Lewis Structures - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 26
Title:
Lewis Structures
Description:
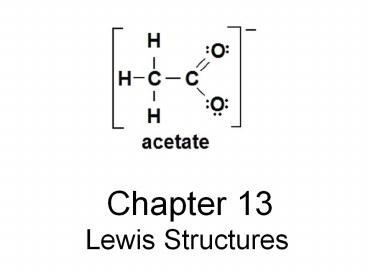
Chapter 13 Lewis Structures Lewis Structures Lewis structures are diagrams that show the bonding between atoms of a molecule, and the lone pairs of valence electrons ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:129
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Lewis Structures
1
Chapter 13
- Lewis Structures
2
Lewis Structures
- Lewis structures are diagrams that show the
bonding between atoms of a molecule, and the lone
pairs of valence electrons in the molecule.
3
(No Transcript)
4
(No Transcript)
5
(No Transcript)
6
(No Transcript)
7
Steps for Writing Lewis Structures
- Count the total number of outer level (valence)
electrons. To do this use the Roman numeral
from the group number above each element in the
periodic table. - PO4
- PO43-
- PO43
8
Steps for Writing Lewis Structures
- Determine the layout of the molecule. The
formula of the molecule will often give you a
hint as to its layout. For example in the
molecule H3CCH3 there are two carbon atoms in the
center with three hydrogen atoms bonded to each
carbon. - Carbon is always central
- Hydrogen is never central
- The element with the lowest electronegativity is
central - The element which you have the least of is
usually central - Group 17 elements are usually not central (unless
you have no other choice) because they can only
form single bonds. - After determining the layout of the molecule.
Arrange the elements symmetrically around your
central atom(s).
9
Steps for Writing Lewis Structures
- 3. The valence electrons from step 1 are now
used to stabilize the atoms. This is done by
using shared pairs (bonds) (see Table 1) to
attach the atoms to the central atom. Use single
bonds for all atoms first.
Note the strengths and lengths of the different
types of bonds.
10
Steps for Writing Lewis Structures
- 3. After adding single bonds you may find that
the atoms still need more valence electrons to
achieve their octets. If more valence electrons
are needed use unshared pairs (lone pairs) (see
Table 1) around each atom to give the atom an
octet (8 valence electrons). There are some
exceptions to the octet rule. The most common
exception is hydrogen which only requires 2
electrons to fill its outer level and become
stable.
11
Steps for Writing Lewis Structures
- 3. The valence electrons from step 1 are now
used to stabilize the atoms. This is done by
using shared pairs (bonds) (see Table 1) to
attach the atoms to the central atom. Use single
bonds for all atoms first. - After adding single bonds you may find that the
atoms still need more valence electrons to
achieve their octets. If more valence electrons
are needed use unshared pairs (lone pairs) (see
Table 1) around each atom to give the atom an
octet (8 valence electrons). There are some
exceptions to the octet rule. The most common
exception is hydrogen which only requires 2
electrons to fill its outer level and become
stable. - If you still do not have a stable structure you
may try double and triple bonds if C, N, or O is
involved in the bond.
12
Steps for Writing Lewis Structures
- If you cannot write a stable structure for the
molecule using rules 1 3 add or remove unshared
pairs to/from the central atom until you arrive
at the desired number of valence electrons
determined in step 1. This may give you a
structure that appears to be unstable however
some molecules can form which do not have stable
octets. - Common exceptions to the octet rule H is stable
with 2 valence electrons B is stable with 6
valence electrons.
13
Writing Lewis Structures
- CO2
14
Writing Lewis Structures
- PO43-
15
Writing Lewis Structures
- H2CO
16
Writing Lewis Structures
- BrNO
17
Writing Lewis Structures
- BrNO
18
Steps for Writing Lewis Structures
- Determine the layout of the molecule. The
formula of the molecule will often give you a
hint as to its layout. For example in the
molecule H3CCH3 there are two carbon atoms in the
center with three hydrogen atoms bonded to each
carbon. - Carbon is always central
- Hydrogen is never central
- The element with the lowest electronegativity is
central - The element which you have the least of is
usually central - Group 17 elements are usually not central (unless
you have no other choice) because they can only
form single bonds. - After determining the layout of the molecule.
Arrange the elements symmetrically around your
central atom(s).
19
Writing Lewis Structures
- HCCH
20
Steps for Writing Lewis Structures
- Determine the layout of the molecule. The
formula of the molecule will often give you a
hint as to its layout. For example in the
molecule H3CCH3 there are two carbon atoms in the
center with three hydrogen atoms bonded to each
carbon. - Carbon is always central
- Hydrogen is never central
- The element with the lowest electronegativity is
central - The element which you have the least of is
usually central - Group 17 elements are usually not central (unless
you have no other choice) because they can only
form single bonds. - After determining the layout of the molecule.
Arrange the elements symmetrically around your
central atom(s).
21
Writing Lewis Structures
- HCCH
22
Writing Lewis Structures
- HCCH
23
Writing Lewis Structures
- BeCl2
24
Steps for Writing Lewis Structures
- If you cannot write a stable structure for the
molecule using rules 1 3 add or remove unshared
pairs to/from the central atom until you arrive
at the desired number of valence electrons
determined in step 1. This may give you a
structure that appears to be unstable however
some molecules can form which do not have stable
octets.
25
Homework
- Lewis Structures Worksheet
26
Homework
- Lewis Structures Worksheet