Muscle Info - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 7
Title:
Muscle Info
Description:
Muscle Movements: Prime mover ... Rhomboid shaped muscle A four-sided shape where all sides have equal length, also opposite sides are parallel and opposite angles ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:85
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Muscle Info
1
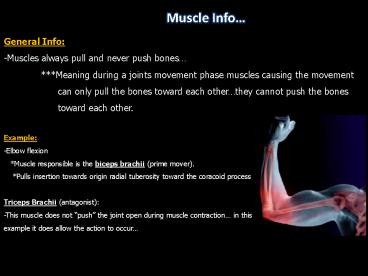
Muscle Info
General Info -Muscles always pull and never push
bones Meaning during a joints movement phase
muscles causing the movement can only
pull the bones toward each otherthey cannot push
the bones toward each other.
Example -Elbow flexion Muscle responsible
is the biceps brachii (prime mover). Pulls
insertion towards origin radial tuberosity toward
the coracoid process Triceps Brachii
(antagonist) -This muscle does not push the
joint open during muscle contraction in this
example it does allow the action to occur
2
Muscle Movements
Muscle Movements Prime mover Muscle with the
major responsibility for a certain
movement Antagonist Muscle that opposes or
reverses the action of a prime mover Synergist
Muscle that aids a prime mover in a movement
Synergists do a similar movement to the prime
mover, but to a lesser degree Synergists also
help reduce undesirable movements (muscles that
stabilize the wrist during elbow flexion) Fixator
Muscles Stabilizes one part of the body during
the movement of another Specifically
stabilizes the origin bone during movement.
Examples would be the erector spinea group of
muscles that keep you upright during movement
3
Naming Muscles
1) Direction of the Muscle Fibers - Named in
reference to an imaginary line (usually the
midline of the body) Example 1)
Rectus means Straight - Rectus Femoris
muscle fibers of the thigh run parallel to that
imaginary line 2) Obliques means neither
parallel nor perpendicular to the long axis of a
body or limb - External Obliques muscle
fibers run at an angle to the midline
4
Naming Muscles
2. Relative Size of the Muscle Maximus largest
Minimus smallest Longus longest
Example 1) Gluteus Maximus - Largest of
the gluteal muscles (medius / minimus) 2)
Gluteus Minimus - Largest of the gluteal
muscles 3) Extensor Pollicus Longus -
Longest of the extensor muscles of the posterior
lower arm.
5
Naming Muscles
3. Location of the Muscle Named for the bone
with the muscles are associated . Example
Temporalis Overlies the temporal bone of the
skull Femoris Overlies the femur Anterior
Tibialis Overlies the anterior portion of the
tibia Sternocliedomastoid Overlies the sternum,
clavicle and mastoid processes
4. Number of Origins Name based on the number of
attachment sites (heads) that it has with
bones Example Biceps two origins
Triceps three origins Quadriceps four
origins
6
Naming Muscles
5. Location of the Muscles Origin and Insertion
Named for their attachment sites to bones.
Example Sternocleidomastoid ? Origin on sternum
(Sterno) and Clavicle (cleido) ? Insertion on
mastoid process of temporal bone (mastoid)
6. Shape of the Muscle Named for the distinctive
shape that some muscles have.
Example Deltoid Deltoid means triangular
Rhomboideus Minor Rhomboid shaped muscle A
four-sided shape where all sides have equal
length, also opposite sides are parallel and
opposite angles are equal. (found deep to
tapezium, which would be another good exmaple)
7
Naming Muscles
7. Action of the Muscle Named for actions such
as flexion, extension, adduction and
abduction Example Adductor Longus adducts
the femur Extensor Digitorum Longus Extends the
fingers (found on posterior forearm
area) Extensor Digitorum Longus Extends the
fingers (found on posterior forearm area)