CHAPTER 2- Physical and Chemical Properties of Hydrocarbons - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 17
Title:
CHAPTER 2- Physical and Chemical Properties of Hydrocarbons
Description:
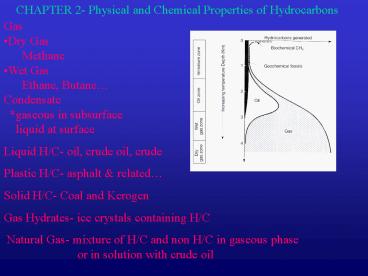
CHAPTER 2- Physical and Chemical Properties of Hydrocarbons Gas Dry Gas Methane Wet Gas Ethane, Butane Condensate *gaseous in subsurface liquid at surface – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:566
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: CHAPTER 2- Physical and Chemical Properties of Hydrocarbons
1
CHAPTER 2- Physical and Chemical Properties of
Hydrocarbons
- Gas
- Dry Gas
- Methane
- Wet Gas
- Ethane, Butane
- Condensate
- gaseous in subsurface
- liquid at surface
- Liquid H/C- oil, crude oil, crude
- Plastic H/C- asphalt related
- Solid H/C- Coal and Kerogen
- Gas Hydrates- ice crystals containing H/C
- Natural Gas- mixture of H/C and non H/C in
gaseous phase - or in solution with crude oil
2
Gases Dissolved- in solution with other liquids
in reservoir Associated- gas cap gas- in gas
phase above liquid Non associated- little or no
crude in reservoir Organic vs inorganic Wet vs
Dry Gas- dry lt0.1 g/mcf Sweet vs Sour- H2S in
sour gas
3
H/C gases- major constituent - H/C paraffin
series CH4 most common, C2, C3, Ethane,
butane (the inferior gas), propane all
common All others uncommon
4
Methane- swamp gas, fire damp- Coal mine
shale gas- drillers term Genesis- mantle b
iogenic gas thermogenic gas 20 of natural gas
produced is Biogenic (methane only)
5
(No Transcript)
6
Inert Gases
He, Ar, Ra He- 5 ppm in atmosphere up to
8 in reservoirs He-rich deposits derived from
U, Th, Ra- i.e. granites and shales-
basement rock Natural production rate from
parent low, expulsion and transport rate
high Panhandle Hugoton Field, gas processing
plant since 1929, contains 1.86 He
7
Nitrogen inorganic- volcanic in
origin organic- degradaton of ammonia and
nitrates shallow diagenesis Fig. 2.2 97 N
2 He 1 CO2 Atmospheric N also Trapped in
connate gas
8
Hydrogen H- rare highly reactive and
mobile 1.36 TCF found in Mississippian Age
sediments in Kansas 40 H, 60 N, CO2, Ar, CH4-
thermogenically mature, never escaped CO2-
Biogenic and Volcanic major constituent of
volcanic gas 3CH4 6O2 3CO2 6H2O CaCO3
H2 Ca H2O CO2- Acids flowing through
limestones
9
H2S Free gas and highly soluble Major concern
when drilling- kills people on rigs in the USA
several times a year Highly corrosive to steel-
sour gas and oil Low H2S- bad, drives production
costs up- have to scrub out High H2S- good,
produce S Volcanic and biogenic origin CaSO4
2CH2O CaCO3 H2O CO2 H2S 2CH2O organic
matter Also associated with carbonates and Pb-Zn
deposits and deep basin brines Anydrite ?
calcite- exothermic- hot enough to mobilize
Pb-Zn sulfide brines
10
Crude Oil Mixture of H/C in a liquid phase which
remains a liquid at the surface Yellow, green,
brown, black Wide variety of viscosities Most
lighter than water Vary in Specific
Gravity Chemistry- C, H, V, Ni, no two oils the
same. Ponca Crude, 234 compounds
11
Hydrocarbons- cont. Paraffins- alkanes-
straight chain carbon with branching n lt 5 gas
at surface 5 lt n 1lt 5 liquid at surface ngt 15
grade into solid wax for given molecular
wt. Straight chain higher boiling point than
isomers Isomers-branching
12
Naphthenes Cyclo alkanes- single bond All
liquids at surface Aromatics Benzene ring
structure Liquid at surface Occurrence Toluenegt
xylenegtbenzene
13
Hetero compounds Organic compounds containing O,
N, S metals, acids, esters, Ketones, phenols,
alcohols In younger oils- fatty acids,
isoprenoids, naphthenic and carboxylic
acids Sulfur also common, both as H2S and other
phases Nearly any ions found in sedimentary
minerals can be found in crude Va N occur as
organometallics generally in porphyrin- derived
from chlorophyll and hemoglobin Metals most
often associated with resins Sulfur and
asphaltene fraction most common in shallow,
younger, degraded crude.
14
Classification of Crude Oil Many classification
schemes engineering based- refineries Physical
properties viscosity boiling pt refractive
index molecular wt density
15
Classification of Crude Oil geochemical based-
maturation, genesis, and history and other
geoparameters of occurrence. Molecular
structure key to source and geological history
16
Classification of Crude Oil
Paraffins, Naphthenic and intermediates based on
distillation factors time and temperature Tissot
and Welte (1978) used ratio between para naph
aromatics Oils vary not only w/ age, but w/
variatin in source and degree of Degradation-
degradatin causes wide variations , esp.
w/shallow oils
17
Gas Hydrates