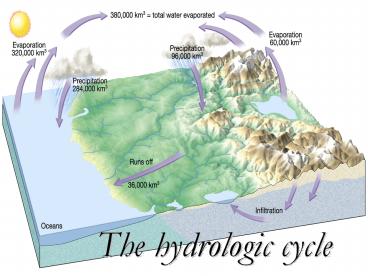
The hydrologic cycle - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
The hydrologic cycle
Description:
Title: Suspended Load River Animations stream velocity and deposition flood plain delineation geography animations oxbow lake formation The Water Cycle Animation ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:243
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: The hydrologic cycle
1
The hydrologic cycle
2
The Water Cycle
- The Water Cycle Animation
- Ground Water
3
Sources of Earths water
4
RIVER FeaturesHeadwaters
- Beginning of a stream high elevation.
5
Watershed
- Land from which water runs off into a stream.
6
Tributary
- Feeder stream that flows into a main stream.
7
Divide
- Elevated region that separates 2 watersheds.
8
Coastal Plain
9
Floodplain
- Part of the valley floor that may be covered with
water during a flood. - Flood Plain Delineation
- Flood Plain Formation
10
(No Transcript)
11
Meander - E
- Wide curve in a stream channel.
12
Erosion Deposition along a meandering stream
13
Oxbow
14
(No Transcript)
15
Cut Bank - E
- The area of active erosion on the OUTSIDE of a
meander.
16
Point Bar - D
- A crescent-shaped accumulation of sand and gravel
deposited on the INSIDE of a meander.
17
(No Transcript)
18
Oxbow
- Water remaining in an isolated meander in a
floodplain. - oxbow lake formation
19
Upper Mississippi River (Missouri)
20
Delta - D
- Fan-shaped deposit of sediments at the mouth of a
stream formed when rivers erode and transport
sediments. When the river slows down, it deposits
sediments.
21
(No Transcript)
22
(No Transcript)
23
Common stream measurements
- Gradient/Slope rise change in elevation
- run
distance - Discharge - how much water flows through a river
in 1 second - Discharge (l x w x d) / time
- Greater discharge more sediment it can carry
more erosion it can cause - Stream Load size of sediment
24
Describe sediment carried by streams
- Bed load- heavy sediment, skips along bottom
- Suspended load- small particles, makes water look
cloudy. - Dissolved load- minerals (or pollutants) in
solution - Load Animation
- Another Animation!
- Stream Velocity Load Deposition
25
Describe the 3 ways rivers erode sediment.
- Headward stream lengthening
- Downcutting mountainous areas form v-shaped
valleys - Meandering
- Lateral stream widening (occurs more than
downcutting in flatter areas). - Formation of a V-Shaped Valley
26
How river systems change from young to mature!
- MATURE
- Wide Channels
- Large floodplains
- Lateral erosion
- Gentle slopes
- Meanders, oxbows
- Fine sediment
- YOUNG
- Narrow channels
- Small floodplains
- Downcutting
- Steep slopes
- Rapids, waterfalls
- Coarse sediment
Life Cycle of a River Overview
27
Trace the path(s) that 99 of water travels
through the Great Lakes watershed.
28
(No Transcript)
29
Fig. 19.7, p. 484
30
Great Lakes Watershed
31
FLOODS
- Stream overflows channel
- Causes
- Weather events
- Dams break
- () Provides fertilizer for floodplain
- (-) Most destructive of all geologic hazards
32
Missouri Mississippi Rivers (Satellite view
near St. Louis)
33
Same satellite view during flooding in 1993
34
Describe human decisions that increase the risk
of flooding.
- Disturbing vegetation that uses water and returns
it to the atmosphere before flooding occurs. - Building
- Grazing animals
- Farming practices like clear-cutting land
- Cutting down forests
35
FLOOD CONTROL
- Dams
36
Fig. 13-12, p. 325
37
Glen Canyon Dam, Page, AZ (Lake Powell in
background, Colorado River in foreground)