Reaction
Scavenging of Alkyl Halides
Chlorination
28
Polymer-Bound Triphenylphosphine-Pd(0)
- Bound Catalyst for Suzuki type Cross- Coupling
Reactions - Simplified product isolation
- Insensitive to air, light and moisture
- Easy Handling
- Shelf-stable at room temperature
- Capacity 0.1 mmol/g
29
PS-TPP-Pd Catalyst for Suzuki Coupling
- 0.5 mol of PS-TPP-Pd used
- Reactions performed under air, no inert
conditions required - Reaction scale 1.0 mmol
- DME EtOH H2O 2 2 1
- Purification Partition water/DCM silica pad
- Products isolated in high purity and yield
- Low palladium level in products (lt 60 ppm)
30
PS-TPP-Pd Suzuki Coupling Data Set
31
Suzuki Coupling Using N-Heterocyclic Halides
- Products isolated in high purity and yield by
MP-TsOH catch and release - Partition with water/DCM prior to catch and
release - Reaction scale 1.0 mmol
32
PS-PPh3-Pd / MP-BH4 Deprotection of N-Alloc
- 2 mol of PS-PPh3-Pd and 3 eq MP-BH4used
- Reactions performed at rt under air, no inert
conditions required - Reaction scale 1.0 mmol
- DCM MeOH H2O 5 4 1
- Isolation Filter through Na2SO4 plug,
concentrate - Products isolated in high purity and yield
- Low palladium level in products (lt 100 ppm)
33
Reductive Deprotection of N-Alloc Scope Studies