Viruses - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
Title:
Viruses
Description:
Viruses Ebola Influenza Rabies HIV West Nile Virus – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:310
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: Viruses
1
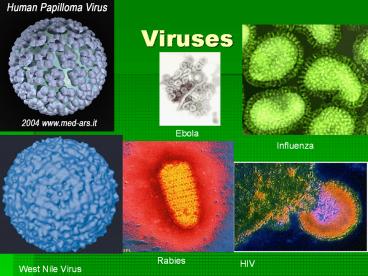
Viruses
Ebola
Influenza
Rabies
HIV
West Nile Virus
2
General Characteristics
- 1.Very small
- - 10 -1000 nanometers
- - 10 1000 x 10 -9 m
- - Cannot be seen without an
- electron microscope
3
General Characteristics
- 2. Various Shapes
4
General Characteristics
Protein Coat
- 3. Structure
- Two Parts
- Nucleic acid
- Protein Coat
- (Capsid)
Nucleic Acid
5
General Characteristics
- 4. Acellular
- - no cell
- - no organelles
- - no metabolism
- - cannot be killed with antibiotics
6
General Characteristics
- 5. Nucleic acid
- - Has DNA
- - or RNA (retro viruses)
- - (never both)
- ?s 1-6
DNA
RNA
7
General Characteristics
- Nucleic Acids
- 1. DNA deoxyribonucleic acid
- - Double strand
- - Contains genes for making viral
- proteins (requires 2 steps)
8
General Characteristics
- Nucleic Acids
- 2. RNA ribonucleic acid
- - Single strand
- - Retro virus
- - contains code for directly
- producing viral proteins
9
General Characteristics
- 6. Mutates very easily
- - no cell
- - no protection from mutagens
- E.g. chemicals, radiation,
- uv light exposure
10
General Characteristics
- 7. Virus Latin for poison
11
General Characteristics
- 8. Obligate intercellular Parasite
- - Cannot reproduce EXCEPT inside
- a host cell
- - No metabolism
- outside host cell
- - Inside host,
- uses cells reproduction
- metabolic mechanisms
12
General Characteristics
- 9. Some have an envelope
- Membrane surrounding protein coat
- Made of glycoproteins
13
Examples of Viruses
- Common Cold
- Polio
- Rabies
- HIV
- Hepatitis A,B, C
- Herpes ( E.g. Chicken pox)
- Measles
- Smallpox
- ?s 8-13
- Ebola
- Hanta
- HPV (Human papilloma virus)
- Mumps
- Rubella
- Epstein-Barr
- SARS
- can cause cancer
14
Viral Cycles
- Two Types of Viral Cycles
- 1. Lytic
- 2. Lysogenic
15
Lytic Cycle
- Immediate viral replication
- Viral DNA injected into host cell
- Viral DNA put into host genome
- Synthesis Assembly of virus
- Cell lysis (rupture) tissue damage
- New viruses emerge to infect new cells
16
Lysogenic Cycle
- Viral replication is delayed
- Viral DNA put into host genome
- Host cells divide, including viral genes
- 3. When organism is stressed ?
- ? lytic cycle begins
- ? viral replication (cell lysis) etc.
- ?s 7-12
17
Lytic vs Lysogenic Cycle
New viruses emerge
Viral DNA
Injection
Bacterial genome
Lysis
Assembly
Many divisions
Synthesis
18
How do Viruses do Harm?
- Possible effects
- 1. Lyse cells (Tissue damage)
- 2. Release viral toxins
- 3. Prevent hosts cell division
- 4. Disrupt formation of host chromosomes
19
How do Viruses do Harm?
- 5. Disrupt lysosomal function
- 6. Can cause uncontrolled cell division (cancer)
- 7. Can cause changes in cell membrane
- (immune system destroys host cells)
20
Duration of Viral Infections
- Acute rapid onset, death or recovery
- (most viruses)
- Chronic recurs again again
- - latent period virus dormant between
flare-ups - E.g. Herpes simplex
- (cold sores)
21
Prevention
- Vaccines
- Live or killed virus injected
- Host immune system makes antibodies
- When infected, host immune system ready to kill
virus
22
Treatment
- Antiviral drugs
- Interfere with viral replication
- E.g. AZT ( for AIDS)
- E.g. Interferon (for Hepatitis C)
- 2. Supportive Therapy
- Reduce fever (E.g. aspirin, Tamiflu)
- Make host comfortable
- Wait until virus runs its course ?s 14-19
23
Viroids
- Nucleic acid (RNA) only
- No protein coat
- Common in plants
24
Prions
- Protein only
- No nucleic acid
- Replicate by bumping proteins, causing refolding
in shape of prion - Cause diseases of nervous system
25
Prions
- E.g.
- Kreutzfeld-Jakobs disease
- Bovine Spongiform Encephalopathy
- (BSE) aka Mad cow disease)
26
Prions
- 2. Chronic wasting disease
- Deer and elk
27
Prions
- 3. Scrapie usually fatal sheep disease
28
Prions
- 4. Kuru
- Papua New Guinea
- Headhunters (cannibalistic tribes)
Word to your mama!
29
Viruses
- Are they living or nonliving ?
- Are they smart nucleic acids?
- Why cant we kill them?
- ?s 20-25