Kingdom Animalia - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 37
Title:
Kingdom Animalia
Description:
Kingdom Animalia Pictures of Birds Owl Eagle Chicken Pelican Penguin Duck Subphylum Vertebrata Class Mammalia Layer of fat; hair; feed young with milk from mother ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:680
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Kingdom Animalia
1
Kingdom Animalia
2
General Characteristics
- Multicellular (made of more than 1 cell)
- Eukaryotic (have a nucleus)
- Heterotrophs (cannot make their own food) that
ingest their food - Lack cell walls
3
- Cells are organized into tissues that make up
organs - Most reproduce sexually (DNA contributed from 2
parents) - Most are motile (can move)
4
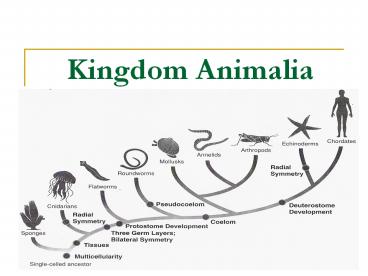
Animals are described according to their
arrangement of body part or symmetry.
5
Animal Kingdom Phyla
- INVERTEBRATES - do not have a backbone
6
Phylum Porifera
- Aquatic (live in the water)
- Lack true tissues organs
- Sessile (cant move) adults
- Filter feeders (strain tiny floating organisms
from the water)
7
Examples of Porifera
Bath Sponge (loofah)
8
Phylum Cnidaria
- Aquatic
- Radial symmetry (body plan in which body parts
repeat around the center of the body) - Tentacles bear stinging nematocysts
- Some members are sessile
9
Examples Cnidarians
Portuguese man-of-war
Moon Jellyfish
Sea Anemone
Coral Reef
10
Phylum Platyhelminthes
- Flatworms
- Bilateral symmetry (body plan in which only a
single, imaginary line can divide the body into
two equal halves) - Some free-living and some parasitic (live in and
take in nutrients from another organism)
11
Examples Flatworms
Planarian (free-living)
Liver Fluke (parasites)
- Tapeworm (parasites)
- comes from undercooked meats
12
Phylum Nematoda
- Roundworms
- Digestive system has two openings a mouth and
an anus (this is the first group of Animals that
has this trait)
13
Examples Roundworms
14
Heartworm
15
Phylum Annelida
- Segmented worms
- Digestive system has 2 openings
- Closed circulatory system (blood is contained
within a network of blood vessels)
16
Examples Segmented Worms
Fanworm (live in salt water)
Earthworm (terrestrial- live on land)
Leech (most live in fresh water)
17
Phylum Mollusca
- Soft-bodied often with a hard shell
- Digestive system with 2 openings
- Muscular foot can be used for crawling,
burrowing or as tentacles to capture prey
18
Examples Mollusks
19
Phylum Arthropoda
- Exoskeletons (external skeleton)
- Jointed appendages (structures such as legs and
antennae that extend from the body wall) - Open circulatory system (blood is not always
contained within a network of blood vessels) - Largest animal phylum
20
Examples Arthropods
Tick
Scorpion
Trilobite
Spider
Crayfish
Crab
Barnacles
Grasshopper
Ant
Centipede
Millipede
21
Phylum Echinodermata
- Live in salt water
- Spiny Skin
- Radial symmetry in adults
- Endoskeleton (internal skeleton)
22
Examples Echinoderms
23
Phylum Chordata
- Dorsal (runs along the back), hollow nerve cord
- Tail during at least part of development
24
Subphylum Urochordata
- live in salt water examples sea squirts
(tunicates)
Sea Squirts (Tunicates)
25
Subphylum Cephalochordata
- fishlike live in salt water examples
Lancelets (Amphioxus)
Lancelets (Amphioxus)
26
Subphylum Vertebrata
- most possess a backbone endoskeleton head with
a skull brain
27
Subphylum Vertebrata
- Class Myxini live in salt water tentacles
around mouth slimy example hagfishes
28
Subphylum Vertebrata
- Class Cephalaspidormorphi live in fresh salt
water no jaws circular mouth lined with
toothlike structures example lampreys
29
Subphylum Vertebrata
- Class Chondrichthyes have jaws, fins
endoskeleton of cartilage most live in salt
water Examples sharks rays
Chondro cartilage
30
Subphylum Vertebrata
- Class Osteichthyes have jaws, fins
endoskeleton of bone aquatic
Tuna
Salmon
Goldfish
Eel
Osteo bone
31
Subphylum Vertebrata
- Class Amphibia adapted primarily to life in wet
places smooth, moist skin adults either aquatic
or terrestrial
Frog
Salamander
Toad
32
Subphylum Vertebrata
- Class Reptilia most adapted to terrestrial
life dry, scale-covered skin
Lizard
Alligator
Snake
Crocodile
Turtle
Tortoise
33
Subphylum Vertebrata
- Class Aves feathered over much of body, scales
on legs feet, hollow bones for flying
34
Pictures of Birds
Pelican
Eagle
Owl
Chicken
Penguin
Duck
35
Subphylum Vertebrata
- Class Mammalia Layer of fat hair feed young
with milk from mother most have 4 legs
36
Pictures of Mammals
Shrew
Kangaroo
Walrus
Duckbill Platypus
Rabbit
Armadillo
Monkey
Horse
Bats
Elephant
Bear
Dolphin
Cat
Mouse
Whale
37
And last but not least,
- Humans