Vertebrate Tissues - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 24
Title:
Vertebrate Tissues
Description:
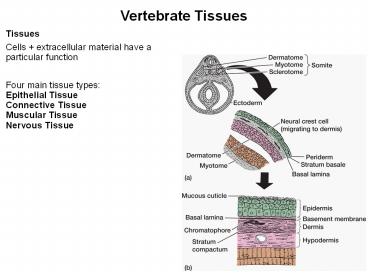
Vertebrate Tissues Tissues Cells + extracellular material have a particular function Four main tissue types: Epithelial Tissue Connective Tissue Muscular Tissue – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:160
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Vertebrate Tissues
1
Vertebrate Tissues
Tissues Cells extracellular material have a
particular function Four main tissue
types Epithelial Tissue Connective
Tissue Muscular Tissue Nervous Tissue
2
Vertebrate Tissues
Organs 2 or more tissues Histology the study
of tissues
3
EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX
Synthesized by the cells Can play vital role in
many physiological processes ranging from growth
and development to cell death Overproduction or
disruption of matrix can lead to a disease state
(chronic heart failure, metastasis) Composition
of matrix Depends on tissue type Two main
components Proteoglycans and insoluble
protein fibers (collagen, fibronectin,
laminin)
4
Hyaline Cartilage
Clear, glassy matrix fine dispersed collagen
fibers chondrocytes in small clusters enclosed
in lacunae Over ends of bones at movable joints
sternal ends of ribs supportive material in
larynx, trachea, bronchi and skeleton of embryos.
5
EXTRACELLULAR MATRIX
Amount of matrix in the tissue Nerve and
Muscle have very little matrix Connective
Tissues (cartilage, bone, blood) have lots
of matrix
6
CELL JUNCTIONS
D
7
CELL JUNCTIONS
During growth and development, cells form
cell-cell adhesions, both temporary and
permanent Formed by Cell Adhesion Molecules
(CAMS) Permanent cell-cell adhesions become cell
junctions 1. Gap Junction allows direct
cell-cell communication 2. Tight Junction
blocks movement of materials between cells 3.
Desmosome or Anchoring Junction holds cells to
one another and to the extracellular matrix
8
CELL JUNCTIONS
Formed by Cell Adhesion Molecules (CAMS) See
Table 3-3, p. 72 CAMS are membrane-spanning
proteins, form both cell junctions and transient
cell adhesions Needed for normal growth and
development Examples of transient cell
adhesions 1. Nerve cell adhesion molecules
(NCAMS) help growing nerve cells move across the
extracellular matrix 2. Cell adhesions helps WBCs
move out of circulation and into infected
tissues 3. Allows clumps of platelets to cling to
damaged vessels
9
CELL JUNCTIONS
D
10
CELL JUNCTIONS
1. Gap Junction allows direct cell-cell
communication Allows chemical and electrical
signals to pass rapidly from cell to
cell Connexins (cylindrical proteins)
interlock to create hollow channels for the
signals to pass through Channels can open or
close to regulate passage Found in many tissues
and organs Muscle, nerve, liver, pancreas,
ovary, thyroid
11
CELL JUNCTIONS
2. Tight Junction blocks movement of materials
between cells Formed by cell membranes of
adjacent cells partly fusing together along with
2 proteins claudins and occludins The barrier
properties of these tight junctions are dynamic
can be altered depending on need, giving them
variable degrees of leakiness Found in
intestinal tract and kidney (regulate what enters
and leaves the body) These junctions also make
up the blood-brain barrier
12
CELL JUNCTIONS
3. Desmosome or Anchoring junction holds cells
to one another and to the extracellular
matrix like a button or a zipper In
vertebrates, cell-cell anchoring junctions are
created by CAMS called cadherins Cell-matrix
anchoring junctions use CAMS called
integrins Integrins can also bind to signaling
molecules
13
Epithelial Tissue
Highly cellular One or more layers of closely
adhering cells Cells joined by special cell
junctions Covers / lines parts of the body Forms
a flat sheet with the upper surface exposed to
the environment or an internal body
cavity Avascular no blood vessels Depends on
underlying connective tissue for
oxygen Innervated have nerve endings Can
regenerate rapidly
14
Epithelial Tissue
Attached to underlying layers by non-cellular
basement membrane (basal surface of cells) made
of collagen and adhesive proteins Classified by
1. Cell shape Squamous Flat cells Cuboidal
Cube (box) shaped cells Columnar Tall columns of
cells 2. Number of layers Simple one
layer Stratified more than one layer
15
Epithelial Tissue
16
Simple Squamous Epithelium
Simple Squamous Single row of flat cells Allows
rapid diffusion of substances secretes serous
fluid
Special types of slippery simple squamous
epithelium Endothelium (inner covering)
Slippery lining of blood vessels and
heart Prevents blood cells from sticking
(clotting) Mesothelium (middle covering)
Slippery lining of the peritoneal, pleural and
pericardial cavities Reduces friction
17
Simple Cuboidal Epithelium
Single row of cube-shaped cells Reabsorption
secretion (sweat, oil, poison etc.)
Simple Columnar Epithelium
Single row of tall, narrow cells vertically
oriented, oval nuclei in basal half of
cell Absorption secretion secretion of mucus
Pseudostratified Epithelium
Single row of cells not all reach the free
surface Basal cell nuclei give stratified
look Secretes/propels respiratory mucus
18
Stratified Epithelia
Composed of more than one layer of cells named
for shape of surface cells exception is
transitional epithelium (urinary bladder) Deepest
cells sit on basement membrane
19
Stratified Epithelia
Variations keratinized epithelium has surface
layer of dead cells nonkeratinized epithelium
lacks the layer of dead cells
Covered with layer of compact, dead squamous
cells packed with protein keratin
Forms abrasion-resistant, moist, slippery layer
20
Stratified Cuboidal Epithelium
Stratified Cuboidal Cells
- Two or more layers of cuboidal cells surface
cells square - Secretion
Transitional Epithelium
Multilayered epithelium with rounded surface
cells that flatten when the tissue is
stretched Stretches to allow filling of urinary
tract Found in urinary tract -- kidney, ureter,
bladder
21
Glands
Single cells Goblet cells Multicellular Simple
unbranched duct Compound branched
ducts Tubular form tubes Alveolar (AKA
acinar) spherical sacs Tubuloalveolar (AKA
tubuloacinar) tubes connecting sacs
Special epithelial cells secrete products Mucus,
hormones, milk, sweat, poison, etc.
22
Endocrine Glands
23
Exocrine Glands
24
Epithelial Membranes
Epithelium and connective tissue Cutaneous
membrane covers outer surface (skin) Mucous
membrane line body cavities that exit the
body digestive, respiratory and reproductive
tracts Serous membrane line body cavities that
do not exit the body and cover the organs in the
cavity Layers Parietal connects to the
body cavity wall Visceral connects the organ
to cavity Serous fluid lubricates organs