Renal System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 19
Title:
Renal System
Description:
Renal System Gross structure of the kidneys cortex, medulla (inner and outer zones of outer medulla and papilla or inner medulla), pyramids, renal calyxes and pelvis ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:262
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Renal System
1
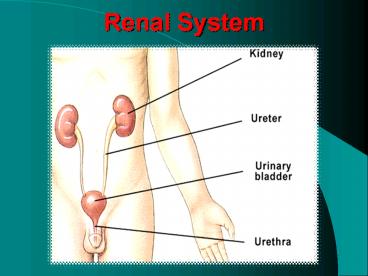
Renal System
2
- Gross structure of the kidneys cortex, medulla
(inner and outer zones of outer medulla and
papilla or inner medulla), pyramids, renal
calyxes and pelvis, ureter. - Gross size and weight (300400 g) of kidneys
(about 0.5 of body weight) - in humans
3
Anatomy of the Kidney
4
- The nephron is the basic unit of renal structure
- and functions.
- It has a malpigian corpuscle with a vascular
glomerulus within a matrix formed by mesangial
cells and an epithelial Bowmans capsule. - The capsule joins a series of tubules starting
with the proximal tubule and followed by the loop
of Henle the distal tubule.
5
- Nephron
- Glomerulus
- Bowmans Capsule
- Proximal Convoluted Tubule
- Loop of Henle
- I. Proximal straight tubule
- ii. Descending Thin Limb
- iii. Ascending Thin Limb
- iv. Distal Straight Tubule
- Distal Convoluted Tubule
6
(No Transcript)
7
branch of renal artery
glomerulus
Bowmans capsule
DCT
PCT
collecting duct
branch of renal vein
capillaries
loop
8
branch of renal artery
glomerulus
Bowmans capsule
DCT
PCT
collecting duct
branch of renal vein
capillaries
loop
9
Anatomy of the Kidney
10
Formation of Urine
- The initial step is the formation of a plasma
ultrafiltrate (plasma without cells or proteins)
at Bowmans space through the action of
hydrostatic pressure in the glomerular
capillaries. - The ultrafiltrate flows along the tubules and is
modified by reabsorption (sodium salts, glucose,
amino acids) and most water from the when of the
tubules back into the pennt? Capsule. - The luminal fluild is also modified by secretion
of solutes from the peritubular (tubule cells)
into the lumen.
11
Tubular Secretion and Reabsorption
12
Function of Collecting ducts
- The collecting ducts make the final fine
adjustments in composition of the urine through
anti-diuretic hormone stimulated water and urea
reabsorption, and aldosterone stimulated Na, K
and H transport.
13
Tubular Reabsorption
- Returns materials from filtrate to blood
- 99 of filtrate reclaimed
- Lose 1.5 2 L/day as urine
- Mechanisms of reabsorption
- Osmosis, Solvent drag, Pinocytosis, Active
transport Diffusion - Amounts reabsorbed depends on
- Need for substance Concentration gradient
- Proximal convoluted tubule
- Always permeable to water, reabsorbs 80 of water
passing through - Active Transport
- Ions-Na, Cl, K, HCO3
- Nutrients
- Passive Transport
- Urea, Lipid-soluble solutes
14
Role of kidney
- Apart from urine formation
- Blood pressure from Renin production
- RBC production from Erythropoietin
15
Kidney Structure
- Arteriole Small artery
- Bowman capsule A cup-shaped capsule surrounding
each glomerulus - Calyx Cup-like collecting region of the renal
pelvis - Catheter A tube for injecting or removing
fluids - Cortex Outer region the renal cortex is the
outer region of the kidney - Creatine A waste product of muscle metabolism
- Electrolyte A chemical that carries an
electrical charge on solution - Filtration Process whereby some substances but
not all, - pass through a filter or
other material - Glomerulus Tiny ball of capillaries in cortex
of kidney
16
Kidney Structure
- Hilum Depression or pit in that part of an
organ where blood vessels and nerves enter and
leave - Kidney One of two bean-shaped organs located
behind the abdominal - cavity on either side of the backbone in
the lumbar region - Meatus opening or canal
- Medulla Inner region the renal medulla is the
inner region of the kidney - Nitrogenous wastes Substances containing
nitrogen and excreted - in urine
- Renal artery carries blood to the kidney
17
Kidney Structure
- Renal pelvis - Central blood away from the
kidney. - Renal tubules - Microscopic tubes in the kidney
- Renal vein - Carries blood away from the kidney
- Rennin - A hormone synthesized, stored and
secreted by the kidney - Sodium (Na) - A salt (electrolyte) regulated in
the blood and urine by the kidneys - Trigone - Triangular area in the bladder where
the ureters enter and the urethra exits - Urea - Major nitrogenous waste product excreted
in urine - Ureter - Tube leading from each kidney to the
bladder - Urethra - Tube leading from the bladder to the
outside of the body - Uric acid - Nitrogenous waste excreted in the
urine - Urinary bladder Sac that holds urine
- Voiding Expelling urine (micturation)
- Glomerulonephritis - Inflammation of the kidney
glomerulus (Bright disease)
18
Kidney Structure
- Interstitial nephritis - Inflammation of the
renal interstitium - Nephrolithiasis - Kidney stones (renal calculi)
- Nephrotic syndrome - A group of symptoms caused
by - excessive protein loss in the urine (also called
nephrosis) - Polycystic kidneys - Multiple fluid-filled sacs
(cysts) within and upon the kidney - Pyelonephritis - Inflammation of the renal pelvis
and renal medulla - Renal cell carcinoma - Cancerous tumor of the
kidney in adulthood - Renal failure - Failure of the kidney to excrete
urine - Renal hypertension - High blood pressure
resulting from kidney disease - Wilms tumor Malignant tumor of the kidney
occurring in childhood - Diabetes insipidus - Inadequate secretion or
resistance of the kidney to the action of
antidiuretic hormone (ADH) - Diabetes mellitus - Inadequate secretion or
improper utilization of insulin
19
- Azot (nitrogenous)
- Dips
- Noct (night)
- Olig (few)
- Tripsy (crushing)
- BUN (blood urea nitrogen)
- IVP
- KUB (kidney, ureter, bladder)
- ADH (anti-diuretic hormone)
- UTI (urinary tract infection)
- CRF (chronic renal failure?, corticotropin
releasing factor?) - ARF (acute renal failure?)