SPECIFIC BODY DEFENSES: The Lymphatic and Immune System - PowerPoint PPT Presentation
1 / 21
Title: SPECIFIC BODY DEFENSES: The Lymphatic and Immune System
1
SPECIFIC BODY DEFENSES The Lymphatic and Immune
System
2
I. Basics
- A. Functions
- 1. Absorption and return of excess
fluid the blood stream - 2. Absorption of fat (in the villi of the
small intestine) - 3. Immune System Function
3
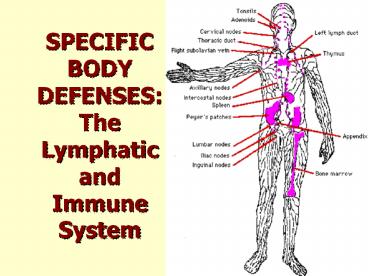
I. Lymphatic System Basics
- B. Composed of
- 1. Lymph interstitial fluid
- 2. Lymph vessels
- a. Closely associated with circulatory
system - b. Similar to veins
- c. Contraction of skeletal mscl causes
movement of lymph fluid through valves
4
I. Basics
- B. Composed of
- 3. Lymph Organs
- a. Lymph nodes
- Areas of Concentrated lymphocytes and macrophages
along the lymphatic vessels - Filter lymph
5
I. Basics
- B. Composed of
- 3. Lymph Organs
- b. Bone Marrow produces
- lymphocytes
- c. Spleen Serves as
- Blood reservoir
- Purifies blood and lymph
6
I. Basics
- B. Composed of
- 3. Lymph Organs
- c. Thymus
- causes pre-T cells to mature to T-cells
- d. Tonsils
- e. Pyers Patches
7
II. Immune Response
- A. Basics
- 1. The body's 3rd line of defense
- 2. Amplifies inflammatory response
- B. Important Aspects
- 1. Antigen specific
- 2. Systemic
- 3. Has memory
8
II. Immune Response
- C. Kinds of Immune Response
- 1. Specific Immunity
- a. Antibodies bind only to antigen
- b. B-lymphocytes antibody prod.
- c. T-lymphocytes produce
lymphokines - 2. Nonspecific Defense
- a. Physical barriers
- b. Tears
- c. Phagocytes
- d. Fever / Inflammation
9
D. Kinds of Immune Response
- 1. Humoral Immunity
- a. Provided by antibodies in the bodies
humors (fluids) - b. Antibodies.
- 1) Are produced by lymphocytes
- 2) Circulate freely in the blood and lymph
- 3) Bind primarily to bacteria, toxins,
free viruses - inactivates marks for destruction
10
D. Kinds of Immune Response
- 2. Cell Mediated Immunity
- a. Provided by nonantibody- producing
lymphocytes - b. Directly attack and lyse body cells.
- 1) containing viruses or parasite
- 2) Cancer cells
- 3) Foreign grafts
- c. Release chemical mediators
- 1) enhances inflammatory resp.
- 2) Help activate lymphocytes or macrophages
11
III. Cells of the Immune Sys.
- B. Natural Killer Cells
- 1. Similar to the killer T cell
- 2. Function as effector cells that directly
kill certain tumors and viral-infected cells - 3. kill their targets without a prior
"conference" in the lymphoid organs. - 4. More efficient if 1st activated by T-cells
12
III. Cells of the Immune Sys.
- C. B Cells
- 1. production of antibodies
- 2. Antibody production and binding to a
foreign substance or antigen, often is critical
as a means of signaling other cells to engulf,
kill or remove that substance from the body
13
III. Cells of the Immune Sys.
- D. Granulocytes or Polymorphonuclear
(PMN) Leukocytes - 1. neutrophils
- 2. Important in the removal of bacteria and
parasites
14
III. Cells of the Immune Sys.
- E. Macrophages and Dendritic Cells
- 1. regulate immune responses
- 2. antigen-presenting cells (APC)
- 3. Functions
- Phagocytes
- Secretion of cytokines
- Antigen presentation
15
III. Cells of the Immune Sys.
- F. Dendritic Cells
- 1. antigen-presenting cells
- 2. More efficient APC than macrophages
- 3. capture antigen or bring it to the lymphoid
organs where an 4. bind high amount of HIV, and
may be a reservoir of virus
16
III. OTHER
- A. Active, Passive and Acquired Immunity
- 1. Active Immunity
- achieved by responses of ones immune
system - 2. Passive Immunity
- achieved with exogenous immune cells or
products
17
III. OTHER
- A. Active, Passive and Acquired
Immunity - 3. Acquired Immunity
- comes from infection or from a new borns
mothe 4. Artificial Immunity - comes from immunizations
18
III. OTHER
- C. Autoimmune diseases
- 1. diseases caused by failure of the immune
system to recognize self - 2. Examples
- a. rheumatoid arthritis (joints)
- b. lupus erythematosus (connective
tissue) - c. Graves disease (thyroid)
19
III. OTHER
- D. AIDS - Immunodeficiency Syndrome
- 1. Causes death
- 2. Caused by Human Immunodeficiency
Virus (HIV) - 3. kills T-4 lymphocytes
- 4. T-4 lymphocytes induce
- B-lymphocytes to fight infection
- 5. Debilitated immune system
20
III. OTHER
- D. AIDS - Immunodeficiency Syndrome
- 6. no cure for HIV
- 7. HIV infection causes AIDS, and AIDS
allows other infections to kill the person
with the HIV infection
21
D. Kinds of Immune Response
- 2. Cell Mediated Immunity
- a. Provided by nonantibody- producing
lymphocytes - b. Directly attack and lyse body cells.
- 1) containing viruses or parasite
- 2) Cancer cells
- 3) Foreign grafts
- c. Release chemical mediators
- 1) enhances inflammatory resp.
- 2) Help activate lymphocytes or macrophages