INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 27
Title:
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
Description:
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM Terms to remember Tissue Organ Organ system Dermatology: branch of science specializing in diagnosing and treating skin disorders. – PowerPoint PPT presentation
Number of Views:295
Avg rating:3.0/5.0
Title: INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
1
INTEGUMENTARY SYSTEM
2
Terms to remember
- Tissue
- Organ
- Organ system
- Dermatology branch of science specializing in
diagnosing and treating skin disorders.
3
Integumentary System
- Skin accessory structures (hair, nails, glands,
some receptors) - System most widely exposed to trauma, infection,
disease - Skin is the largest organ in surface area and
weight - Adult skin 2 square meters (22sq.ft.)
4
Components of Integumentary System
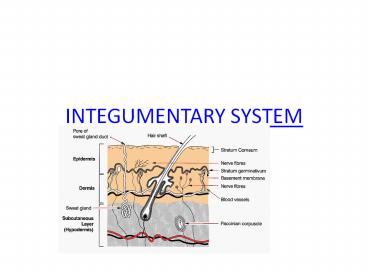
- Skin layers
- Epidermis (outer)
- Dermis (middle)
- Subcutaneous layer a/k/a hypodermis (inner)
- Accessory structures located in the dermis
- Nails
- Glands
- Pili (hair)
- Sense receptors
5
Functions of the Skin
- Protection-of underlying tissues and organs
- Excretion-of salts, water and organic wastes
- Maintenance of normal body temperature
- Synthesis of Vitamin D
- Storage of nutrients
- Sensory function-detection of touch, pressure,
pain and temperature.
6
EPIDERMIS
- Outer layer
- Made of stratified squamous epithelium
- keratinocytes cells containing keratin (protein
for waterproofing) - Melanocytes cells containing melanin (pigment)
- Thick skin has 5 layers and thin skin has only 4
7
EPIDERMAL LAYERS (STRATA)
- Stratum Germinativum (Basale)
- Single, bottom mitotic layer
- Stratum Spinosum
- 8-10 cell layers
- Stratum Granulosum
- 5 cell layers release lipids
- Stratum Lucidum
- 5 cell layers only present in thick skin
- Stratum Corneum
- 30 cell layers, dead calluses form here
8
Skin Pigmentation
- Carotene, a yellow-orange pigment
- Melanin, a brown-black pigment protects against
UV damage - Hemoglobin, a red pigment
- These pigments are also responsible for the
variety of hair colors.
9
Pigment Conditions
- Albinism inherited disorder, where the
individual is unable to produce melanin. - Vitiligo irregular white spots due to lack of
melanin. - Freckles irregular dark spots due to
concentrated areas of melanin - Nevus birthmark or mole
- Cyanosis bluing of skin or nails due to hypoxia
or anoxia - Jaundice yellowing of skin or eyes due to
build-up of bilirubin in blood - Erythema reddening of the skin due to engorged
capillaries (exercise, heat, infection)
10
Albinism Vitiligo
11
Nevus Cyanosis
12
Jaundice Erythema
13
DERMIS
- Below epidermis
- contains collagen and elastin fibers in outer
regions - Contains connective tissue, adipose tissue and
sensory receptors in inner layer - Surface area is increased by dermal papillae
(which give us fingerprints)
14
SUBCUTANEOUS / HYPODERMIS
- Also called the subQ layer
- Found below dermis
- Contains connective tissue, such as adipose and
areolar
15
Hair
- a/k/a pili
- Hair functions-protection from UV light, cushion
a blow and insulate the head, prevent entry of
foreign materials. - Anatomy of hair (see p. 123)
- Shaft, root, follicle, bulb, matrix, papilla
- Normal hair loss 100 hairs/day
- Arrector pili muscles goosebumps
16
Hair structure
17
Glands
- Sebaceous Glands (oil)-secrete sebum. Provides
lubrication and inhibits growth of bacteria. - Sudoriferous Glands (sweat)- secrete
perspiration. Functions to regulate body
temperature and excrete waste. - Apocrine concentrated in axilla genital
regions - Eccrine widely distributed on body
- Mammary Glands (milk)- modified sweat glands
- Ceruminous Glands (wax) secrete cerumen
modified oil glands
18
Glands
19
Nails
- Tightly compressed cells packed with keratin.
- Know the parts (see p. 122)
- Free edge
- Nail body
- Lunula
- Cuticle
- Nail root
- Nail bed
20
Nail structures
21
Receptors
- Thermoreceptors temperature
- Meissners corpuscle fine touch vibration
- Pacinian corpuscle pressure
- Ruffinis corpuscle stretching
- Nociceptors itch, tickle, and pain
- Hair root plexus sensations on skin
22
Receptor location
23
Skin Damage
- Burns
- Caused by UV light, chemicals, abrasion
- 3 types
- 1st degree epidermis affected reddening of
skin, but no blistering - 2nd degree dermis affected blisters present and
can be painful - 3rd degree various layers of SubQ and lower are
affected usually not painful require grafting
dehydration probable
24
1st degree burns
25
2nd degree burns
26
3rd degree burns
27
REVIEW
- Skin Cross-Section
- Another Cross-Section
- Yet Another Cross-Section
- Burn Review