Lesson 2: The Human Alimentary Canal - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Lesson 2: The Human Alimentary Canal
Description:
Lesson 2: The Human Alimentary Canal Human Alimentary Canal Mouth Pharynx Esophagus Stomach Small intestine Large intestine Rectum Anus Accessory Organs Salivary ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:837
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Lesson 2: The Human Alimentary Canal
1
Lesson 2 The Human Alimentary Canal
2
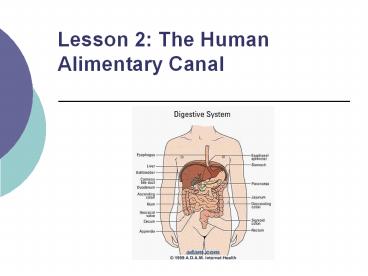
The Human Alimentary Canal
includes the entire tube from the mouth all the
way to the anus
3
Human Alimentary Canal
- Mouth
- Pharynx
- Esophagus
- Stomach
- Small intestine
- Large intestine
- Rectum
- Anus
4
Accessory Organs
Organs that are involved in digestion but that
food does not pass directly through
- Salivary glands
- Secrete saliva
- Liver
- Secretes bile
- Gallbladder
- Stores and concentrates bile
- Pancreas
- Secretes digestive enzymes
5
Types of Digestion
- Physical Digestion
- Food is physically broken down
- Example Teeth chew food
- Chemical Digestion
- Food is broken down by acids, bases or enzymes in
the human alimentary canal - Example HCl in stomach
6
Mouth (Oral Cavity)
- Site of Ingestion
- Salivary Amylase breaks carbohydrates into
simpler sugars
??? What type of digestion takes place in the
mouth? Physical? Chemical?
7
Saliva
- Produced by salivary glands at back of mouth and
under tongue - Saliva includes
- Salivary amylase (enzyme)
- Bicarbonate (buffer)
- Mucins (bind food into bolus)
- Water
8
Salivary Glands
- Accessory Organ found at back of mouth and under
tongue - Releases salivary amylase into the mouth
9
Swallowing
Once chewed, food is called a bolus
- Tongue forces food into pharynx
- Epiglottis closes off the trachea to prevent
choking (breathing temporarily stops) - Bolus moves into oesophagus
10
Pharynx (The throat)
- No physical or chemical digestion occurs here
- Links in with the respiratory system
11
Esophagus
- Function to transport food from mouth to the
stomach - Food considered a BOLUS at this stage
- wet ball of chewed food
How does the bolus get from the mouth to the
stomach?
12
Peristalsis
Peristalsis waves of muscular contraction that
move food along the human alimentary canal
13
Stomach
Discuss the types of digestion occurring in
the stomach
- Muscular sac-like organ
- Lined with a thick protective mucus
- The stomach lining secretes Gastric Juices that
contain - Hydrochloric Acid
- Pepsinogen (inactive form of pepsin)
- Mucus
14
Chemical Digestion in the Stomach
- Pepsinogen is activated by the acid HCl in the
stomach and becomes pepsin - Pepsin chemically digests protein into amino
acids
15
Physical Digestion
- Food is mixed and moved by waves of stomach
contractions (peristalsis) - Becomes Chyme thick liquid made of partially
digested food and stomach juices
16
Small Intestine
- Over 6.5 meters long
- Duodenum
- First 10 cm of small intestine
17
What happens in the small intestine?
- Pancreatic juices neutralise acidic chyme
- Digestion is completed in duodenum
- Liver secretes bile, via gallbladder, which
emulsifies fats - Pancreas secretes various enzymes which complete
the breakdown of protein, carbs and fats - Absorption takes place of digested products into
bloodstream
18
- LIVER
- produces bile which breaks up the larger fats
(emulsification)
- GALLBLADDER
- stores the bile until needed
19
Large Intestine
- Function to absorb water into blood
- Also the site of vitamin K production
- End section rectum anus
20
Stages of Digestion
- Ingestion the process by which food is taken
into the body - Digestion - the process of breaking up complex
substances into simpler substances. - Absorption the process by which digested food
diffuses into blood - Assimilation - the conversion or incorporation of
absorbed simple food into the complex substances
that are useful in our bodies - Egestion - the elimination of undigested food
(faeces) from the body
YOU DECIDE! Look at your diagram of the Digestive
System. Where does each stage of digestion take
place? Hint Some stages take place at multiple
locations
21
Warning Do not confuse Egestion with Excretion
- Egestion removal of undigested food (faeces)
via the anus - Excretion removal of waste products of
metabolism (like urine, carbon dioxide, sweat)
22
(No Transcript)