Integumentary system - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 28
Title:
Integumentary system
Description:
Integumentary system Function Of Skin Protection - Prevent drying (lipids), outside agents from inside (barrier and pH), UV rays (melanin) Body temperature regulation ... – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:83
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Integumentary system
1
Integumentary system
2
Function Of Skin
- Protection - Prevent drying (lipids), outside
agents from inside (barrier and pH), UV rays
(melanin) - Body temperature regulation (Thermoregulation)
Dilation / contraction of blood vessels, sweating - Sensation - Receive sensory information-
receptors for temperature and pressure - Secretion sebum, excretion too sweat, vitamin
D production due to UV rays (low dose)
3
Keratinization
- Skin cell process of being keratinized newly
formed cells in the stratum germinativum divide
and push upward to the surface, they fill up with
keratin, a protein. They move upward and lose
their nucleus and die. The cells become horny.
Takes 28 days.
4
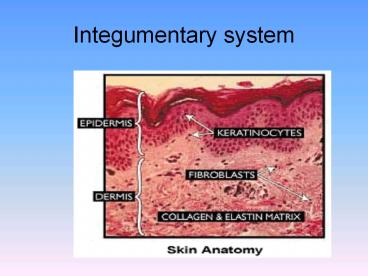
Structure Of Skin
5
Structures
- Epidermis-Top Layer, Stratified Squamous
epithelial, no blood vessels, diffusion (O2 ,
nutrients) Has five layers - Stratum Corneum- (horny Layer) outer layer. Scale
like cells (dead) that continually shed. barrier - Stratum lucidium- (clear Layer) transparent layer
under the stratum corneum. Small cells that light
can pass through. - Stratum Granulum (granular layer) layer, the
cells look like distinct granules. The cells are
almost dead (keratinization), they are pushed to
the surface to replace the cells that were shed
from the stratum corneum. Lost nuclei and become
brittle. - Stratum spinosum (spiny lavers) desmosomes
interlocking cellular bridges, polyhedron shape. - Stratum Germinativum (regenerative layer)
Basal, deepest layer. Responsible for the growth
(mitosis) of the epidermis. Melanocytes skin
color
6
Skin structure picture cont
7
Structures
- Dermis- Corium, true skin, Middle Layer, Dense
connective tissue, blood, lymph vessels, nerves,
muscles, glands, hair follicles, papillar below
epidermis, reticular above subcutaneous - Hypodermis / subcutaneous- Bottom layer, Adipose
- Sebaceous Gland- Oil, Near hair, rich in lipids
- Sudoriferous- Sweat, pore to outside, water and
salt - Arrector Pili- Smooth muscle, Contracts to form
goose bumps (hair stands on end) - Nerve- Pain, Pressure, temperature
8
Sebaceous gland
- The Sebaceous gland is an oil gland. It is
connected to the hair follicles. Everywhere on
your body has an oil gland except for your palms
and the soles of your feet. Sebum flows through
the oil ducts leading to the mouths of the hair
follicles. Sebum lubricates and protects hair /
skin. Acne pore clogged with sebum. Oxidizes
blackhead, Pus filled white head / pimple. Deep
clog boil,holocrine
9
Sudoriferous gland
- The sudoriferous gland is a sweat gland. 2 types
Eccrine produce sweat, Apocirne bodys
natural scent. Both merocrine All the parts of
your body have sweat glands. It regulates body
temperature. The excretion of sweat is controlled
by the nervous system. Sweating is important for
survival because it keeps temperature from going
really high. It allows the body to be cooled by
the evaporation of sweat. - Some things that can make your temperature go
high is Exercising ,Being sick
10
Skin coloring differences
- Skin Differences
- The color differences depend primarily on the
amount of melanin (blood supply too). The tiny
grains of pigment (melanin) deposited in the
stratum germinativum of the epidermis and the
papillary layers of the dermis. The color of
pigment varies from person to person. The
distinctive color of the skin is a hereditary
(genetic) trait and varies among races and
nationalities. Dark skin contains more active
melanin Albinism, genetic, absence of melanin.
11
Skin Coloring
- Melanin- Pigments responsible for coloring,
Protects from UV light - Albinism- Lack of Melanin, Genetic
- Carotene- Yellow pigment, Source of Vitamin A,
Skin yellow by consumption - Cyanosis- Bluish color, Lack of O2
- Birth Marks- congenital (at birth), Disorder of
blood vessels in dermis - Jaundice yellow skin (billirubin build up)
impared liver function - Rash / lesion Scarlet fever, strep infection
due to toxins released allergic reaction
12
HAIR STUCTURE
- 12 scales / cuticle
- 13 cortex
- 14 medulla
- 15 melanocytes
- 16 keratinocytes
- 17 dermal papilla
13
Hair- Trichology
- Main characteristic of mammals, none palms, soles
,external genitalia - Shaft- Hair above the surface
- Roots- Below the surface
- 3 Layers of hair- Cuticle (outer layer,), Cortex
(hard inner layer, pigment), Medulla (soft
center) - Hair Follicle- Where hair is found in dermis
- Dermal Papilla- Blood vessels provide hair with
nutrients to grow
14
Anatomic parts of hair
- Cortex
- Cuticle
- Medulla
- Hair root
- Hair shaft
- Follicle
- Hair bulb
- Dermal papilla
- Arrector pilli
- Sebaceous gland
15
Hair Growth
- Begin with cells deep in follicle at bulb growing
by mitosis - Anagen- Growth phase, hair makes new keratinized
cells, ½ an inch per month, 3-5 years - Catagen- The transition phase, the follicle
shrinks and detaches from papilla(1-2 Weeks) - Telogen- Resting phase, hair is shed(3-6 Months)
- Entire Cycle- Every 4-5 years
16
Hair texture
- Straight, wavy or curly (kinky)
- Alpha keratin cross links.
- Permanent wave Chemical reducing agent break
disulfide bonds, chemical oxidizing agent make
new cross links.
17
Hair color
- Pigment in cortex give the colors
- Gray lack of pigment in cortex
- White no pigment and air bubbles in shaft
- Trauma cause premature gray / white
18
Nails- Onyx
- Nail Bed- Nail attaches to skin
- Nail Root-(Matrix) where nail is formed
- Lunula- white cresent, half-moon, visible matrix,
air mixed with keratin - Nail Body- Plate- visible part of nail
- Cuticle- Overlap skin (stratum corneum) around
the nail, eponychium - Grows 1/8 in. per month, grows continuously, no
resting stage
19
NAIL STRUCTURE
20
Disorders
- Acne- Disorder of the hair follicle and sebaceous
gland - Impetigo- Bacteria making blisters that break to
form a yellow crust - Measles- A rash, by virus, damage fetus
- Cold Sores- Herpes simplex 1, Virus
- Warts- Uncontrolled growth of epidermis papilloma
virus - Ring Worm- Fungal infection, scaly patches
21
Disorders
- Eczema- Inflammation of the skin
- Psoriasis- Increase cell division in the stratum
basal, thicker skin - Chicken Pox/Shingles- Virus, remains dormant with
the nerve cells, painful lesions along dermatones
- Dandruff (Pityriasis)- Excessive shedding of
epithelial cells - Lice (Pediculosis)- Itching, slight rash
- Vitiligo irregular patches of skin lacking
pigment.
22
Burns description
- First Degree- Only epidermis, red painful, slight
edema (swelling) Heal without scaring in a week,
sunburn - Second Degree- Into the dermis, blisters,
epidermis from hair follicle - Third Degree- Tissue completely destroyed, Heals
from edge of burn, painless because receptors are
damaged, scaring, sometimes skin graphs
23
Burns diagrams
24
Aging
- Skin becomes thinner
- Loss of elasticity
- Wrinkles sagging
- Less oil and sweat production
- Age spots loss of melanocytes around it
- Gray in hair lack of melanin
25
Wrinkles
26
Cancers
- Uncontrolled growth
- Skin cancer (most common type)
- Basal Cell Carcinoma- (Most frequent) Stars in
Stratum Basal - Squamous Cell Carcinoma- Cells above stratum
basal- Keratin bumps - Melanoma- Rare but deadly in melanocytes- in a
mole (group of melanocytes)
27
Skin cancers
28
Skin cancers