RNA%20VIRUSES - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
RNA%20VIRUSES
Description:
RNA VIRUSES All are ss (single stranded) ... Arthropods: Mosquitoes, ticks, flies Arboviruses: Toga, Flavi, Bunya, Rabdo, ... Document presentation format: – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:219
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: RNA%20VIRUSES
1
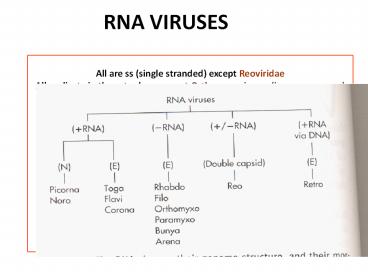
RNA VIRUSES
- All are ss (single stranded) except Reoviridae
- All replicate in the cytoplasm except
Orthomyxoviruses (in some process) -
2
Single-stranded RNA (linear), strand,
nonenvelopedpico small, Icosahedral
- Involving humans
- Enterovirus
- Polioviruses, Coxsackieviruses A, B and
Echovirus (acid- stable) - Rhinovirus (common cold, acid-laible)
- Hepatovirus, Hepatitis A virus
- Involving animals
- Foot-and-mouth disease of cattle
- Encephalomyocarditis of rodents
poliomyelitis
3
Single-stranded RNA (linear), strand,
nonenvelopedcup- like surface, Icosahedral
- Norovirus (Norwalk agent) causes acute epidemic
gastroenteritis - Similar to picornaviruses but slightly larger
4
Astroiviridae
Single-stranded RNA (linear), strand,
nonenvelopedstar- like surface, Icosahedral
- causes gastroenteritis in humans and animals
- Similar in size to picornaviruses
5
Hepeviridae
Genome ssRNA (Linear), strand, nonenveloped,
Icosahedral
- Human Hepatitis E virus cause acute hepatitis
6
Double-stranded RNA (linear), strand,
nonenveloped, two or three shell, Icosahedral,
segmented (10-12)Rota wheel-shape appearance,
Respiratory Enteric Orphan (REO)
- Rotavirus acute gastroenteritis,
- Coltivirus arbovirus (Colorado tick fever)
- Genome segment reassortment occurs readily
7
- An ecologic grouping (not a virus family) of
viruses with diverse - physical and chemical properties.
- Arboviruses infect humans, mammals, birds, and
snakes - Arboviruses are transmitted by arthropods
- Arthropods Mosquitoes, ticks, flies
- Arboviruses Toga, Flavi, Bunya, Rabdo, Arena
and Reo viruses - Human pathogens include dengue, yellow fever,
- encephalitis viruses, and others.
8
Single-stranded RNA (linear), strand,
enveloped, Icosahedral
- Alphavirus (arbovirus)
- Include EEE, WEE, VEE (Eastern, western and
venezuelan equine encephalitis viruses) - Rubivirus (rubella virus)
9
Single-stranded RNA (linear), strand,
enveloped, unknown symmetry
- Flaviviruses (Arboviruses) Yellow fever,
dengue, St. Louis Encephalitis and West Nile
viruses - Hepaciviruses Hepatitis C virus
10
Coronaviridae
- Petal-shaped surface, like a solar corona
- More human coronaviruses cause upper respiratory
infections - Severe acute respiratory syndrome (SARS)
11
Single-stranded RNA (linear), strand, helical
symmetry, bullet shape, enveloped
- Lyssavirus (rabies virus)
- Cause numerous animal diseases
12
Bornaviridae
- Single-stranded RNA (linear), strand, helical
symmetry, enveloped - Borna disease virus (BDV)
- neurotropic in animals and belongs a severe
(frequently fatal) neurological disease of horses
and sheep
13
Single-stranded RNA (linear), strand,
enveloped,Helical symmethery, large peplomer
- Ebola and Marburg viruses, causing hemorrhagic
fever in Africa - Require maximum containment conditions
(Biosafety Level 4) for handling
14
Single-stranded RNA (linear), - strand,
segmented (6-8),shift and drift antigenic,
Helical symmetry , enveloped,
- The segmented nature of the viral genome permits
ready genetic reassortment - Influenza virus (Influenza A, B and C viruses)
- Haemagglutinin (HA) and neuraminidase (NA)
15
Paramyxoviridae
Genome ss RNA ,(-) RNA , linear Virion
Helical symmetry , pleomorphic , enveloped
Genetically stable
- Paramyxoviruses (parainfluenza, mumps virus H,
N) - Morbillivirus (measles virus, H, N-)
- Pnuemonovirus (respiratory syncytia virus,
metapneumovirus, H-, N-)
16
Single stranded RNA (circular), strand or
ambisense, segmented (3)
Helical symmetry, enveloped
- budding from Golgi
- Most are arboviruse Sand fly fever ,California
encephalitis virus, La crosse , Crimian-congo
fever viruses are Arbovirus and cause hemorrhagic
fever - Hantaviruses are transmitted by infected rodents
via aerosols. (They cause hemorrhagic fevers and
nephropathy as well as a severe pulmonary
syndrome)
17
Single-stranded RNA (circular), strand or
ambisense, segmented (2), sandy shape, Helical
symmetry
- The virions incorporate host cell ribosomes
during maturations, which gives the particles a
"sandy" appearance (sandy) - Lassa Fever (Africa), Tacaribe virus complex
(junin and machupo viruses, America) cause
hemorrhagic fever in human - Cause chronic infections in rodents
18
Single-stranded RNA (linear), strand,
icosahedralenveloped, two copy of genome
Includes all RNA tumor viruses Use reverse
transcriptase to produce DNA from viral genome
- Lentivirus (HIV, Visna of sheep)
- Leukemia and sarcoma viruses of animals and
humans (HTLV-1) - Foamy viruses of primates
19
General steps in viral replication cycles
1- Attachment, penetration and uncoating 2-
Expression of viral genome and synthesis of viral
components 3- Morphogenesis and release
20
Viral replication basic principles
Host cell
Protein synthesis is directed exclusively by the
cellular machinery
21
Attachment
- The first step in infection of a cell is
attachment to the cell surface, interaction of a
virion which a specific receptor site on the
surface on the cell. - Receptor molecules differ for different viruses
but are generally glycoproteins. - - In some cases
- virus binds protein sequences (eg,
picornaviruses) - in others oligosaccharides (eg, orthomyxoviruses
and paramyxoviruses
)
Viral glycoproteins
Cell receptor
22
Penetration
- After binding, particle taken up inside the cell.
- Enveloped viruses
- (A) Entry by fusing with the plasma membrane.
Some enveloped viruses fuse directly with the
plasma membrane. Thus, the internal components of
the virion are immediately delivered to the
cytoplasm of the cell - (B) Entry via endosomes at the cell surface .
Some enveloped viruses require an acid pH for
fusion to occur and are unable to fuse directly
with the plasma membrane. - Non-enveloped viruses Non-enveloped viruses may
cross the plasma membrane directly or may be
taken up into endosomes. They then cross (or
destroy) the endosomal membrane
23
Uncoating, Expression of viral genome and
synthesis of viral components
- Uncoating is the physical separation of the
viral nucleic acid from capsid - The infectivity of the parental virus is lost at
the uncoating stage - Specific mRNAs must be transcribed from the viral
nucleic acid for successful expression and
duplication of genetic information. - Then, virus use cell components to translate the
mRNA.
Host cell
24
Morphogenesis and release
- Newly synthesized viral genomes and capsid
polypeptides assemble together to form progeny
viruses. - Virus may be released due to cell lysis, or, if
enveloped, may bud from the cell. Budding viruses
and do not necessarily kill the cell. - - Thus, some budding viruses may be able to set
up persistent infections. - Icosahedral capsids
can condense in the absence of nucleic acid - - Nucleocapsids of viruses with helical symmetry
cannot form without viral RNA
25
(No Transcript)